Understanding And Managing Partitions In Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding and Managing Partitions in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing Partitions in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing Partitions in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding and Managing Partitions in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding and Managing Partitions in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 What are Partitions and Why are They Important?
- 3.2 Types of Partitions in Windows 10
- 3.3 Managing Partitions in Windows 10
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Tips for Managing Partitions in Windows 10
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding and Managing Partitions in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
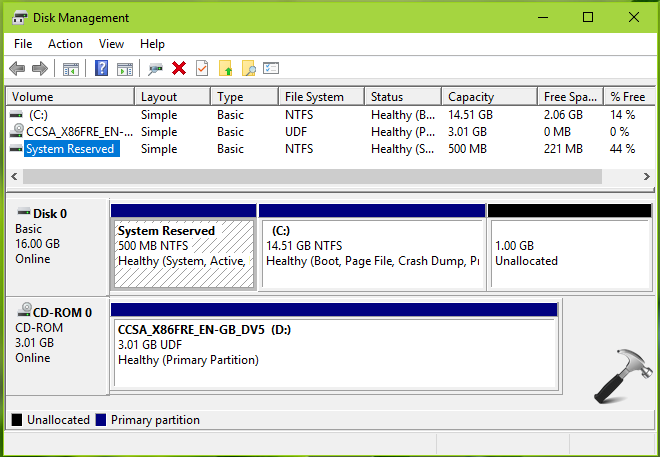
The installation of Windows 10 on a computer typically involves the creation of one or more partitions on the hard drive. These partitions are essentially logical divisions of the physical storage space, allowing for a more organized and efficient management of data. This article delves into the intricacies of partitions in Windows 10, exploring their significance, the various types available, and the tools for managing them after installation.
What are Partitions and Why are They Important?
Partitions act as containers for different operating systems, applications, and data. They are akin to separate rooms within a house, each with its own designated purpose. Without partitions, the entire hard drive would be a single, monolithic space, making it difficult to manage and potentially leading to data conflicts.
Key Benefits of Partitions:
- Enhanced Data Organization: Partitions enable users to segregate different types of data, such as operating systems, applications, and personal files. This promotes a structured file system and simplifies data retrieval.
- Improved System Security: Separating the operating system from user data enhances security. If a virus or malware infection compromises one partition, the other partitions remain unaffected.
- Enhanced Performance: By allocating specific storage space for different tasks, partitions optimize the performance of the operating system and applications. This can lead to faster boot times and improved application responsiveness.
- Multiple Operating Systems: Partitions are essential for dual-booting, allowing users to install and run multiple operating systems on the same computer.
- Data Recovery: In the event of a system failure, recovering data from a separate partition is often easier and less prone to data loss.
- Flexible Storage Allocation: Partitions allow users to adjust the storage space allocated to different applications and files according to their needs.
Types of Partitions in Windows 10
Windows 10 recognizes several types of partitions, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Primary Partitions:
- These are the most common type of partitions, typically used to store the operating system and user data.
- A hard drive can have up to four primary partitions.
2. Extended Partitions:
- Extended partitions are used to create logical drives within a single partition.
- They are not directly accessible by the operating system and require the creation of logical drives within them.
3. Logical Drives:
- Logical drives are created within an extended partition and are directly accessible by the operating system.
- They are essentially individual storage spaces within the extended partition.
4. System Partitions:
- System partitions are specifically designed to store system files, such as the boot files and registry.
- These partitions are usually small and are typically hidden from the user.
5. Boot Partitions:
- Boot partitions are used to store the files required to boot the operating system.
- These partitions are typically small and are usually created during the initial installation of Windows.
