Unlocking The Power Of Proximity: A Deep Dive Into Near Field Communication Technology
Unlocking the Power of Proximity: A Deep Dive into Near Field Communication Technology
Related Articles: Unlocking the Power of Proximity: A Deep Dive into Near Field Communication Technology
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Power of Proximity: A Deep Dive into Near Field Communication Technology. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Power of Proximity: A Deep Dive into Near Field Communication Technology
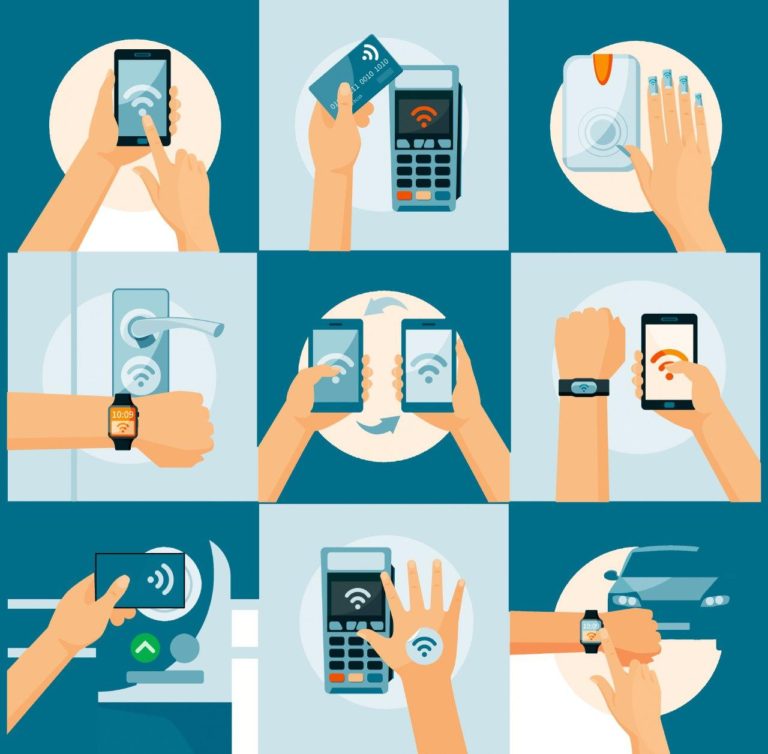

Near field communication (NFC) has quietly revolutionized the way we interact with the world around us. This wireless technology, operating at extremely short distances, allows devices to communicate seamlessly, transforming everyday interactions into effortless transactions, data exchanges, and even secure authentication.
Understanding the Basics of NFC
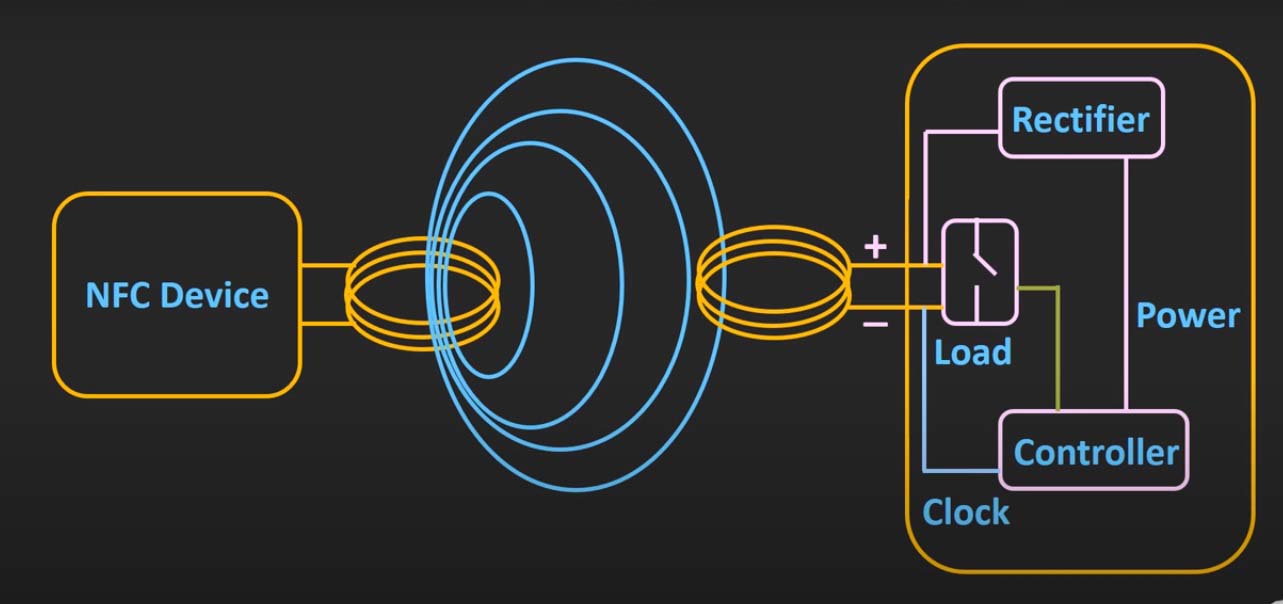
NFC is a subset of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, operating on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Unlike other wireless technologies that rely on radio waves to transmit data over longer distances, NFC operates in the near field, typically within a range of a few centimeters. This proximity-based communication ensures a secure and efficient transfer of information.
How NFC Works:
- Electromagnetic Induction: NFC devices, equipped with antennas, generate electromagnetic fields. When two NFC-enabled devices come within close proximity, their electromagnetic fields interact.
- Data Transfer: This interaction enables the transfer of data between devices. The data exchange can be either passive, where one device acts as a reader and the other as a tag, or active, where both devices participate in the communication process.
- Secure Communication: NFC leverages encryption protocols to ensure secure data transmission. This feature makes NFC ideal for applications requiring secure authentication, such as mobile payments and access control systems.
The Evolution of NFC Technology:
NFC’s journey began in the early 2000s, gaining momentum with the introduction of smartphones and contactless payment systems. The technology has since evolved significantly, with advancements in speed, range, and security.
Key Features of NFC:
- Short-Range Communication: NFC operates within a very limited range, typically a few centimeters, ensuring secure communication and minimizing interference.
- Low Power Consumption: NFC devices consume minimal power, making them suitable for battery-powered devices.
- Fast Data Transfer: NFC allows for rapid data exchange, making it ideal for applications requiring quick transactions.
- Secure Communication: NFC utilizes encryption protocols to protect data during transmission, making it secure for sensitive information.
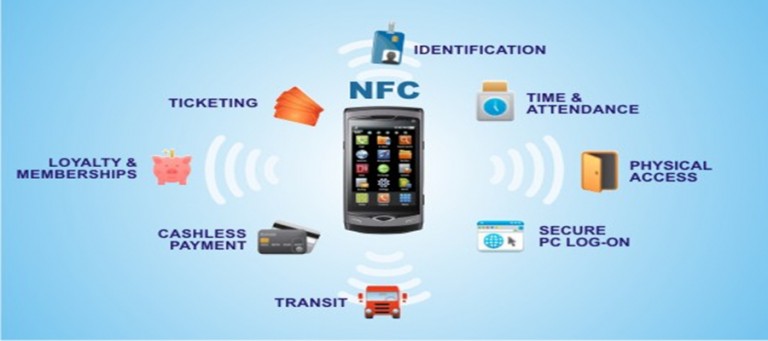
Real-World Applications of NFC:
NFC has permeated various aspects of our lives, revolutionizing how we interact with technology and our surroundings. Here are some prominent applications:
1. Mobile Payments: NFC is the backbone of contactless payments, allowing users to make purchases using their smartphones or other NFC-enabled devices. This technology has transformed the retail landscape, providing a convenient and secure alternative to traditional payment methods.
2. Access Control: NFC is widely used for access control systems, enabling users to unlock doors, gates, and other secured areas using their NFC-enabled devices. This technology enhances security by providing a convenient and reliable authentication method.
3. Data Transfer: NFC facilitates the swift transfer of data between devices, including files, contacts, and other information. This feature simplifies the sharing process, eliminating the need for physical cables or complicated Bluetooth pairing procedures.
4. Transportation Ticketing: NFC is increasingly employed in public transportation systems for contactless ticketing. Passengers can simply tap their NFC-enabled devices to access public transport services, eliminating the need for physical tickets and streamlining the travel experience.
5. Healthcare: NFC finds applications in healthcare, enabling secure identification of patients, tracking medical records, and facilitating communication between medical devices. This technology enhances patient safety and improves the efficiency of healthcare operations.
6. Smart Home Integration: NFC enables seamless communication between smart home devices, allowing users to control appliances, lighting, and other home automation systems using their NFC-enabled devices. This technology provides a convenient and intuitive way to manage a smart home environment.
7. Marketing and Advertising: NFC offers innovative possibilities for marketing and advertising. Businesses can integrate NFC tags into their products or marketing materials, allowing customers to access product information, promotional offers, and interactive experiences using their NFC-enabled devices.
8. Security and Authentication: NFC plays a crucial role in secure authentication and access control. Its short-range communication and encryption capabilities make it ideal for verifying identities, granting access to secure areas, and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
9. Industrial Applications: NFC finds applications in various industrial settings, including asset tracking, inventory management, and process automation. This technology enables efficient data collection, real-time monitoring, and improved operational efficiency.
10. Gaming and Entertainment: NFC is being integrated into gaming consoles and other entertainment devices, enabling players to interact with games and content in innovative ways. This technology opens up new possibilities for immersive and interactive gaming experiences.
Benefits of NFC Technology:
- Convenience: NFC simplifies everyday interactions, eliminating the need for physical keys, cards, or cables.
- Security: NFC leverages encryption protocols to ensure secure data transmission, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Efficiency: NFC enables fast and efficient data exchange, streamlining transactions and processes.
- Versatility: NFC finds applications in various industries and sectors, offering a wide range of possibilities.
- Cost-Effectiveness: NFC technology is relatively inexpensive, making it accessible for various applications.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite its numerous benefits, NFC faces some challenges and considerations:
- Limited Range: NFC’s short-range communication can be a limitation in certain scenarios where longer distances are required.
- Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between different NFC devices and platforms can be challenging.
- Security Concerns: While NFC offers robust security features, potential vulnerabilities remain, requiring ongoing security measures.
- User Adoption: Widespread user adoption is crucial for the success of NFC applications, requiring education and awareness campaigns.
FAQs about NFC:
Q: Is NFC the same as Bluetooth?
A: No, NFC and Bluetooth are distinct technologies. While both facilitate wireless communication, NFC operates at much shorter distances and relies on electromagnetic induction, while Bluetooth uses radio waves for longer-range communication.
Q: Is NFC secure?
A: Yes, NFC utilizes encryption protocols to ensure secure data transmission. However, it’s crucial to use reputable NFC-enabled devices and applications to minimize security risks.
Q: What are some common NFC-enabled devices?
A: Smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, payment cards, access cards, and some smart home devices are commonly equipped with NFC capabilities.
Q: How can I enable NFC on my device?
A: Enabling NFC on your device typically involves navigating to the settings menu and activating the NFC function. The specific steps may vary depending on your device and operating system.
Q: What are some tips for using NFC safely?
A:
- Be cautious of public NFC readers: Avoid using your NFC-enabled device near public NFC readers unless you’re sure of their legitimacy.
- Keep your device secure: Use strong passwords and enable security features on your device to protect your data.
- Update your device software: Regular software updates often include security patches that enhance the protection of your device.
Conclusion:
NFC technology has become an integral part of our digital world, facilitating seamless communication and simplifying our everyday interactions. Its short-range communication, low power consumption, and robust security features make it ideal for a wide range of applications, from mobile payments and access control to smart home integration and industrial automation. As NFC technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative and transformative applications in the future, shaping the way we interact with technology and our surroundings.
-17102022.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Power of Proximity: A Deep Dive into Near Field Communication Technology. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply