The Power Of Proximity: Understanding Near Field Communication
The Power of Proximity: Understanding Near Field Communication
Related Articles: The Power of Proximity: Understanding Near Field Communication
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Proximity: Understanding Near Field Communication. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Proximity: Understanding Near Field Communication
-17102022.jpg)
Near field communication (NFC) has become an integral part of our daily lives, quietly facilitating a range of interactions from contactless payments to data sharing. This technology, built upon the principles of electromagnetic induction, allows two devices to communicate wirelessly when placed in close proximity, typically within a few centimeters. While seemingly simple, NFC technology encompasses a complex interplay of electromagnetic fields and data transfer protocols, offering a unique set of advantages that have revolutionized various sectors.
Understanding the Fundamentals
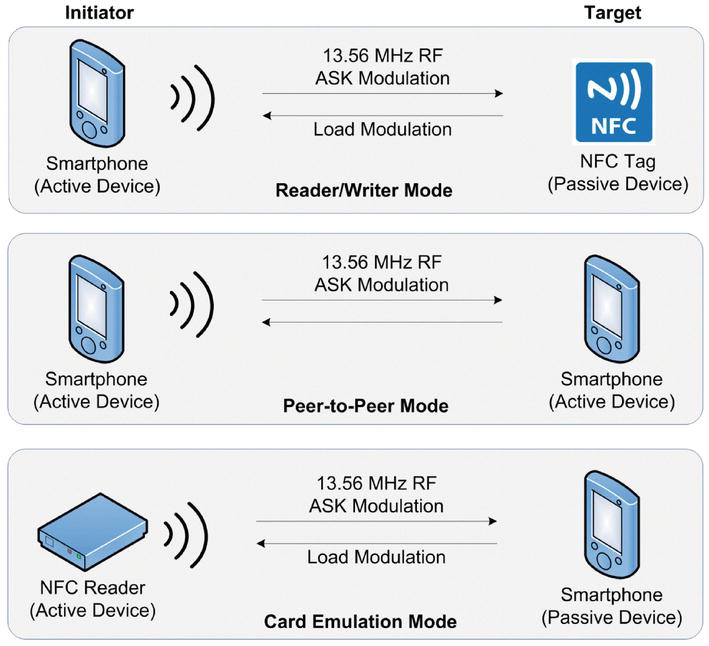
NFC operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, a phenomenon where a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a nearby conductor. This principle is harnessed to enable communication between two devices, one acting as the transmitter and the other as the receiver. The transmitter generates a time-varying magnetic field that induces a current in the receiver, enabling the transfer of data.
The communication process is initiated when two NFC-enabled devices are brought within close proximity. This proximity triggers an exchange of data packets through a standardized protocol, ensuring compatibility between different devices. NFC utilizes a variety of frequencies, typically operating at 13.56 MHz, which allows for efficient data transfer over short distances.
Exploring the Applications
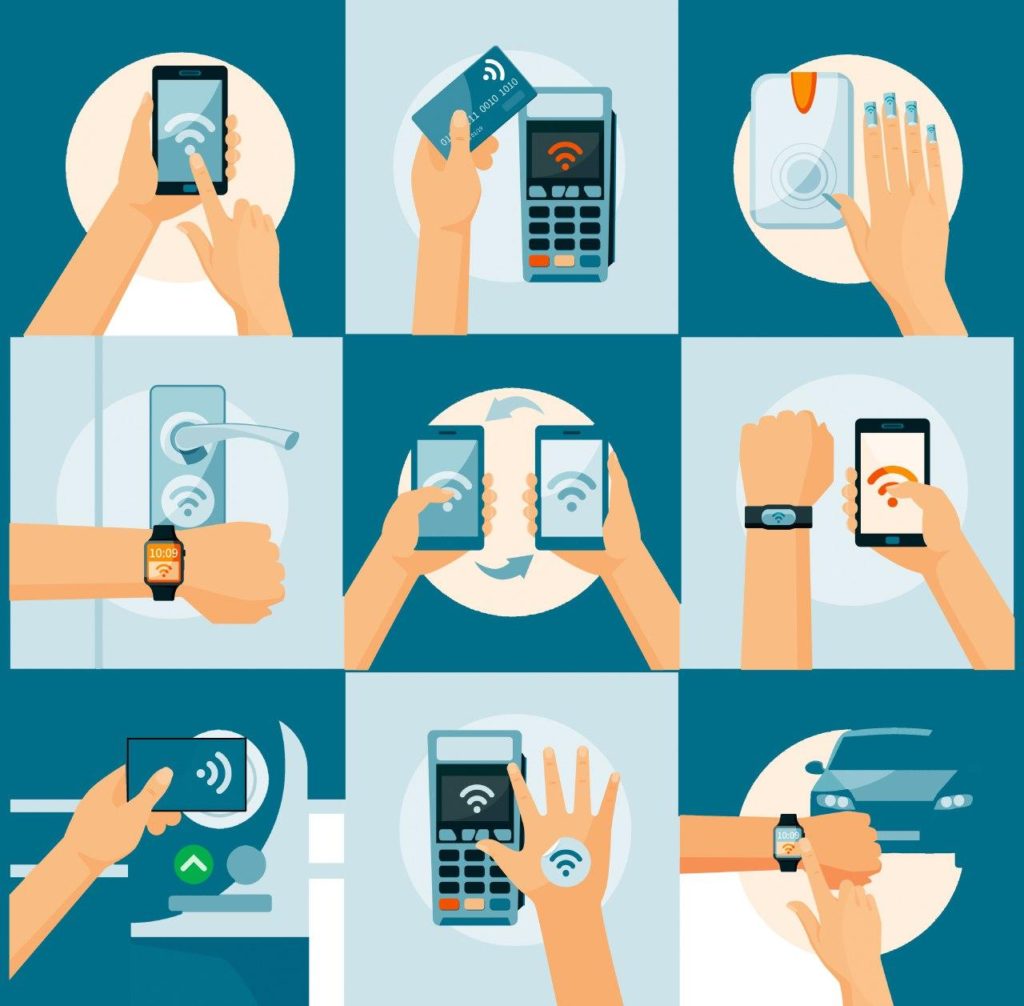
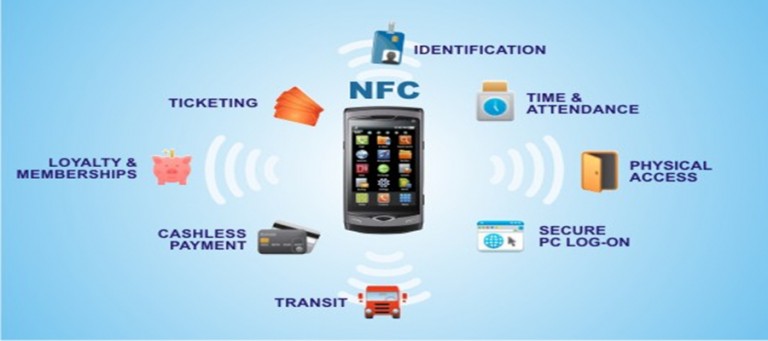
NFC technology finds diverse applications across various sectors, offering a convenient and secure method for data exchange and device interaction. Some of the most prominent applications include:
-
Contactless Payment: NFC has revolutionized the payment industry by enabling quick and secure transactions through contactless cards and mobile devices. Users can simply tap their NFC-enabled device at a point-of-sale terminal to complete a transaction, eliminating the need for physical cards or cash.
-
Data Sharing: NFC facilitates seamless data sharing between devices, allowing users to transfer files, share contact information, or connect to Wi-Fi networks with a simple tap. This feature simplifies data exchange and eliminates the need for manual pairing or complex configuration processes.
-
Device Pairing: NFC enables effortless pairing between devices, simplifying the process of connecting headphones, speakers, or other peripherals. This eliminates the need for manual pairing procedures and streamlines the user experience.
-
Access Control: NFC technology is widely used in access control systems, allowing users to unlock doors, gates, or other restricted areas using NFC-enabled key cards or mobile devices. This technology provides a secure and convenient alternative to traditional key-based access methods.
-
Mobile Ticketing: NFC is increasingly used for mobile ticketing, allowing users to store and access tickets for events, transportation, or other services on their smartphones. This eliminates the need for physical tickets and simplifies the ticketing process.
-
Near Field Communication (NFC) in the Automotive Industry: NFC technology is gaining traction in the automotive industry, enabling keyless entry, remote vehicle control, and secure communication between vehicles and roadside infrastructure.
Benefits of Near Field Communication
The widespread adoption of NFC technology can be attributed to its numerous benefits, including:
-
Security: NFC operates within a short range, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to intercept or eavesdrop on data transmissions. This inherent security feature makes NFC a suitable technology for sensitive applications like contactless payments and access control.
-
Convenience: NFC simplifies everyday interactions by eliminating the need for physical cards, cables, or complex pairing procedures. This ease of use has contributed to the widespread adoption of NFC in various sectors.
-
Versatility: NFC technology can be integrated into a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to credit cards and key fobs. This versatility allows for a broad range of applications and enhances the user experience across different platforms.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: NFC technology is relatively inexpensive to implement, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses and consumers alike. This affordability has contributed to its widespread adoption across various industries.
-
Energy Efficiency: NFC operates at low power levels, minimizing energy consumption and extending battery life. This energy efficiency makes NFC a sustainable and environmentally friendly technology.
Addressing Common Concerns
Despite its numerous benefits, NFC technology has also raised some concerns, particularly regarding security and privacy.
-
Security Concerns: While NFC offers inherent security features, potential vulnerabilities exist, particularly in cases of compromised devices or malicious software. Implementing robust security protocols and user authentication mechanisms is crucial to mitigating these risks.
-
Privacy Concerns: NFC technology can be used to track user movements and collect personal data. Ensuring data privacy and user consent is paramount when implementing NFC solutions, particularly in sensitive applications like contactless payments and access control.
FAQs on Near Field Communication
Q: What is the range of NFC communication?
A: NFC communication typically operates within a range of 4 centimeters or less.
Q: Is NFC secure?
A: NFC technology inherently offers security features, but it is essential to implement robust security protocols and authentication mechanisms to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Q: What are the common applications of NFC?
A: NFC finds widespread applications in contactless payments, data sharing, device pairing, access control, mobile ticketing, and automotive systems.
Q: What are the benefits of using NFC?
A: NFC offers numerous benefits, including security, convenience, versatility, cost-effectiveness, and energy efficiency.
Q: What are the potential risks associated with NFC?
A: Potential risks associated with NFC include security vulnerabilities and privacy concerns, which can be mitigated through robust security protocols and user consent mechanisms.
Tips for Using NFC
- Ensure your device is NFC-enabled and properly configured.
- Keep your NFC-enabled device close to the reader or another NFC-enabled device for successful communication.
- Be aware of potential security risks and implement appropriate measures to protect your data.
- Stay informed about NFC technology and its latest developments to maximize its benefits.
Conclusion
Near field communication technology has emerged as a powerful tool for simplifying everyday interactions and enabling seamless data exchange between devices. Its inherent security features, convenience, versatility, and cost-effectiveness have made it an indispensable technology across various sectors. As NFC technology continues to evolve, it is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping our future interactions with technology. By understanding the fundamentals of NFC and its applications, we can leverage its potential to enhance our daily lives and unlock new possibilities for innovation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Proximity: Understanding Near Field Communication. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!




![Photoimpression 4 Download Full Versionl [PATCHED]](http://global.dlink.com.sg/faq/faq_images/116/dsbc110/dsbc110_photoimpression8.gif)


![Realtek Semiconductor Corp Extension Install error in Windows 11 [SOLVED] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KNjMGn4OB8U/maxresdefault.jpg)







































![How to Download and Install Windows 11 Official [Complete Guide] 2022 - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/W9Bgjuh1sas/maxresdefault.jpg)