Understanding The Program Files (x86) Folder In Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Program Files (x86) Folder in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Program Files (x86) Folder in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Program Files (x86) Folder in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Program Files (x86) Folder in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
+folders.jpg)
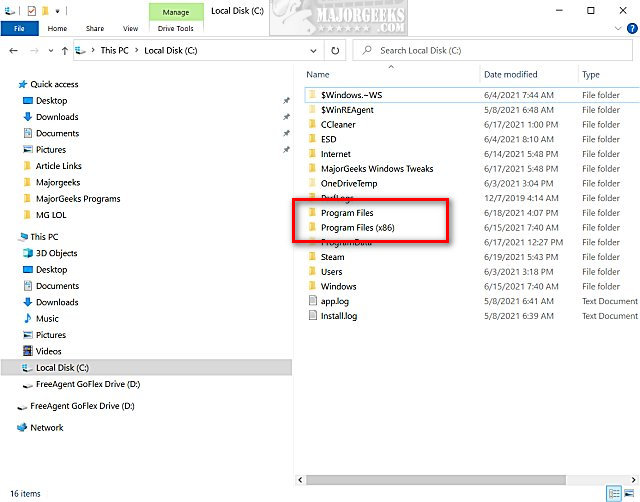
Windows 10, like its predecessors, utilizes a hierarchical file system to organize data and applications. Within this system, the "Program Files" folder serves as a central repository for the majority of installed programs and their associated files. In the case of 64-bit Windows 10, a separate folder named "Program Files (x86)" exists, which is crucial for ensuring compatibility with legacy 32-bit applications.
The Importance of "Program Files (x86)": Compatibility and Legacy Software
The presence of "Program Files (x86)" in 64-bit Windows 10 stems from the need to maintain compatibility with older 32-bit applications. While 64-bit operating systems offer advantages in terms of performance and memory management, many software programs were developed for 32-bit environments. "Program Files (x86)" provides a dedicated space for these legacy applications, allowing them to run seamlessly on a 64-bit platform.
A Deeper Look at the "Program Files (x86)" Folder:
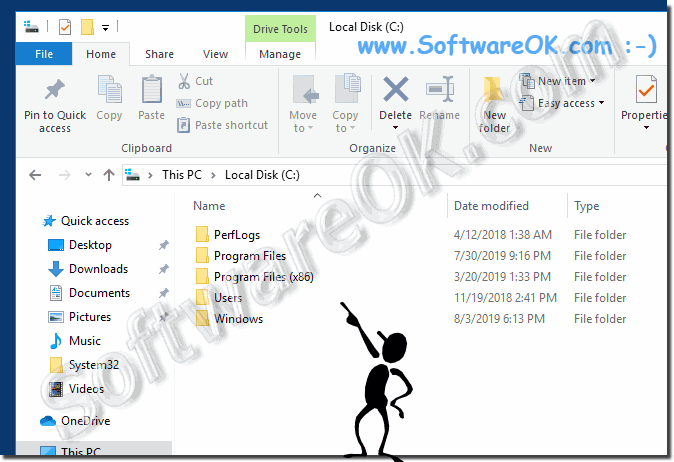
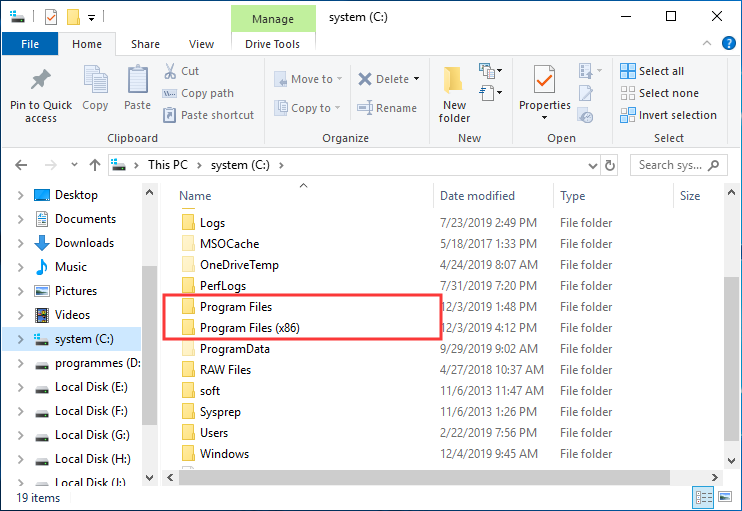
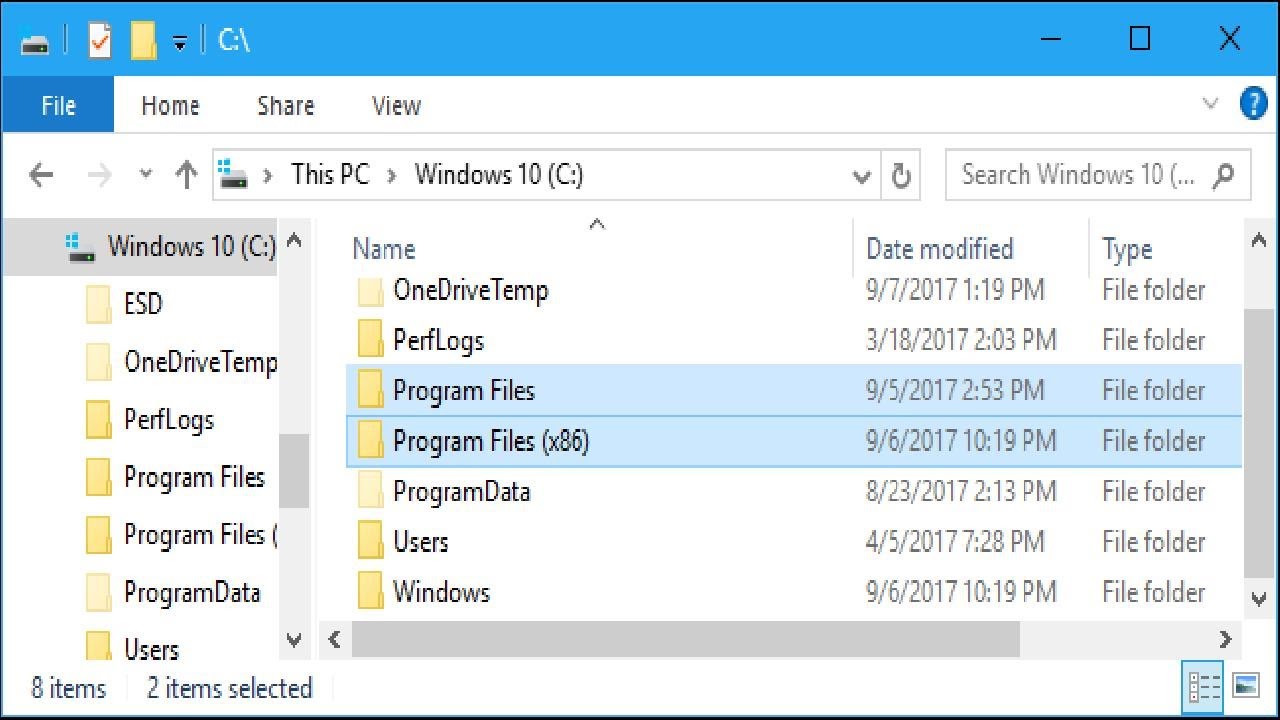
- Location: The "Program Files (x86)" folder is located in the root directory of the system drive, typically "C:Program Files (x86)".
-
Contents: It houses a wide range of program files, including:
- Executable files (.exe): These are the primary files that launch programs.
- Libraries (.dll): These files contain code that programs use to perform specific tasks.
- Configuration files: These files store settings and preferences for individual programs.