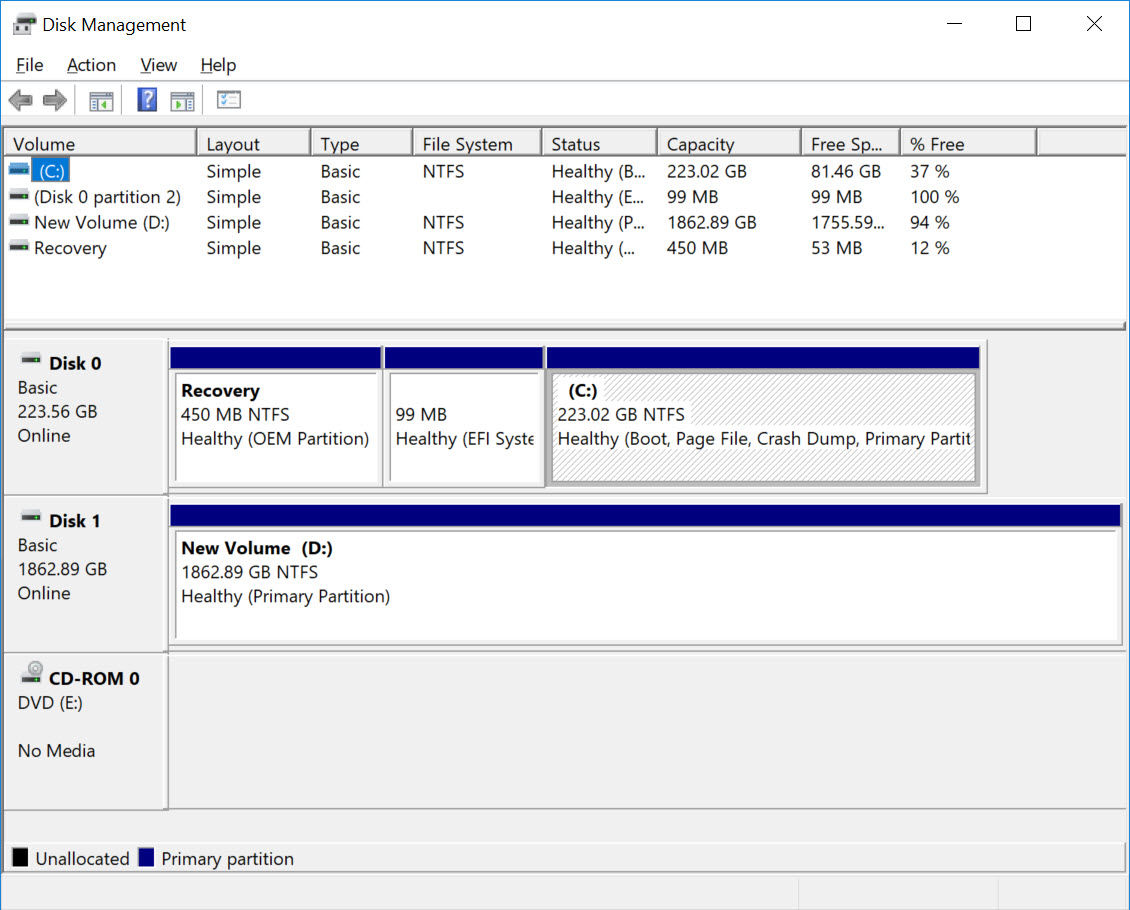
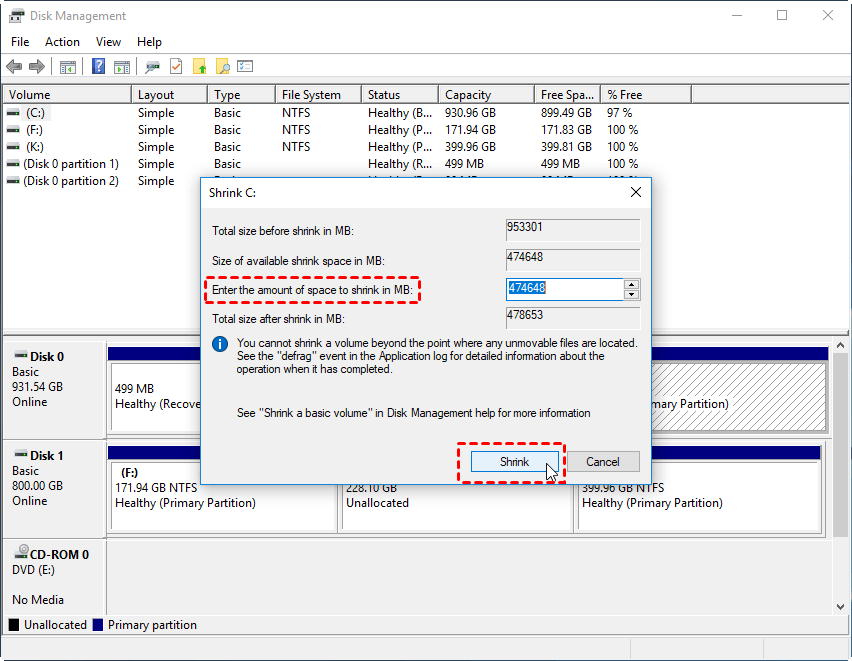
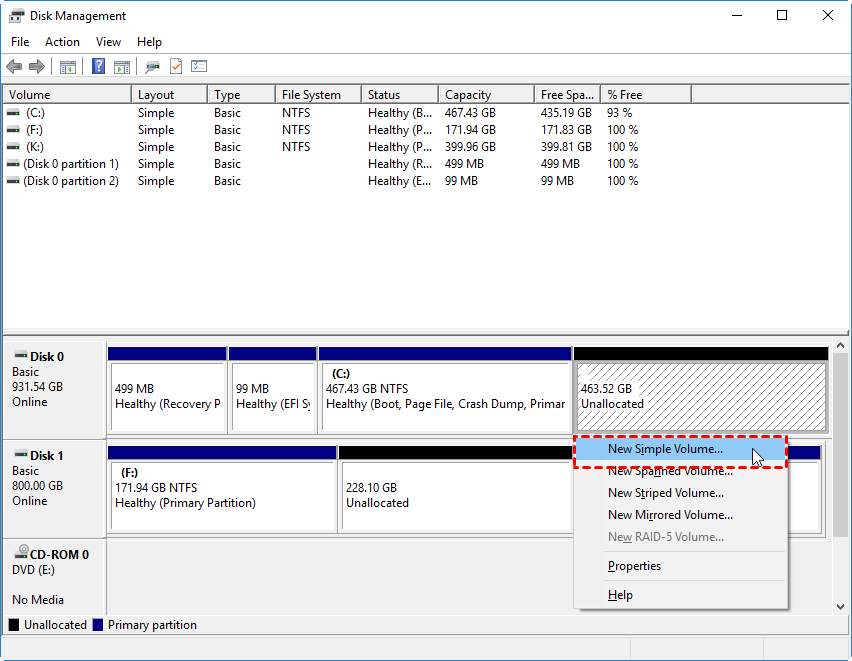
Managing Partitions in Windows 10
Windows 10 offers several built-in tools for managing partitions, allowing users to create, resize, format, and delete partitions as needed.
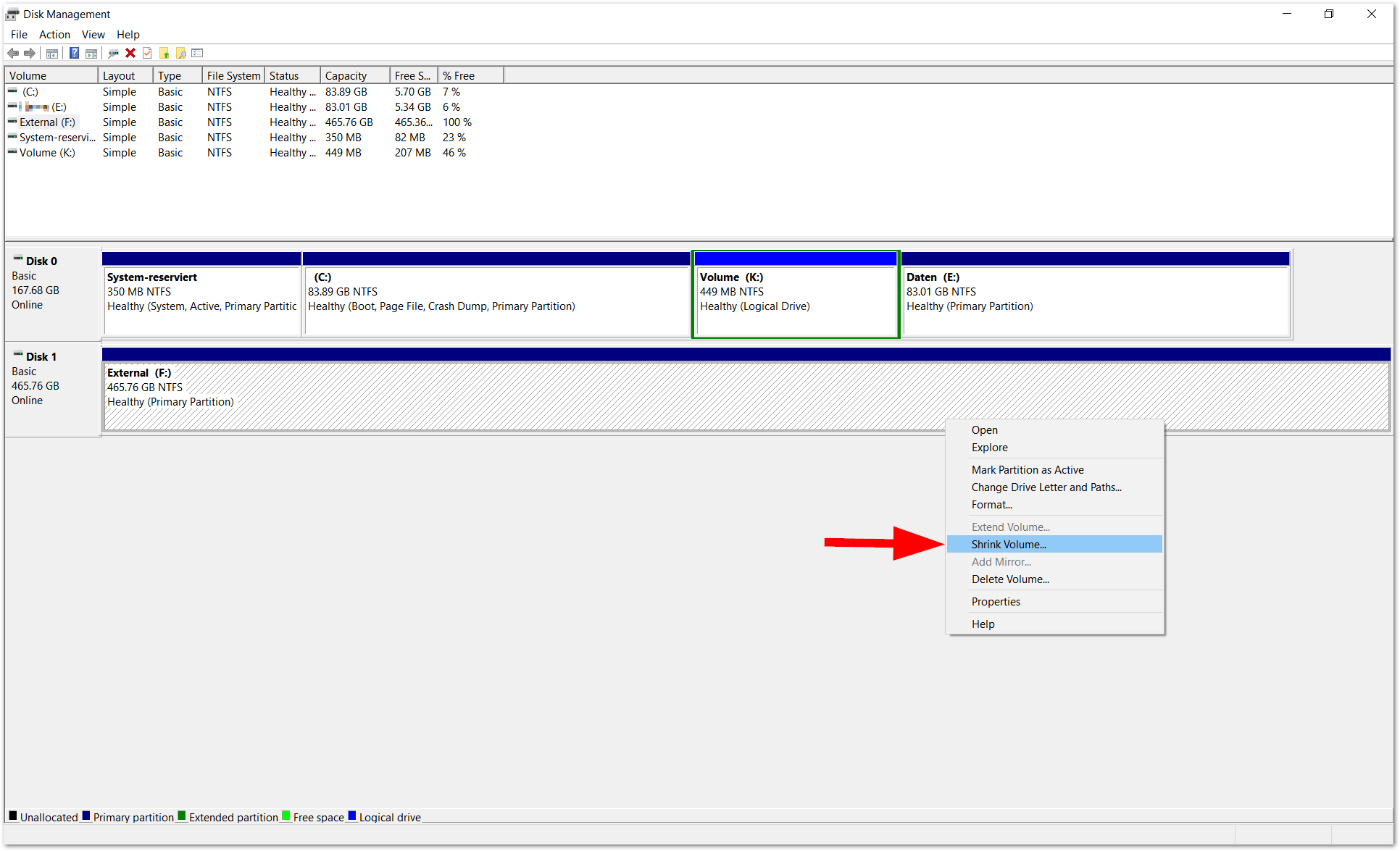
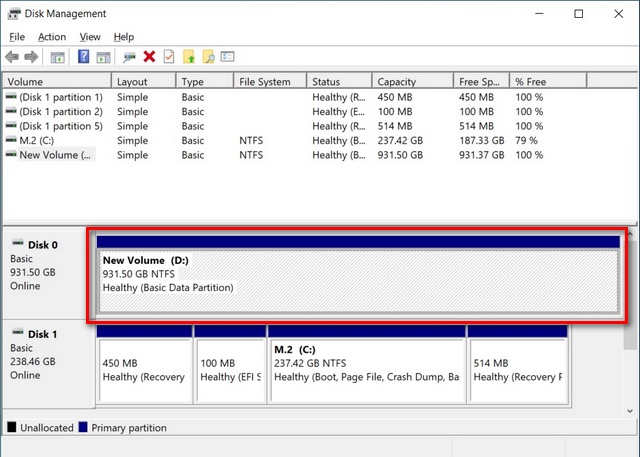
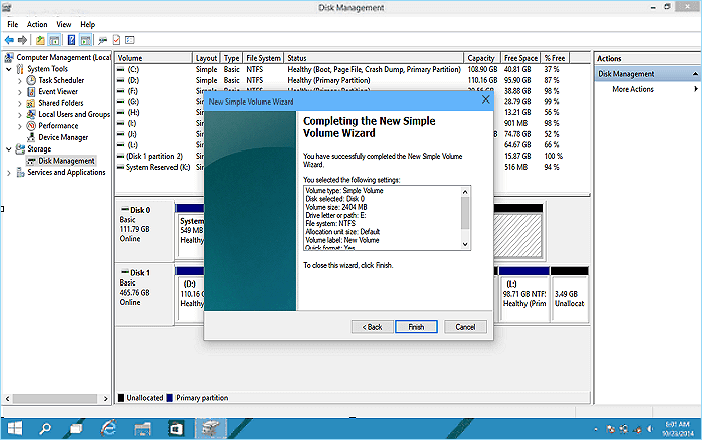
1. Disk Management:
- This tool is accessible through the Windows Control Panel and provides a graphical interface for managing partitions.
- It allows users to create, delete, format, and resize partitions, as well as change drive letters.
2. Command Prompt:
- The Command Prompt offers a more advanced method for managing partitions using command-line commands.
- It allows users to perform more complex operations, such as converting partitions between GPT and MBR formats.
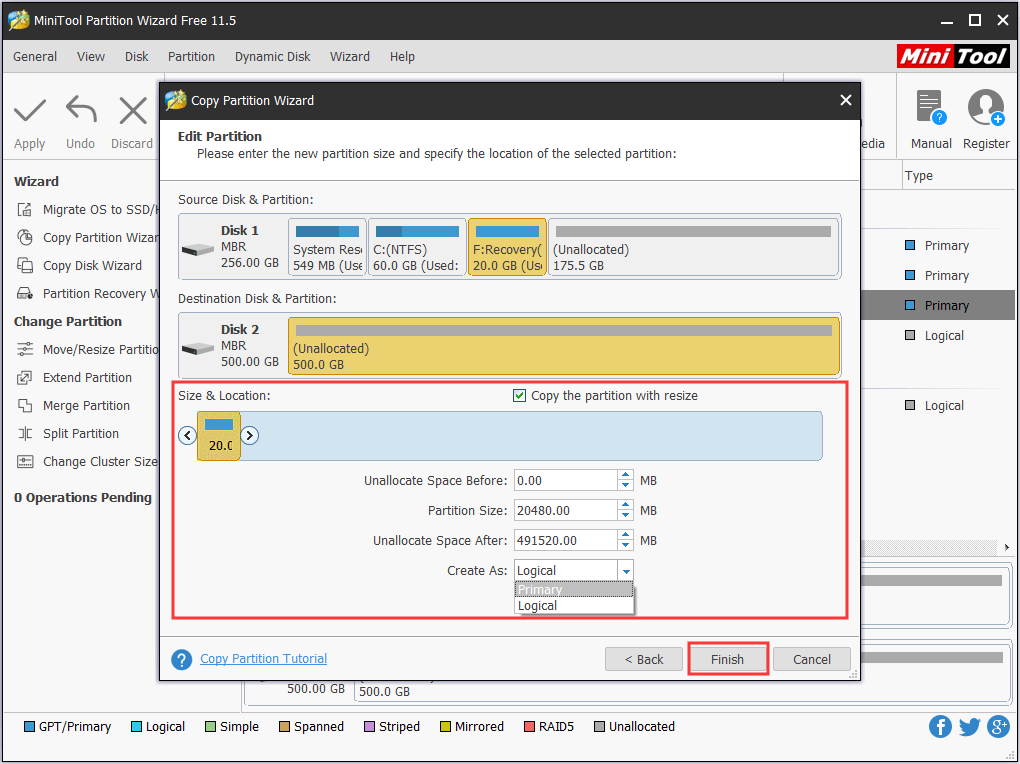
3. Third-Party Partition Managers:
- Several third-party partition managers offer more comprehensive features and advanced options for managing partitions.
- These tools often provide a more user-friendly interface and additional functionalities compared to the built-in tools.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How many partitions should I create?
A: The number of partitions depends on individual needs and preferences. A common approach is to create a separate partition for the operating system and another for user data.
Q2: Can I create a new partition without losing data?
A: Creating a new partition usually requires unallocated space on the hard drive. If the hard drive is full, you may need to resize existing partitions or delete data to create new partitions.
Q3: What is the difference between GPT and MBR partitioning schemes?
A: GPT (GUID Partition Table) is a newer partitioning scheme that offers larger partition sizes and supports more than four primary partitions. MBR (Master Boot Record) is the older scheme, limited to four primary partitions and smaller partition sizes.
Q4: Can I change the drive letter of a partition?
A: Yes, you can change the drive letter of a partition using Disk Management or the Command Prompt.
Q5: What happens if I delete a partition?
A: Deleting a partition will erase all data stored on it. It is crucial to back up important data before deleting any partitions.
Q6: Can I recover data from a deleted partition?
A: Data recovery from a deleted partition is possible using specialized data recovery software. However, the success rate depends on factors such as the type of data loss and the time elapsed since deletion.
Tips for Managing Partitions in Windows 10
- Back up data: Always back up important data before making any changes to partitions.
- Use reputable tools: Stick to reliable partition management tools, whether built-in or third-party.
- Understand the risks: Deleting or resizing partitions can lead to data loss. Proceed with caution.
- Seek professional help: If unsure about partition management, consult a qualified technician.
Conclusion
Partitions play a crucial role in organizing and managing data in Windows 10. Understanding the different types of partitions, their benefits, and the tools for managing them empowers users to optimize their storage space, enhance system security, and improve overall system performance. By employing a structured approach to partition management, users can ensure a seamless and efficient computing experience.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing Partitions in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply