Unveiling The Magic Of Near-Field Communication: A Comprehensive Exploration
Unveiling the Magic of Near-Field Communication: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Magic of Near-Field Communication: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Magic of Near-Field Communication: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Magic of Near-Field Communication: A Comprehensive Exploration

Near-field communication (NFC) has emerged as a ubiquitous technology, seamlessly weaving itself into our daily lives. From contactless payments to data sharing, NFC has revolutionized the way we interact with the world around us. This article delves into the intricacies of NFC, dissecting its workings, highlighting its myriad benefits, and exploring its potential for future innovation.
Understanding the Fundamentals of NFC:
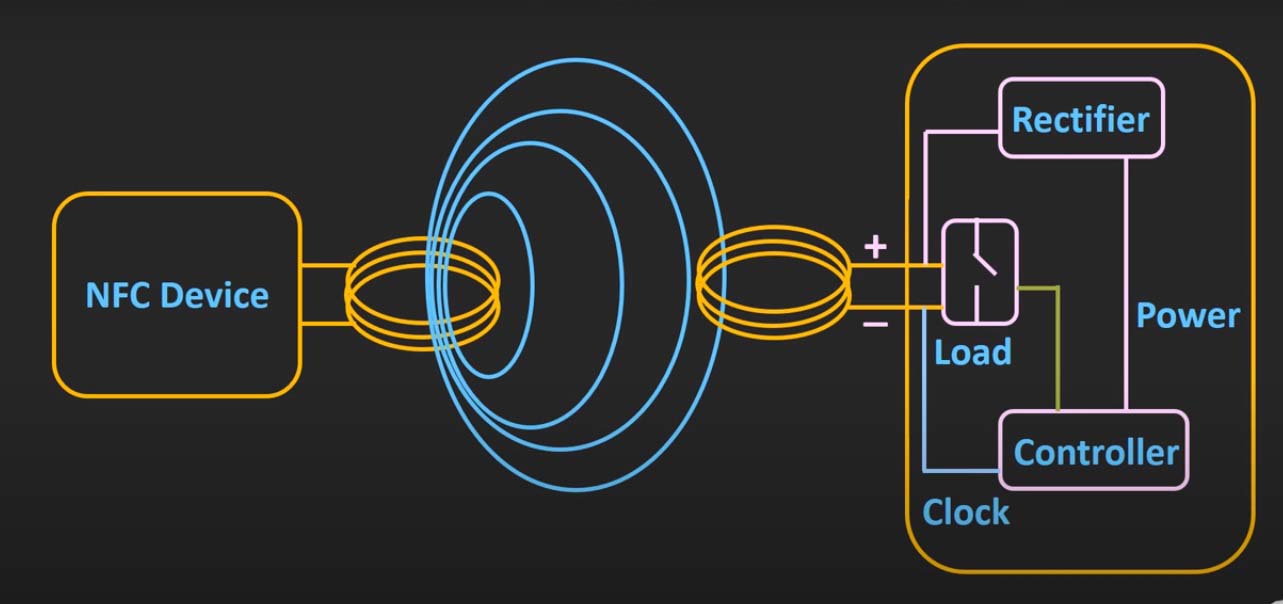
NFC is a short-range wireless communication technology that enables two devices to communicate when they are in close proximity, typically within a distance of a few centimeters. This communication occurs through electromagnetic induction, where one device acts as a transmitter, generating an electromagnetic field, and the other device acts as a receiver, capturing the field’s energy.
The Core Components of NFC:
The foundation of NFC lies in its core components:
- Antenna: The antenna acts as the conduit for electromagnetic waves, transmitting and receiving signals between devices.
- Transceiver: This component is responsible for modulating and demodulating the signals, converting data into electromagnetic waves and vice versa.
- Controller: The controller manages the overall operation of the NFC system, orchestrating communication protocols and data transfer.
- Secure Element (SE): This element, present in NFC-enabled devices, provides a secure environment for storing sensitive information like payment details or personal data.
NFC Communication Modes:
NFC operates in two distinct modes:
- Passive Mode: In this mode, one device acts as a passive tag, solely receiving data from an active device. This mode is commonly used for applications like contactless payments and data sharing.
- Active Mode: Both devices act as active participants, transmitting and receiving data simultaneously. This mode is often employed for peer-to-peer communication, such as file sharing between two NFC-enabled smartphones.
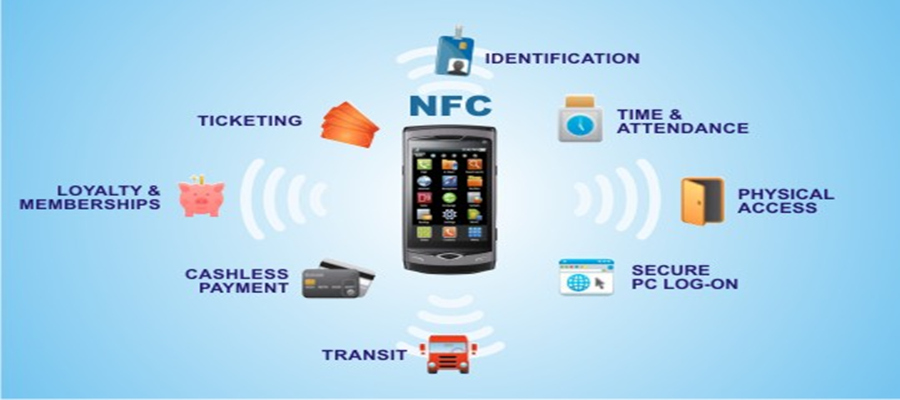
The Power of NFC: Benefits and Applications:
NFC’s versatility and ease of use have led to its widespread adoption across various industries and applications:
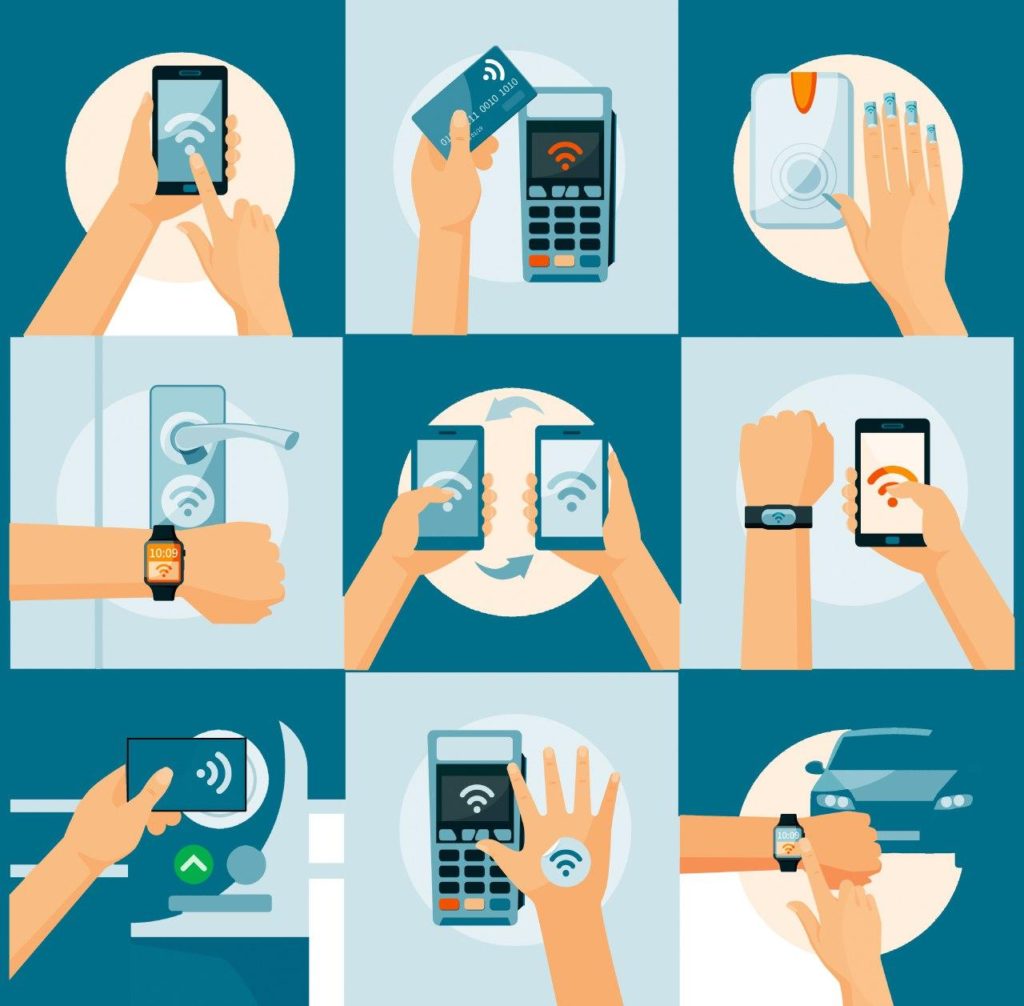
- Contactless Payments: NFC has transformed the way we pay, enabling seamless transactions by simply tapping a smartphone or contactless card against a compatible terminal. This eliminates the need for physical cash or card swiping, promoting speed and convenience.
- Data Sharing: NFC facilitates the effortless transfer of data between devices, such as sharing contact information, photos, or website URLs. This eliminates the need for cumbersome pairing procedures or internet connections.
- Access Control: NFC enables secure access to buildings, vehicles, or other restricted areas, replacing traditional key cards with NFC-enabled devices. This enhances security and simplifies access management.
- Mobile Ticketing: NFC empowers users to store and access electronic tickets for events, transportation, or other services directly on their smartphones, eliminating the need for physical tickets.
- Near-Field Communication Tags (NFC Tags): These passive NFC devices can store information and interact with NFC-enabled devices, enabling applications like product information, interactive experiences, or even triggering actions like playing music or turning on lights.
Exploring the Future of NFC:
NFC continues to evolve, with ongoing advancements and emerging applications:
- Enhanced Security: The integration of advanced security protocols, such as encryption and authentication mechanisms, enhances the security of NFC transactions, safeguarding sensitive data.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: NFC is playing a crucial role in the burgeoning IoT ecosystem, enabling seamless communication between devices and facilitating remote control and data exchange.
- Emerging Applications: NFC is finding new applications in areas like healthcare, where it can be used for patient identification, medication tracking, and remote monitoring.
FAQs on Near-Field Communication:
Q1: How does NFC differ from Bluetooth or Wi-Fi?
A: While NFC, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi are all wireless communication technologies, they differ in their range, speed, and applications. NFC operates over very short distances, typically a few centimeters, making it ideal for contactless payments and data sharing. Bluetooth offers a longer range, up to 10 meters, and is suitable for connecting devices like headphones and speakers. Wi-Fi provides the longest range, covering entire homes or offices, and is primarily used for internet connectivity.
Q2: Is NFC secure?
A: NFC incorporates various security measures to protect data during communication. Encryption protocols ensure that data is transmitted in an encoded form, making it unintelligible to unauthorized parties. Authentication mechanisms verify the identity of devices involved in the communication, preventing unauthorized access.
Q3: What devices support NFC?
A: Most modern smartphones, tablets, and even some wearable devices are equipped with NFC capabilities. Additionally, NFC readers are widely available in retail stores, public transportation systems, and other locations that accept contactless payments.
Q4: How can I enable NFC on my device?
A: Enabling NFC on your device typically involves navigating to the device settings menu and toggling the NFC switch to the "on" position. The specific steps may vary depending on the device manufacturer and operating system.
Q5: What are some tips for using NFC?
A: To optimize your NFC experience, consider the following tips:
- Ensure NFC is enabled: Verify that the NFC setting on your device is turned on before attempting to use NFC features.
- Keep devices close: Ensure that the devices involved in the communication are within a few centimeters of each other for successful data transfer.
- Avoid interference: Keep NFC devices away from metallic surfaces or other potential sources of electromagnetic interference that could disrupt communication.
- Update software: Regularly update your device’s software to ensure compatibility with the latest NFC features and security enhancements.
Conclusion:
NFC has revolutionized the way we interact with the world around us, providing a seamless and secure platform for contactless payments, data sharing, access control, and a myriad of other applications. As technology continues to evolve, NFC is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping our future, connecting devices and enabling innovative solutions in diverse industries. The future of NFC holds immense potential, promising to further simplify and enhance our daily lives.

-17102022.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Magic of Near-Field Communication: A Comprehensive Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply