Navigating The "Out Of Memory" Message In Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the "Out of Memory" Message in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the "Out of Memory" Message in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the "Out of Memory" Message in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the "Out of Memory" Message in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the "Out of Memory" Message in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Root Causes of Memory Exhaustion
- 3.2 Identifying the Culprit: Diagnosing the Memory Shortage
- 3.3 Strategies for Reclaiming Memory and Preventing Future Issues
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying the "Out of Memory" Message
- 3.5 Conclusion: Maintaining Memory Health for Optimal Performance
- 4 Closure
Navigating the "Out of Memory" Message in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
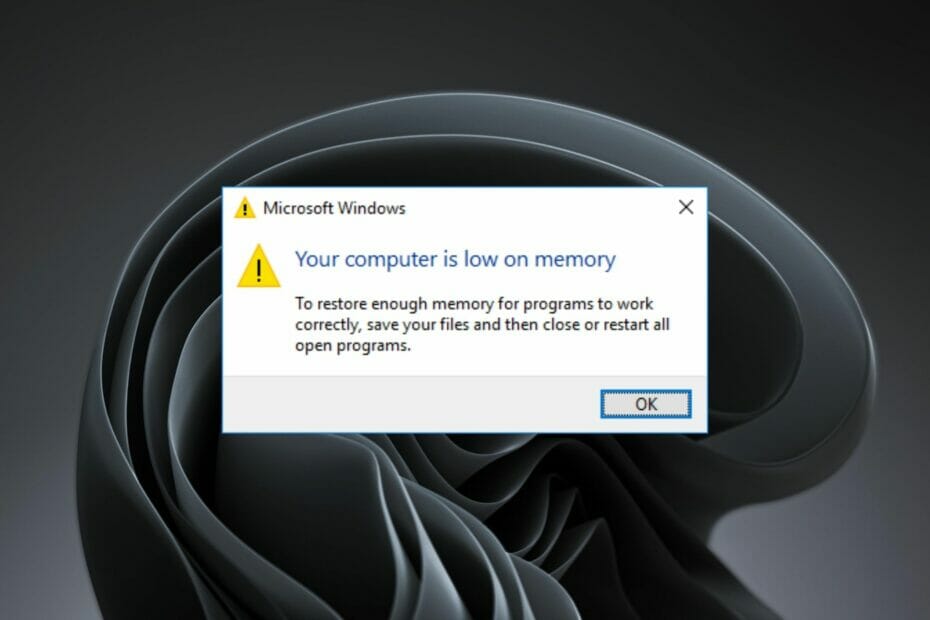
The infamous "out of memory" message, a ubiquitous error across operating systems, can be a frustrating experience for Windows 11 users. This message signals a critical situation where the system’s available memory (RAM) is insufficient to meet the demands of running applications. Understanding the causes behind this error is crucial for resolving it effectively and ensuring a smooth computing experience.
Understanding the Root Causes of Memory Exhaustion
The "out of memory" message in Windows 11 is a symptom of a fundamental issue: the operating system is unable to allocate the required memory for applications to function properly. This can arise from a multitude of factors, each demanding its own approach to resolution:
1. Insufficient RAM: The most straightforward cause is simply not having enough RAM installed. Windows 11, with its advanced features and potential for multitasking, requires a significant amount of RAM to operate efficiently. If your system’s RAM capacity is insufficient, running multiple demanding applications or programs simultaneously can lead to memory exhaustion.
2. Memory Leaks: Memory leaks occur when programs fail to release memory resources they no longer require. This can result in a gradual accumulation of unused memory, eventually leading to a shortage. Memory leaks can be caused by programming errors or faulty applications.
3. System Processes: Windows itself consumes a significant amount of memory to manage system processes, background tasks, and essential services. If these processes are consuming an excessive amount of memory, it can lead to a shortage for user applications.
4. Resource-Intensive Applications: Certain applications, particularly those involving graphics processing, video editing, or gaming, demand substantial memory resources. Running multiple such applications concurrently can easily deplete the available memory.
5. Malware or Viruses: Malicious software can consume system resources, including memory, leading to a shortage. This can occur through background processes, excessive data transfers, or even by intentionally corrupting system files.
6. Hardware Issues: In rare cases, faulty RAM modules or other hardware components can contribute to memory exhaustion. This can involve issues like faulty memory controllers or defective RAM chips.
Identifying the Culprit: Diagnosing the Memory Shortage
Pinpointing the exact cause behind the "out of memory" message requires a systematic approach:
1. Task Manager Analysis: The Task Manager is a powerful tool for monitoring system resource usage. By examining the "Performance" tab, you can observe memory usage patterns and identify potential culprits. Look for applications consuming excessive amounts of memory, particularly those exhibiting a steady increase over time.
2. Event Viewer Inspection: The Event Viewer provides a detailed log of system events, including errors and warnings. Examining the "System" log may reveal specific errors related to memory exhaustion, providing valuable clues about the underlying issue.
3. Memory Diagnostic Tools: Windows 11 includes built-in memory diagnostic tools that can test your RAM for errors. These tools can help identify faulty RAM modules that might be contributing to memory issues.
4. Third-Party Memory Monitoring Tools: Numerous third-party memory monitoring tools offer more advanced features for analyzing memory usage. These tools can provide detailed information about individual processes, memory allocation patterns, and potential leaks.
5. System File Checker (SFC) and Disk Cleanup: Running the SFC command and performing a Disk Cleanup can help identify and resolve issues with corrupted system files that might be contributing to memory exhaustion.
Strategies for Reclaiming Memory and Preventing Future Issues
Once you’ve identified the root cause of the "out of memory" message, you can implement appropriate strategies to resolve the issue and prevent its recurrence:
1. Increase RAM: If your system is consistently experiencing memory shortages, increasing RAM is the most direct solution. This ensures sufficient resources for running applications and system processes without conflict.
2. Close Unnecessary Programs: Regularly close applications you’re not actively using to free up memory. This is particularly important when running resource-intensive programs.
3. Manage Startup Programs: Disable unnecessary programs from launching at startup. These programs consume memory even when not in active use, potentially contributing to memory shortages.
4. Update Drivers and Software: Outdated drivers and software can cause memory leaks or inefficiencies. Ensure your system is running the latest drivers and software versions.
5. Run Disk Cleanup: Regularly perform a Disk Cleanup to remove unnecessary files and free up disk space. This can indirectly improve system performance and memory management.
6. Defragmentation: Defragmenting your hard drive can improve system performance, including memory allocation. This is particularly beneficial if you experience slowdowns or frequent memory errors.
7. Scan for Malware: Regularly scan your system for malware using a reputable antivirus program. Malware can consume system resources, including memory, leading to shortages.
8. Utilize Memory Optimization Tools: Consider using memory optimization tools that can help manage memory usage, close unnecessary processes, and prevent memory leaks.
9. Monitor System Processes: Regularly monitor system processes using the Task Manager to identify those consuming excessive amounts of memory. This can help you identify and potentially terminate resource-hungry processes.
10. Consider Hardware Upgrades: If your system is consistently experiencing memory issues despite optimization efforts, consider upgrading your hardware, including the RAM, to ensure sufficient resources for modern applications.
Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying the "Out of Memory" Message
1. What are the common symptoms of an "out of memory" issue in Windows 11?
Common symptoms include slow performance, application crashes, unresponsive programs, error messages related to memory allocation, and system freezes.
2. Is "out of memory" always due to insufficient RAM?
While insufficient RAM is a common cause, other factors like memory leaks, resource-intensive applications, and malware can also contribute to memory exhaustion.
3. How much RAM does Windows 11 require?
The recommended RAM for Windows 11 varies depending on usage. For basic tasks, 4GB is sufficient, but for more demanding tasks like gaming or video editing, 8GB or more is recommended.
4. Can I safely increase RAM on my Windows 11 computer?
Yes, you can safely increase RAM on your Windows 11 computer. Ensure you purchase compatible RAM modules for your system and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installation.
5. What are some common memory optimization tools available for Windows 11?
Popular memory optimization tools include CCleaner, Advanced SystemCare, and Memory Optimizer Pro. These tools can help manage memory usage, close unnecessary processes, and prevent memory leaks.
6. Is it safe to use memory optimization tools?
While many memory optimization tools are safe and effective, it’s important to choose reputable tools from trusted sources. Avoid tools that promise unrealistic performance gains or make claims about "cleaning" the registry.
7. What if I have already upgraded my RAM and am still experiencing memory issues?
If you’ve upgraded your RAM and are still experiencing memory issues, consider investigating other factors like memory leaks, resource-intensive applications, or malware.
8. Can I use a virtual memory file to address "out of memory" issues?
While using a virtual memory file can temporarily alleviate memory shortages, it is not a long-term solution. It involves using hard drive space as a temporary memory buffer, which can significantly slow down system performance.
9. What are some preventative measures to avoid future "out of memory" messages?
Regularly monitor system processes, close unnecessary applications, update drivers and software, scan for malware, and consider increasing RAM if necessary.
10. When should I contact a technician for assistance with "out of memory" issues?
If you’ve exhausted all troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing frequent memory issues, it’s advisable to contact a qualified technician to diagnose and resolve the problem.
Conclusion: Maintaining Memory Health for Optimal Performance
The "out of memory" message in Windows 11 is a clear indication of a critical resource shortage. Understanding the potential causes and implementing effective troubleshooting strategies is crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient computing experience. By addressing memory issues proactively, you can ensure that your system operates at peak performance, free from the frustrating limitations of memory exhaustion.

![Memory Management Blue Screen on Windows 11 [Fix]](https://cdn.windowsreport.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/memory-management-error-windows-11.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the "Out of Memory" Message in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!

















![Change the Administrator Account in Windows 11 [5 Quick Ways]](https://cdn.windowsreport.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/windows-11-change-administrator.jpg)
























![qBitTorrent Review 2024 [Features, Security, Pricing & More]](https://www.cloudwards.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/qbittorrent-main-ui.png)