Understanding Network Throttling In Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Network Throttling in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Network Throttling in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Network Throttling in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Network Throttling in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide

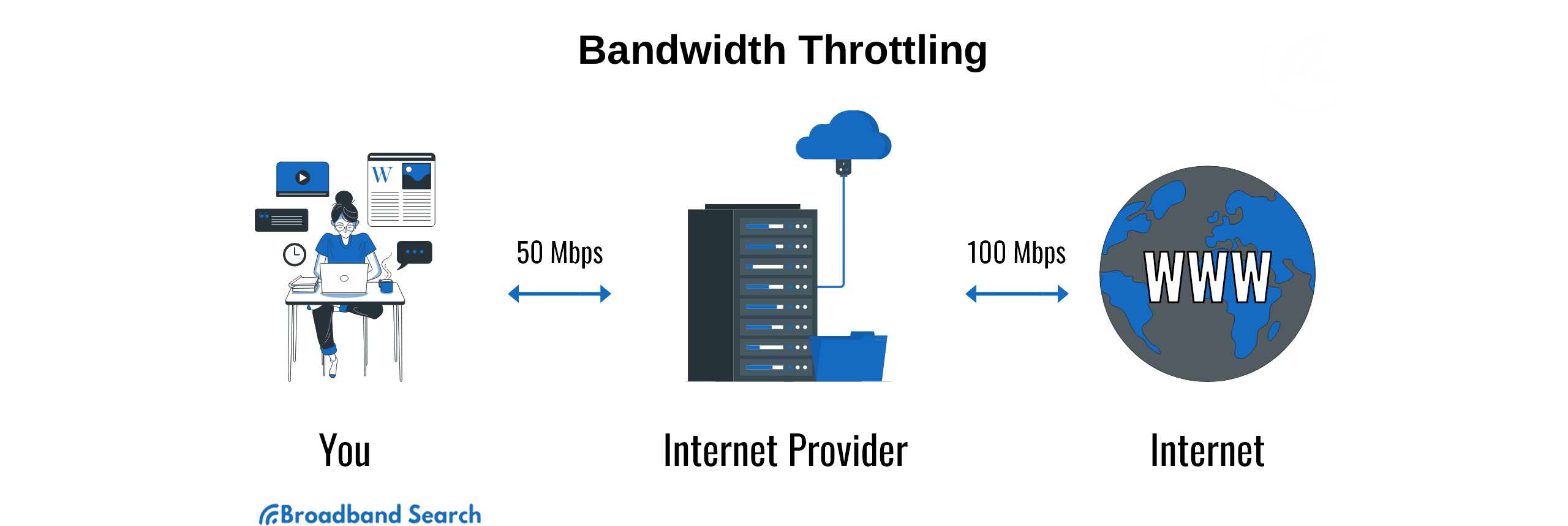
Network throttling is a mechanism employed by operating systems, including Windows 10, to manage network bandwidth allocation. It involves prioritizing certain network traffic over others, ensuring that critical applications receive sufficient bandwidth while less important tasks are temporarily slowed down. This process is crucial for maintaining system stability and optimizing user experience, particularly when dealing with limited bandwidth or high network demands.
How Network Throttling Works in Windows 10
Windows 10 utilizes a sophisticated network prioritization system that dynamically adjusts network traffic based on various factors. These factors include:
- Application Priority: Windows assigns priority levels to different applications. Applications deemed critical, such as system processes, updates, and real-time communication tools, are given higher priority, while background tasks, such as file downloads and streaming services, are often assigned lower priority.
- Network Connection Type: The type of network connection, whether wired or wireless, influences network prioritization. Wired connections generally receive higher priority due to their inherent stability and higher bandwidth capabilities.
- Network Usage: Windows monitors network usage patterns and adjusts bandwidth allocation accordingly. If a network is heavily congested, applications with lower priority may experience throttling to ensure that essential processes continue smoothly.
- User Preferences: Windows allows users to manually adjust network priorities for individual applications, granting them more control over bandwidth allocation.
Benefits of Network Throttling in Windows 10
Network throttling offers several benefits for Windows 10 users:
- Improved System Performance: By prioritizing critical system processes, network throttling ensures that essential tasks, such as system updates and security checks, are not hindered by other network activities. This contributes to a smoother and more responsive user experience.
- Enhanced Network Stability: During periods of high network traffic, network throttling helps prevent network congestion and potential disruptions by prioritizing essential traffic. This ensures that critical applications continue to function smoothly, even under heavy load.
- Optimized Bandwidth Utilization: By allocating bandwidth strategically, network throttling ensures that critical applications receive the necessary resources, while less important tasks are temporarily slowed down. This optimizes bandwidth utilization and prevents network bottlenecks.
- Improved User Experience: By ensuring that essential applications receive adequate bandwidth, network throttling enhances the overall user experience, making online activities more enjoyable and efficient.
Understanding Network Throttling in Practice
While network throttling operates behind the scenes, users can observe its effects in various scenarios:
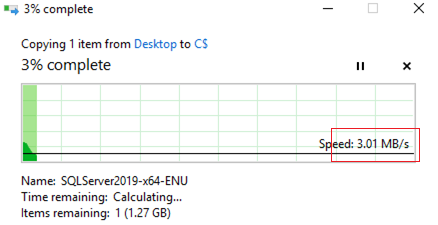
- Slow Downloads or Streaming: When network resources are limited, applications with lower priority, such as file downloads or streaming services, may experience temporary slowdowns due to network throttling.
- Lag in Online Games: Online games often require high bandwidth and low latency. Network throttling can temporarily affect game performance during periods of high network activity, resulting in lag or stuttering.
- Delayed System Updates: System updates are critical for maintaining system security and stability. Network throttling ensures that these updates receive sufficient bandwidth, even when other network activities are ongoing.
Managing Network Throttling in Windows 10
Windows 10 provides users with several options for managing network throttling:
- Network & Internet Settings: The "Network & Internet" settings allow users to adjust network priority for individual applications. Users can prioritize specific applications, ensuring they receive sufficient bandwidth, even during periods of high network activity.
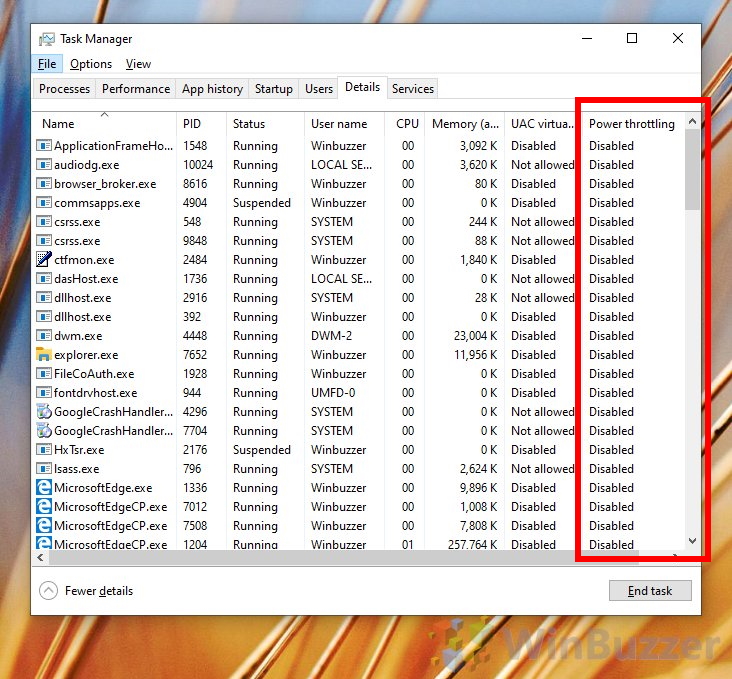
- Task Manager: The Task Manager provides insights into network usage and allows users to identify applications that are consuming excessive bandwidth. This information can be used to adjust network priorities and optimize bandwidth allocation.
- Third-Party Software: Several third-party network management tools offer more advanced features for managing network throttling, allowing users to fine-tune bandwidth allocation and optimize network performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is network throttling a security threat?
A: Network throttling itself is not a security threat. However, it is important to be aware that malicious software could potentially exploit network throttling mechanisms to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.
Q: Can network throttling be disabled?
A: While it is technically possible to disable network throttling, it is generally not recommended. Disabling network throttling can lead to network instability, reduced system performance, and potential security vulnerabilities.
Q: How can I identify if network throttling is affecting my internet connection?
A: You can identify network throttling by observing unusual slowdowns in specific applications, particularly during periods of high network activity. You can also use network monitoring tools to track bandwidth usage and identify potential bottlenecks.
Tips for Optimizing Network Throttling in Windows 10
- Prioritize Critical Applications: Ensure that essential applications, such as system updates, security software, and real-time communication tools, are assigned high priority in network settings.
- Monitor Network Usage: Regularly monitor network usage to identify applications that are consuming excessive bandwidth. Adjust network priorities accordingly to ensure that critical applications receive sufficient resources.
- Use Wired Connections When Possible: Wired connections generally provide more stable and reliable network performance compared to wireless connections.
- Optimize Network Settings: Ensure that your network settings are configured optimally for your specific needs and environment.
- Consider Third-Party Network Management Tools: Explore third-party network management tools to gain more control over network throttling and optimize bandwidth allocation.
Conclusion
Network throttling is an essential mechanism in Windows 10 that helps manage network bandwidth allocation, ensuring that critical applications receive sufficient resources while less important tasks are temporarily slowed down. By understanding how network throttling works and utilizing the available management tools, users can optimize network performance, improve system stability, and enhance the overall user experience. While network throttling may occasionally lead to temporary slowdowns in certain applications, it ultimately contributes to a more efficient and reliable network environment.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Network Throttling in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply