Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide

Encountering a Windows 10 boot failure can be a frustrating experience, leaving users unable to access their data and applications. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the common causes behind these issues and offer practical solutions to resolve them.
Understanding the Problem: Why Windows 10 Might Not Boot
The inability of Windows 10 to boot successfully can stem from a multitude of factors, ranging from simple hardware malfunctions to complex software conflicts. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Here are some of the most common reasons behind a non-booting Windows 10 system:
1. Hardware Malfunctions:
- Damaged or Failing Hard Drive: A faulty hard drive is a primary culprit behind boot failures. Physical damage, wear and tear, or logical errors can render the drive unable to access the operating system files.
- Loose or Defective RAM: Defective or improperly seated RAM modules can disrupt the system’s memory access, leading to boot errors.
- Faulty Motherboard: A malfunctioning motherboard, the main circuit board of the computer, can prevent the system from powering up or booting properly.
- Power Supply Issues: An insufficient or faulty power supply can cause instability and prevent the computer from booting.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can damage components and lead to boot failures.
2. Software Conflicts and Errors:
- Corrupted System Files: Essential system files can become corrupted due to software updates, malware infections, or hardware failures, preventing Windows from loading.
- Boot Sector Errors: The boot sector, a crucial part of the hard drive responsible for initiating the boot process, can be damaged, leading to boot failures.
- Driver Issues: Incompatible or outdated drivers can cause conflicts, leading to system instability and boot problems.
- Malware Infection: Malware can corrupt system files, modify boot settings, or block access to the operating system, causing boot failures.
- Recent Software Changes: Installing new software or making significant system changes can sometimes lead to unforeseen conflicts and boot issues.
3. BIOS/UEFI Settings:
- Incorrect Boot Order: If the boot order in the BIOS/UEFI settings is incorrect, the system may try to boot from an unavailable device instead of the hard drive.
- Disabled Boot Options: Certain BIOS/UEFI settings, such as secure boot or legacy boot, can be accidentally disabled, preventing the system from booting.
Troubleshooting Boot Issues: A Step-by-Step Approach
1. Initial Checks:
- Power Cycle: Restart the computer by completely shutting it down and then turning it back on. This can sometimes resolve temporary issues.
- Check for Visual Cues: Observe the computer screen for any error messages, beeps, or flashing lights. These can provide clues about the cause of the boot problem.
2. Troubleshooting Hardware Issues:
- Test RAM: If possible, remove and reseat the RAM modules, or test them individually using a known working module.
- Check Hard Drive Connections: Ensure the hard drive is securely connected to the motherboard.
- Inspect for Physical Damage: Check for any visible damage to the motherboard, RAM, or other components.
- Test Power Supply: If possible, test the power supply with a known working unit.
3. Troubleshooting Software Issues:
- Boot into Safe Mode: Attempt to boot into Safe Mode, which loads a minimal set of drivers and services, to diagnose software conflicts.
- Run System File Checker (SFC): The SFC command can scan for and repair corrupted system files.
- Run CHKDSK: The CHKDSK command can scan for and repair errors on the hard drive.
- Use a Bootable USB Drive: Create a bootable USB drive with a recovery tool, such as the Windows 10 installation media, to access advanced troubleshooting options.
4. Troubleshooting BIOS/UEFI Settings:
- Access BIOS/UEFI Settings: Enter the BIOS/UEFI settings by pressing the appropriate key during startup (usually F2, F10, or Delete).
- Check Boot Order: Ensure that the hard drive is set as the primary boot device.
- Enable Boot Options: Verify that necessary boot options, such as secure boot or legacy boot, are enabled.
5. Other Troubleshooting Tips:
- Disconnect External Devices: Temporarily disconnect any external devices, such as USB drives or printers, to rule out conflicts.
- Check for Malware: Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus software.
- Restore System to an Earlier Point: If possible, use the System Restore feature to revert to a previous working state.
- Perform a Clean Install: If all else fails, consider performing a clean install of Windows 10, which will erase all data on the hard drive and install a fresh copy of the operating system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: What if I can’t access the BIOS/UEFI settings?