- Data files: These files store data used by programs, such as user documents or game save files.
- Organization: Programs are typically organized within "Program Files (x86)" by their publisher or developer. For instance, the folder "Adobe" might contain all files related to Adobe products.
Benefits of Using "Program Files (x86)":
- Compatibility: The folder ensures that older 32-bit applications can function correctly on 64-bit Windows 10.
- Organization: Keeping program files in a dedicated location improves system organization and simplifies software management.
- Security: By separating 32-bit and 64-bit applications, potential conflicts and security vulnerabilities are minimized.
Navigating the "Program Files (x86)" Folder:
The "Program Files (x86)" folder can be accessed through the File Explorer in Windows 10. Users can navigate to this folder by typing "C:Program Files (x86)" in the address bar or by browsing through the "This PC" window.
Exploring the "Program Files (x86)" Folder:
- Finding specific program files: Users can search for specific files within the "Program Files (x86)" folder by using the search bar in the File Explorer.
- Identifying program versions: By examining the folder structure, users can determine the installed versions of different programs.
- Troubleshooting application issues: The "Program Files (x86)" folder can be a valuable resource for troubleshooting application problems. By examining the files and settings within the program’s folder, users can often identify and resolve issues.
Key Considerations:
- Modifying files within "Program Files (x86)": While navigating the folder is generally safe, modifying or deleting files within "Program Files (x86)" should be done with caution. Incorrect modifications can lead to application malfunctions or system instability.
- Software installation: When installing new software, the installer typically places the program files in the appropriate location, either "Program Files" or "Program Files (x86)", based on the program’s compatibility.
- System updates: Windows updates may modify or replace files within "Program Files (x86)" to ensure optimal performance and security.
FAQs Regarding "Program Files (x86)":
Q: Can I delete the "Program Files (x86)" folder?
A: Deleting the "Program Files (x86)" folder is not recommended. It is an integral part of the Windows operating system and contains essential files for running legacy applications. Deleting it will render these applications unusable.
Q: Why do I need two "Program Files" folders?
A: The two "Program Files" folders are necessary to accommodate both 64-bit and 32-bit applications. The "Program Files" folder is for 64-bit applications, while "Program Files (x86)" is for 32-bit applications.
Q: How do I know if a program is 32-bit or 64-bit?
A: The program’s installer or its description often indicates its bitness. Alternatively, you can right-click the program’s executable file, select "Properties," and check the "Compatibility" tab.
Q: Can I move programs from "Program Files (x86)" to another location?
A: Moving programs from "Program Files (x86)" to another location is generally not recommended. It can disrupt the program’s functionality and lead to unexpected behavior.
Q: Should I install 32-bit or 64-bit applications?
A: If your system is 64-bit, installing 64-bit applications is generally preferred for better performance. However, if a program is only available as a 32-bit version, you can install it in "Program Files (x86)".
Tips for Managing "Program Files (x86)":
- Regularly clean up the folder: Deleting unnecessary files from "Program Files (x86)" can free up disk space and improve performance.
- Use a disk cleanup tool: Windows includes a built-in disk cleanup tool that can identify and remove unnecessary files, including those in "Program Files (x86)".
- Scan for malware: Regularly scan the "Program Files (x86)" folder for malware using a reputable antivirus program.
- Back up important files: Create backups of important files within "Program Files (x86)" to safeguard against data loss.
Conclusion:
The "Program Files (x86)" folder plays a crucial role in ensuring compatibility for legacy applications on 64-bit Windows 10. By providing a dedicated space for 32-bit software, the folder facilitates seamless operation while maintaining system stability and organization. Understanding its purpose and navigating its contents empowers users to manage their software effectively, troubleshoot issues, and optimize their Windows 10 experience. While it is important to treat the folder with respect and avoid unnecessary modifications, "Program Files (x86)" remains a vital component of the Windows ecosystem, ensuring continued access to a vast library of software.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Program Files (x86) Folder in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply