Understanding And Managing Internet Bandwidth Allocation On Personal Computers
Understanding and Managing Internet Bandwidth Allocation on Personal Computers
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing Internet Bandwidth Allocation on Personal Computers
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing Internet Bandwidth Allocation on Personal Computers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing Internet Bandwidth Allocation on Personal Computers
In the digital age, high-speed internet access is paramount for seamless online experiences. However, users often encounter situations where their internet connection feels sluggish, despite having a robust plan. This perceived slowdown can be attributed to a phenomenon known as internet bandwidth allocation, where the computer itself prioritizes different applications and tasks, potentially limiting the bandwidth available for specific activities. Understanding the mechanisms behind this allocation and its implications is crucial for optimizing online performance.
The Role of Bandwidth Allocation in Internet Performance:
Internet bandwidth, often measured in megabits per second (Mbps), represents the maximum amount of data that can be transferred between a computer and the internet in a given time frame. While internet service providers (ISPs) provide a specific bandwidth capacity, the actual speed experienced by a user can vary significantly due to factors such as network congestion, website server performance, and, importantly, the computer’s own internal bandwidth management.
The computer’s operating system, through its network stack, plays a critical role in managing internet bandwidth allocation. It prioritizes different applications based on a variety of factors, including:
- Application type: Some applications, like video streaming or online gaming, require significant bandwidth for real-time data transfer. These applications are often prioritized by the operating system to ensure smooth performance.
- User activity: The operating system might allocate more bandwidth to applications actively in use, while limiting bandwidth for background tasks or applications that are not currently in focus.
- Network conditions: If the internet connection is experiencing congestion or high latency, the operating system might prioritize applications based on their sensitivity to latency. For example, real-time video conferencing might be prioritized over file downloads.
The Impact of Bandwidth Allocation on User Experience:
This intricate interplay of factors can result in noticeable differences in internet performance depending on the user’s activities. For example, a user might experience lag during online gaming while simultaneously downloading a large file, as the operating system allocates more bandwidth to the download task. Similarly, streaming high-definition video might result in buffering or pixelation if the operating system is prioritizing other tasks.
While the operating system’s bandwidth allocation mechanism aims to optimize overall internet performance, it can sometimes lead to undesired outcomes for specific applications. This can be particularly frustrating for users who require consistent bandwidth for demanding tasks like online gaming, video editing, or professional work.
Strategies for Managing Bandwidth Allocation:
Fortunately, users can take several steps to manage internet bandwidth allocation and optimize their online experience:
- Prioritize applications: Many operating systems provide tools for prioritizing specific applications. This allows users to allocate more bandwidth to applications requiring consistent performance, such as online gaming or video conferencing.
- Limit background processes: Background processes, such as software updates, file indexing, or system maintenance tasks, can consume significant bandwidth. Limiting these processes can free up bandwidth for foreground applications.
- Utilize network monitoring tools: Network monitoring tools can provide insights into bandwidth usage patterns, allowing users to identify applications consuming excessive bandwidth and adjust their settings accordingly.
- Optimize network settings: Adjusting network settings, such as MTU size and DNS server configuration, can sometimes improve internet performance by reducing network overhead and optimizing data transfer efficiency.
- Consider dedicated network hardware: For users with demanding online needs, dedicated network hardware, such as a high-performance router or network switch, can provide improved bandwidth allocation and network performance.
Understanding Bandwidth Allocation: A Crucial Skill for Modern Users:
Understanding the intricacies of internet bandwidth allocation is crucial for navigating the modern digital landscape. By comprehending how the operating system manages bandwidth and by implementing strategies for optimization, users can ensure that their internet connection meets their specific needs and provides a seamless online experience.
FAQs on Bandwidth Allocation:
Q: What is the difference between bandwidth and speed?
A: Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over a network connection in a given time frame. Speed, on the other hand, refers to the actual rate at which data is being transferred at a given moment. While bandwidth represents the potential capacity, speed reflects the actual performance at any given time.
Q: How can I identify which applications are consuming the most bandwidth?
A: Network monitoring tools, available for both Windows and macOS operating systems, provide detailed information about network traffic and bandwidth usage. These tools can identify applications consuming excessive bandwidth and help users adjust their settings accordingly.
Q: Can I completely disable bandwidth allocation?
A: While it is not possible to completely disable bandwidth allocation, users can prioritize specific applications or limit background processes to influence the operating system’s allocation decisions.
Q: What are the benefits of prioritizing applications?
A: Prioritizing applications allows users to allocate more bandwidth to applications requiring consistent performance, such as online gaming, video conferencing, or professional work. This can significantly improve the user experience by reducing lag, buffering, and other performance issues.
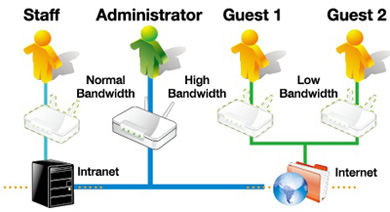
Q: Is it possible to allocate bandwidth to specific devices on a network?
A: Some advanced routers and network management software allow users to allocate bandwidth to specific devices on a network. This can be useful for prioritizing devices for specific tasks, such as allocating more bandwidth to a gaming console or a work computer.
Tips for Optimizing Bandwidth Allocation:
- Regularly monitor network usage: Use network monitoring tools to identify applications consuming excessive bandwidth and adjust settings accordingly.
- Disable unnecessary background processes: Limit background processes, such as software updates, file indexing, and system maintenance tasks, to free up bandwidth for foreground applications.
- Prioritize applications based on usage: Allocate more bandwidth to applications requiring consistent performance, such as online gaming, video conferencing, or professional work.
- Optimize network settings: Adjust network settings, such as MTU size and DNS server configuration, to improve data transfer efficiency and reduce network overhead.
- Consider a dedicated network hardware: For demanding online needs, a high-performance router or network switch can provide improved bandwidth allocation and network performance.
Conclusion:
Internet bandwidth allocation is an integral part of modern computing, influencing the performance of online activities. By understanding the mechanisms behind bandwidth allocation and implementing strategies for optimization, users can ensure that their internet connection meets their specific needs and provides a seamless online experience. While the operating system’s bandwidth management aims to optimize overall performance, users can leverage tools and techniques to prioritize specific applications and minimize the impact of background processes, ultimately enhancing their online experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing Internet Bandwidth Allocation on Personal Computers. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply