Windows 10 Password Expiration: Security, Management, And Best Practices
Windows 10 Password Expiration: Security, Management, and Best Practices
Related Articles: Windows 10 Password Expiration: Security, Management, and Best Practices
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Windows 10 Password Expiration: Security, Management, and Best Practices. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 Password Expiration: Security, Management, and Best Practices

The security of any computer system hinges on robust authentication measures, and Windows 10, like many operating systems, employs password expiration as a key component of its security strategy. This mechanism, while sometimes perceived as an inconvenience, serves a crucial purpose: safeguarding user accounts and sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Understanding the Rationale Behind Password Expiration
Password expiration is not simply a technical quirk; it is a security measure designed to mitigate the risks associated with compromised or outdated passwords. The logic behind this practice is rooted in the following factors:
- Password Compromise: Even with strong passwords, the possibility of compromise remains. Phishing attacks, data breaches, or malware can expose passwords, leaving accounts vulnerable. Regular password changes reduce the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit compromised credentials.
- Password Fatigue: Over time, users may develop predictable patterns in their password choices, making them easier to guess. Forcing periodic password changes encourages users to adopt new, stronger passwords, improving overall security.
- Insider Threats: In scenarios where an employee leaves a company or changes roles, it is crucial to ensure their access to sensitive data is revoked. Password expiration facilitates this by automatically deactivating access after a specified period.
- Compliance Requirements: Many organizations are subject to industry regulations and standards that mandate password expiration policies. These regulations aim to maintain a high level of data security and minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Navigating Password Expiration: A User’s Guide
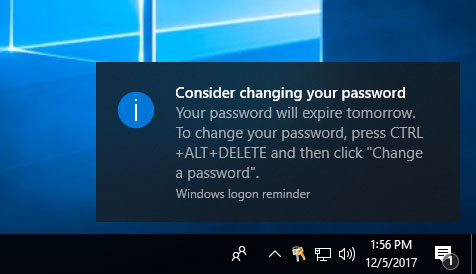
When a Windows 10 password expires, the user is prompted to change it upon login. The system provides a clear notification, directing the user to reset their password. The process typically involves:
- Entering the current password: This step confirms the user’s identity before proceeding with the password change.
- Creating a new password: The user is required to enter a new password that meets the system’s complexity requirements. These requirements typically include a minimum length, a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Confirming the new password: The user must re-enter the new password to ensure accuracy.
- Password change confirmation: Upon successful password change, the user is typically presented with a confirmation message.
Configuration and Management: Empowering System Administrators
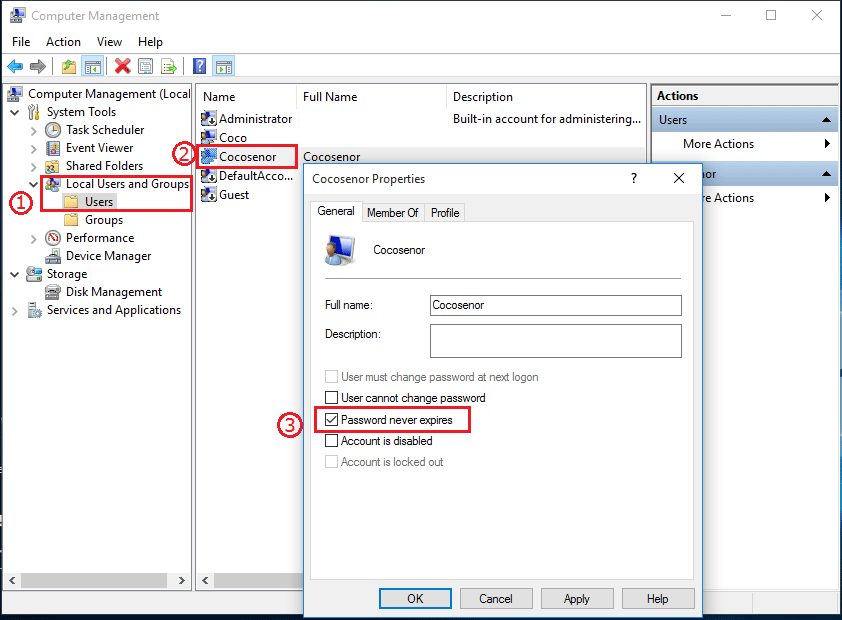
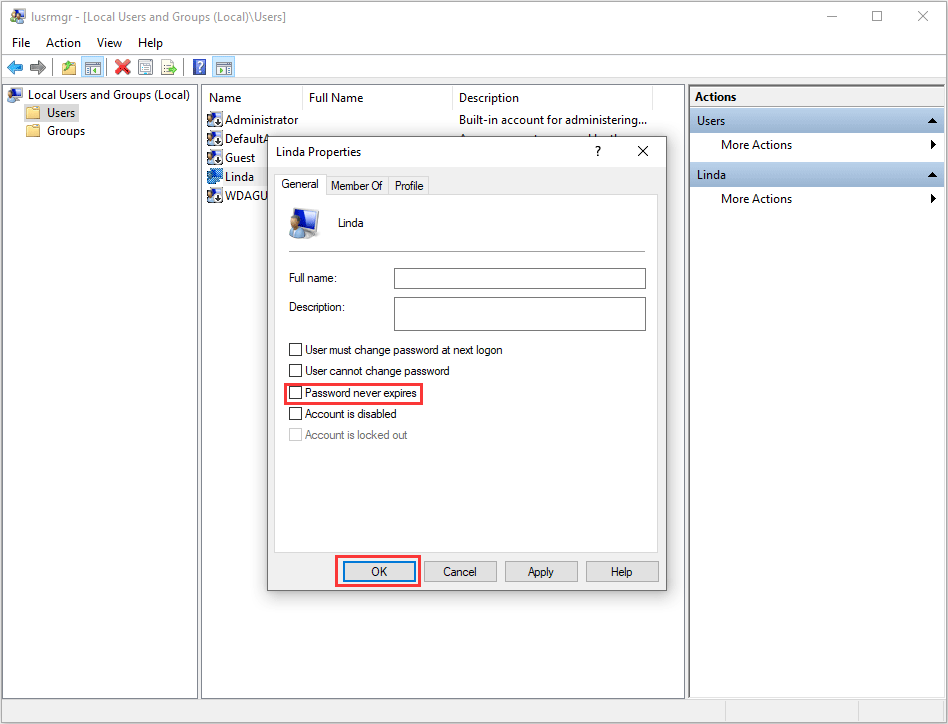
For system administrators, managing password expiration policies is a crucial aspect of maintaining a secure environment. Windows 10 offers a range of configuration options that allow administrators to tailor password policies according to their specific needs:
- Password Expiration Interval: Administrators can define the frequency of password changes, ranging from a few weeks to several months.
- Password Complexity Requirements: These settings control the minimum length and character composition of passwords, ensuring they meet industry best practices.
- Password History: This feature prevents users from reusing previous passwords, promoting stronger password hygiene.
- Account Lockout Policies: Administrators can configure account lockout settings, which temporarily disable access after a specified number of failed login attempts. This mechanism prevents brute-force attacks that aim to guess passwords.
Customization and Flexibility: Balancing Security with User Experience
While password expiration is vital for security, it can sometimes be perceived as an inconvenience. Windows 10 provides options for customization and flexibility to minimize disruption:
- Grace Periods: Administrators can configure grace periods that allow users to continue accessing their accounts for a specified time after the password expiration date. This provides a buffer for users who may be unable to change their passwords immediately.
- Password Reminders: The system can be configured to send email reminders to users approaching their password expiration date, prompting them to proactively update their credentials.
- Password Reset Options: Administrators can implement password reset options that allow users to regain access to their accounts through alternative methods, such as email verification or security questions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Password Expiration in Windows 10
Q: What happens if I don’t change my password when it expires?
A: If you fail to change your password within the grace period, your account will be locked, preventing you from accessing your system.
Q: Can I disable password expiration altogether?
A: While it is technically possible to disable password expiration, it is strongly discouraged. Disabling this feature compromises security and exposes your system to potential vulnerabilities.
Q: How can I reset my password if I forget it?
A: If you forget your password, you can use the Windows 10 password reset feature. This typically involves providing a security question answer or receiving a password reset link through email.
Q: What are the best practices for creating a strong password?
A: A strong password should be at least 12 characters long, include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, and should not be based on personal information easily guessable by others.
Tips for Managing Password Expiration in Windows 10
- Use a Password Manager: Password managers store your passwords securely and can generate strong, unique passwords for each of your online accounts.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide an additional authentication factor, such as a code sent to their phone, in addition to their password.
- Stay Informed: Be aware of the password expiration policies enforced by your organization or system administrator.
- Regularly Review Password Security: It’s good practice to periodically review your password security settings and ensure they remain aligned with best practices.
- Report Suspicious Activity: If you suspect your account has been compromised, report it to your system administrator or security team immediately.
Conclusion
Password expiration in Windows 10 serves as a critical security measure, safeguarding user accounts and sensitive data from unauthorized access. While it may seem like an inconvenience, it is an essential component of a robust security strategy. By understanding the rationale behind password expiration, adhering to best practices for password management, and leveraging the available configuration options, users and administrators can effectively manage password security and maintain a secure computing environment.

![[How To] Configure Password Expiration In Windows 10](https://htse.kapilarya.com/How-To-Configure-Password-Expiration-In-Windows-10-2.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows 10 Password Expiration: Security, Management, and Best Practices. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply