Understanding Disk Partitioning In Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Essence of Disk Partitioning
- 3.2 Benefits of Disk Partitioning
- 3.3 Types of Partitions in Windows 10
- 3.4 Creating Partitions in Windows 10
- 3.5 Considerations for Partitioning
- 3.6 FAQs Regarding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Disk Partitioning in Windows 10
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
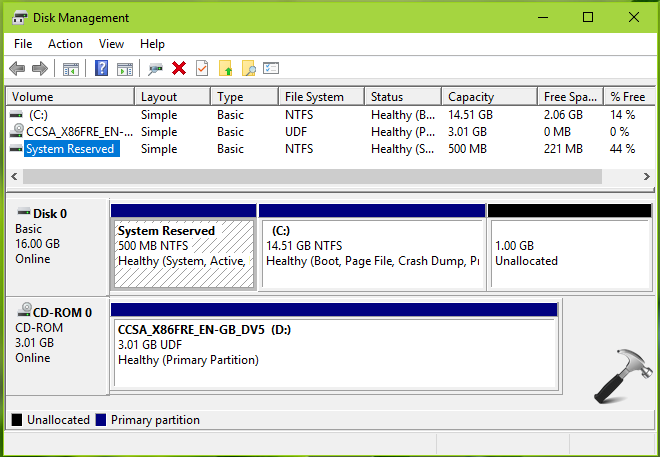
Disk partitioning is a fundamental aspect of managing storage space in Windows 10. It involves dividing a physical hard drive into multiple logical sections, each treated as a separate storage unit. This practice offers numerous advantages, enhancing system organization, performance, and security. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of disk partitioning in Windows 10, providing a clear understanding of its purpose, benefits, and practical implementation.
The Essence of Disk Partitioning
Imagine a large, empty room. Partitioning is akin to dividing this space into smaller, dedicated areas, each serving a specific purpose. Similarly, disk partitioning divides a physical hard drive into logical sections, known as partitions. Each partition acts as an independent storage unit, enabling the user to organize files, install operating systems, or dedicate space for specific applications.
Benefits of Disk Partitioning
1. Enhanced Organization and Management: Partitioning allows for a structured approach to file organization. Users can dedicate partitions for specific purposes, such as storing operating systems, applications, personal data, or backups. This eliminates the clutter of a single, monolithic storage space and facilitates efficient file management.
2. Improved Security: Partitioning provides a layer of security by isolating different data sets. For instance, installing an operating system on a separate partition safeguards it from potential data corruption or malware attacks that might affect other partitions. This approach minimizes the impact of system failures and facilitates data recovery.
3. Enhanced Performance: By dedicating partitions to specific tasks, the system can optimize resource allocation and improve overall performance. For example, installing an operating system on a separate partition with faster read/write speeds can significantly enhance boot times and application launch speeds.
4. Flexibility and Scalability: Partitioning allows for the flexible allocation of storage space. Users can adjust partition sizes based on their evolving needs, adding or removing partitions as required. This flexibility is crucial in managing storage space efficiently, especially when dealing with large data volumes or multiple operating systems.
5. Simplified Data Recovery: Partitioning facilitates data recovery in the event of system failures or hard drive malfunctions. By separating data into different partitions, recovery efforts can focus on specific sections, minimizing the impact on other data sets.
Types of Partitions in Windows 10
1. Primary Partitions: These are the fundamental partitions that can boot an operating system. Windows 10 allows a maximum of four primary partitions on a single hard drive.
2. Extended Partitions: Extended partitions are used to create logical partitions within a single primary partition. This allows for the creation of more than four partitions on a hard drive, albeit with the limitation that only one extended partition can be present.
3. Logical Partitions: These are created within an extended partition and cannot boot an operating system directly. They are typically used for storing data, applications, or backups.
Creating Partitions in Windows 10
Windows 10 provides built-in tools for managing disk partitions, simplifying the process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Accessing Disk Management:
- Press the Windows key + X to open the Quick Access menu.
- Select "Disk Management" from the list.
2. Identifying Available Space:
- The Disk Management window displays all connected hard drives and their partitions.
- Identify the drive you wish to partition and locate any unallocated space.
3. Creating a New Partition:
- Right-click on the unallocated space and select "New Simple Volume."
- Follow the on-screen wizard to configure the new partition’s size, drive letter, and file system.
4. Formatting the Partition:
- The wizard will prompt you to format the new partition. Choose the desired file system (typically NTFS for Windows 10) and assign a volume label.
5. Completing the Process:
- Click "Finish" to complete the partition creation process.
Considerations for Partitioning
- Disk Space Allocation: Carefully consider the size of each partition, allocating sufficient space for the intended purpose.
- File System Choice: Select the appropriate file system for each partition, taking into account compatibility and performance requirements.
- Backup Strategy: Implement a robust backup strategy to safeguard data in the event of system failures or accidental data loss.
FAQs Regarding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10
1. Is partitioning necessary for Windows 10?
While not mandatory, partitioning offers significant benefits in terms of organization, security, and performance. It is recommended for users who want to manage their storage space effectively, especially those with large data volumes or multiple operating systems.
2. Can I partition a drive that already has an operating system installed?
Yes, you can partition a drive with an existing operating system, but proceed with caution. Ensure you have sufficient unallocated space and back up your data before proceeding.
3. How do I resize existing partitions?
Windows 10’s Disk Management tool allows resizing existing partitions, but it may not always be possible to shrink or expand them to the desired size. Third-party partitioning tools often offer more flexibility in resizing operations.
4. Can I delete a partition?
Yes, you can delete a partition, but ensure it does not contain critical data. Remember that deleting a partition will erase all data within it.
5. What is the difference between GPT and MBR partitioning?
GPT (GUID Partition Table) and MBR (Master Boot Record) are two partitioning schemes. GPT supports larger hard drives and offers better security features, while MBR is compatible with older systems.
Tips for Effective Disk Partitioning in Windows 10
- Plan Ahead: Carefully consider the purpose and size of each partition before creating them.
- Use a Partitioning Tool: Third-party partitioning tools offer more advanced features and flexibility compared to Windows 10’s built-in tools.
- Back Up Data: Always back up your data before making any changes to your disk partitions.
- Monitor Partition Usage: Regularly monitor partition usage to ensure sufficient space for all your needs.
Conclusion
Disk partitioning is a powerful tool for managing storage space in Windows 10. By dividing a hard drive into logical sections, users can enhance organization, improve security, optimize performance, and simplify data recovery. Understanding the benefits, types, and processes involved in partitioning allows for informed decisions regarding storage management, ensuring a more efficient and secure computing experience.

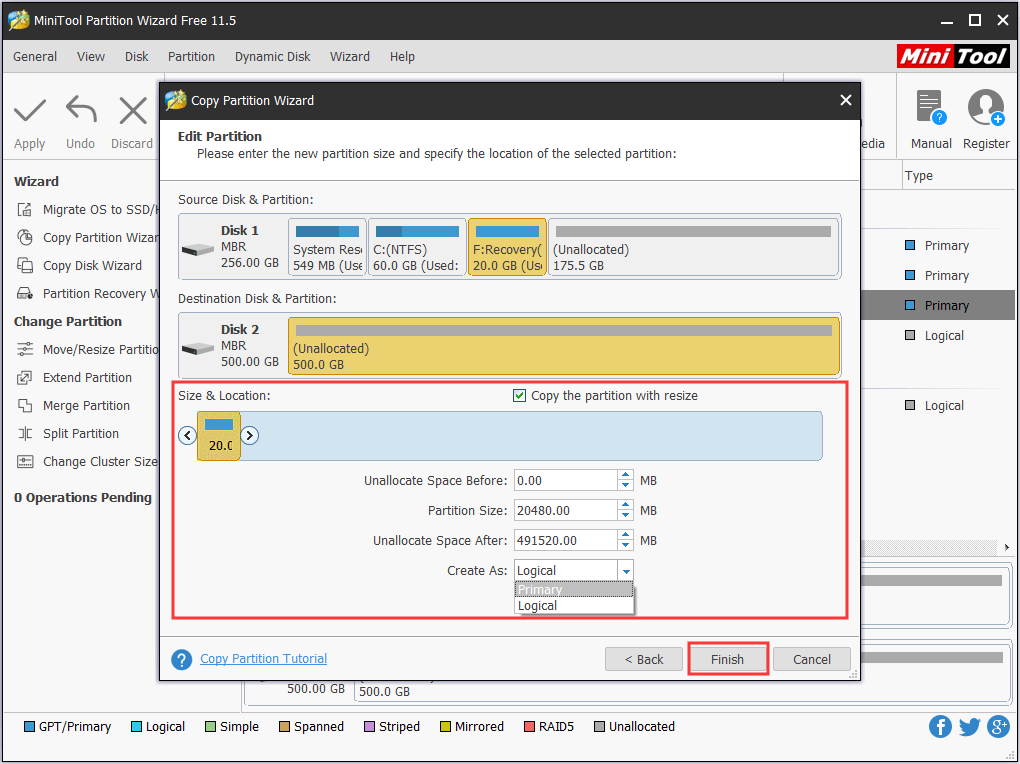
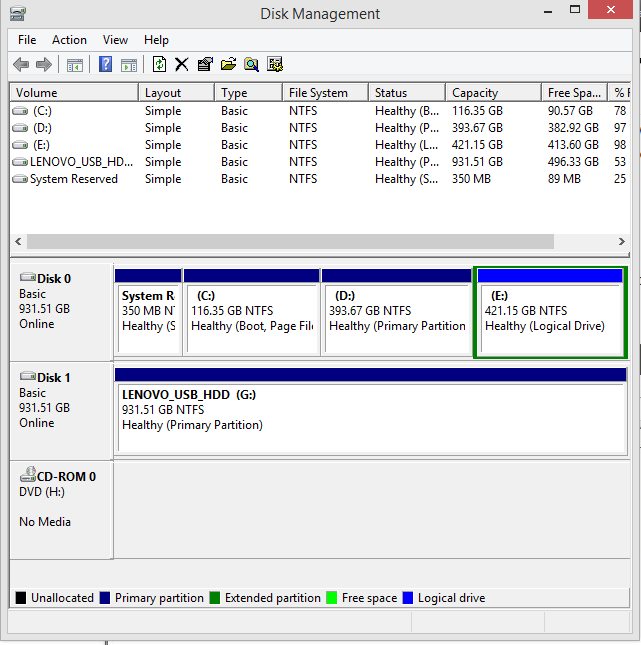

![How To Partition A Hard Drive In Windows 10 [Free, No Software Required]](http://www.techworm.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Disk-Partition-In-Windows-10-1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Disk Partitioning in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply