Disabling Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide To Enhancing System Stability And Troubleshooting
Disabling Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing System Stability and Troubleshooting
Related Articles: Disabling Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing System Stability and Troubleshooting
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Disabling Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing System Stability and Troubleshooting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Disabling Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing System Stability and Troubleshooting

Fast startup, a feature introduced in Windows 8, aims to accelerate the boot process by utilizing a hybrid shutdown mode. While this feature generally provides a faster startup experience, it can also lead to certain complications and limitations. In situations where system stability is paramount, or when troubleshooting complex issues, disabling fast startup might be necessary. This article delves into the intricacies of this feature, exploring its impact, the methods for disabling it, and the potential benefits it can offer.
Understanding Fast Startup
Fast startup, also known as "Hybrid Shutdown," represents a compromise between a traditional shutdown and a hibernation state. Upon selecting "Shut Down," Windows doesn’t completely power off but rather saves the current system state to a hibernation file. This allows for a quicker boot-up process as the system can resume from the saved state instead of loading everything from scratch.
The Trade-offs of Fast Startup
While fast startup generally provides a noticeable speed boost, it comes with certain trade-offs:
- Limited Troubleshooting: Fast startup can hinder troubleshooting efforts. Since the system doesn’t fully shut down, certain system processes and drivers might remain active in the background, making it difficult to isolate and resolve issues.
- Increased System Complexity: The hybrid shutdown mode introduces an additional layer of complexity to the system’s shutdown and startup processes, potentially increasing the likelihood of encountering unexpected behavior or errors.
- Potential Data Integrity Issues: In rare cases, fast startup can lead to data corruption if the hibernation file becomes corrupted or if the system encounters an unexpected shutdown during the hibernation process.
- Incompatibility with Certain Software: Some applications and utilities might not function correctly when fast startup is enabled, as they require a clean system shutdown for proper operation.
Disabling Fast Startup: A Practical Solution
Disabling fast startup is a straightforward process that can be accomplished through the Windows Control Panel or by modifying the system registry.
Using the Control Panel:
- Access Power Options: Open the Control Panel and navigate to "Power Options."
- Choose "Choose what the power buttons do": In the left-hand pane, click on "Choose what the power buttons do."
- Modify Settings: Click on "Change settings that are currently unavailable."
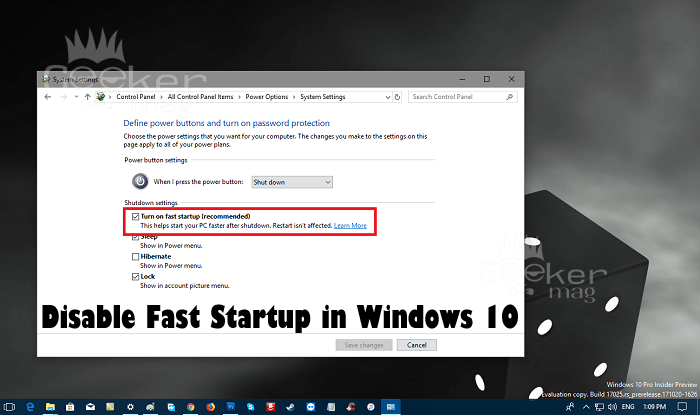
- Disable Fast Startup: Uncheck the box labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
- Save Changes: Click "Save Changes" to apply the modifications.
Using the Registry Editor (Regedit):
- Open Registry Editor: Press "Windows Key + R" to open the Run dialog box. Type "regedit" and press Enter.
-
Navigate to the Registry Key: Navigate to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlPower - Modify the "HiberbootEnabled" Value: Double-click on the "HiberbootEnabled" DWORD value. Set the value data to "0" and click "OK."
- Modify the "FastStartupEnabled" Value: Double-click on the "FastStartupEnabled" DWORD value. Set the value data to "0" and click "OK."
- Close Registry Editor: Close the Registry Editor and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Benefits of Disabling Fast Startup:
Disabling fast startup can offer several benefits, particularly for users who prioritize system stability and troubleshooting capabilities:
- Enhanced Troubleshooting: By disabling fast startup, you ensure a complete system shutdown, allowing for a clean slate for troubleshooting. This eliminates the possibility of lingering processes or drivers interfering with the diagnostic process.
- Improved System Stability: Disabling fast startup can potentially reduce the occurrence of unexpected system behavior or errors related to the hybrid shutdown mode.
- Increased Compatibility: Certain software applications and utilities that require a complete system shutdown for proper functionality will work without issues when fast startup is disabled.
- Reduced Risk of Data Corruption: By eliminating the hibernation file, you reduce the risk of data corruption associated with the fast startup process.
FAQs Regarding Disabling Fast Startup
Q: Will disabling fast startup significantly impact my boot time?
A: While disabling fast startup will result in a slightly longer boot time compared to the fast startup mode, the difference is usually negligible for most users.
Q: Can I revert back to using fast startup after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable fast startup by following the same steps outlined in the Control Panel or Registry Editor instructions, but setting the values to "1" instead of "0."
Q: Is disabling fast startup necessary for all users?
A: Disabling fast startup is not essential for all users. It is primarily recommended for those who frequently encounter system issues, need to perform extensive troubleshooting, or use software that requires a clean system shutdown.
Tips for Disabling Fast Startup
- Backup Your Registry: Before making any changes to the registry, it is always advisable to create a backup of your registry to prevent any potential data loss or system instability.
- Check for Updates: Ensure your system is running the latest Windows updates, as updates often include bug fixes and improvements that might address any issues related to fast startup.
- Monitor System Performance: After disabling fast startup, closely monitor your system’s performance to ensure that the change has not negatively impacted its overall functionality.
Conclusion
Disabling fast startup can be a valuable step for users seeking to enhance system stability, facilitate troubleshooting, and ensure compatibility with specific software applications. While it might slightly increase boot time, the benefits it offers in terms of system reliability and troubleshooting capabilities outweigh the potential performance trade-off for many users. By understanding the intricacies of fast startup and its implications, users can make informed decisions about whether to disable it based on their individual needs and priorities.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Disabling Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing System Stability and Troubleshooting. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!