A: If you are unable to access the BIOS/UEFI settings, it might be due to a hardware issue or a corrupted boot sector. In this case, you may need to use a bootable USB drive with a recovery tool or contact a technician for assistance.
Q: What should I do if I see an error message during boot?
A: Error messages can provide valuable clues about the cause of the boot problem. Search online for the specific error message to find potential solutions.
Q: What if my hard drive is failing?
A: If your hard drive is failing, you may need to replace it. Backup your data to another drive before replacing the hard drive to avoid data loss.
Q: How can I prevent future boot issues?
A: To minimize the risk of future boot problems, regularly back up your data, update your system and drivers, run antivirus scans, and avoid installing untrusted software.
Conclusion:
Resolving Windows 10 boot issues requires a systematic and patient approach. By understanding the common causes, following the troubleshooting steps, and utilizing available tools, users can identify and address the problem effectively. Remember to back up your data regularly to protect against data loss in case of a hardware failure. If you are unable to resolve the issue independently, seeking professional assistance from a qualified technician is recommended.

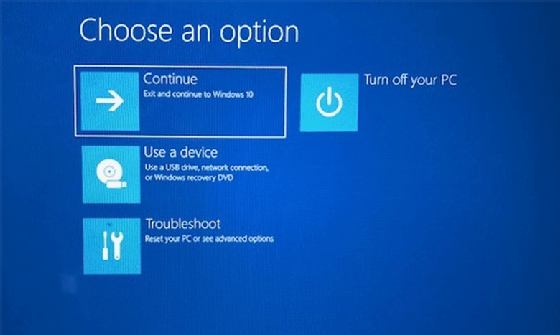
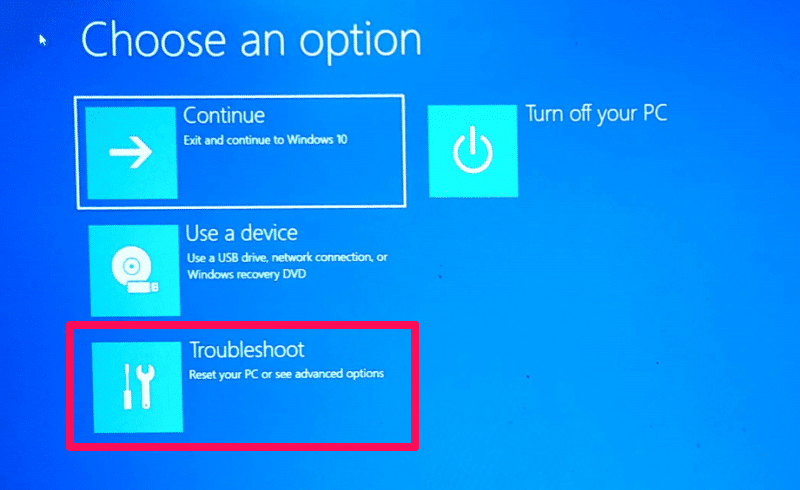
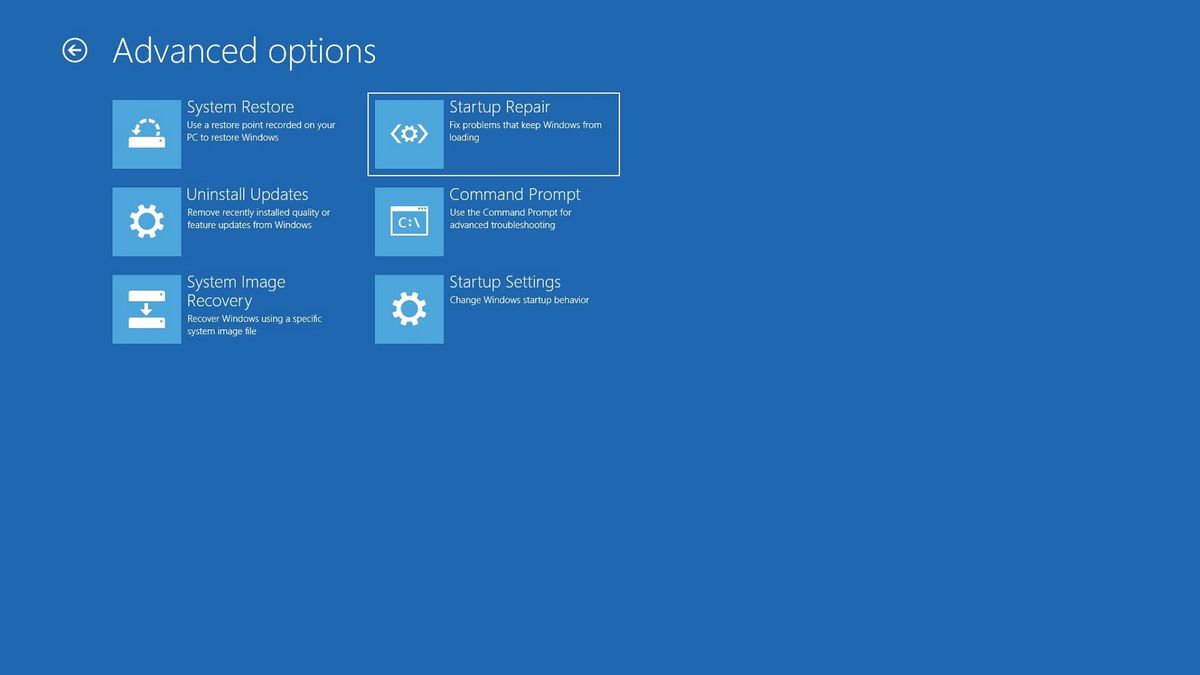
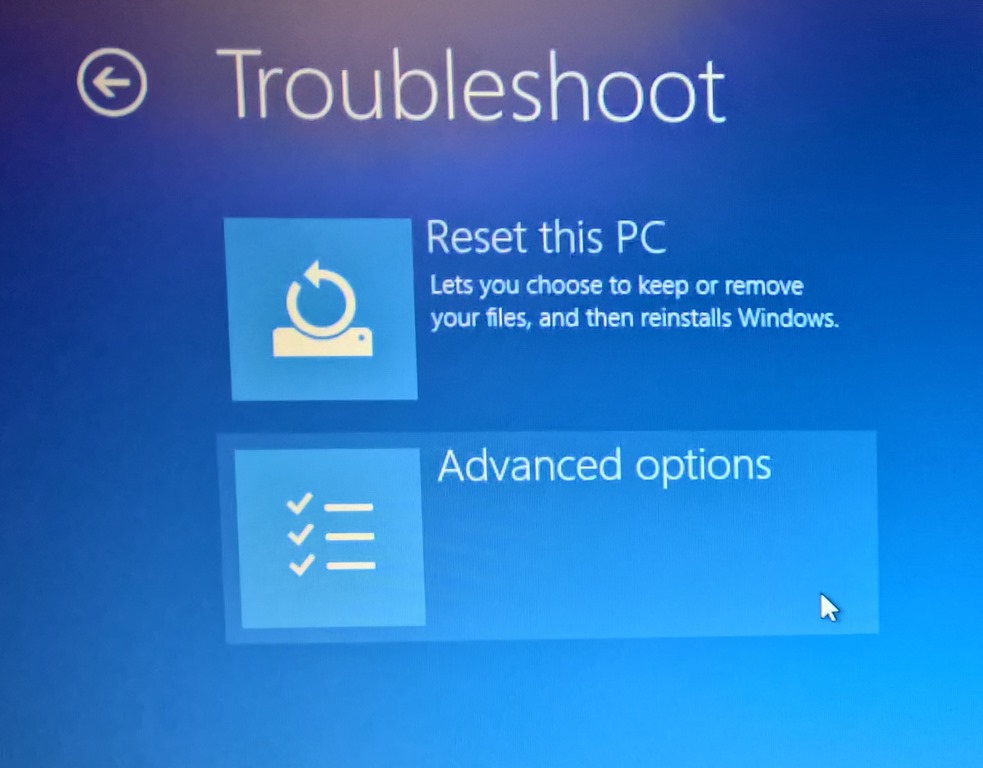

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply