Troubleshooting A Missing Second Monitor In Windows 11
Troubleshooting a Missing Second Monitor in Windows 11
Related Articles: Troubleshooting a Missing Second Monitor in Windows 11
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting a Missing Second Monitor in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting a Missing Second Monitor in Windows 11

The ability to utilize multiple monitors is a highly sought-after feature in modern computing, significantly enhancing productivity and user experience. However, encountering a situation where Windows 11 fails to detect a second monitor can be frustrating. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting this issue, covering a wide range of potential causes and solutions.
Understanding the Issue
Before delving into troubleshooting steps, it is essential to understand the underlying reasons why a second monitor may not be detected. The issue could stem from a variety of factors, including:
- Hardware Problems: Faulty cables, loose connections, or malfunctioning hardware components can prevent the system from recognizing the second display.
- Software Conflicts: Driver incompatibility, outdated software, or system settings can hinder the proper functioning of the display.
- Operating System Errors: Windows 11 may encounter bugs or issues that prevent it from detecting and displaying on the second monitor.
- Incorrect Configuration: Improper settings within the operating system or the graphics driver can lead to the display not being recognized.
Troubleshooting Steps
The following steps outline a systematic approach to diagnose and resolve the issue of a missing second monitor in Windows 11:
1. Verify Hardware Connections
- Cable Integrity: Ensure the HDMI, DisplayPort, or VGA cable connecting the monitor to the computer is securely plugged into both ends. Check for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Cable Compatibility: Confirm that the cable type matches the ports on both the monitor and the computer.
- Monitor Power: Verify that the second monitor is powered on and receiving power.
- Input Source: Select the correct input source on the monitor using the buttons on its control panel.
2. Update Graphics Drivers
- Automatic Updates: Windows Update often automatically installs the latest graphics drivers. Check for updates by going to Settings > Windows Update > Check for updates.
- Manual Updates: Visit the manufacturer’s website for your graphics card (e.g., NVIDIA, AMD, Intel) and download the latest drivers for your specific model and operating system.
3. Configure Display Settings
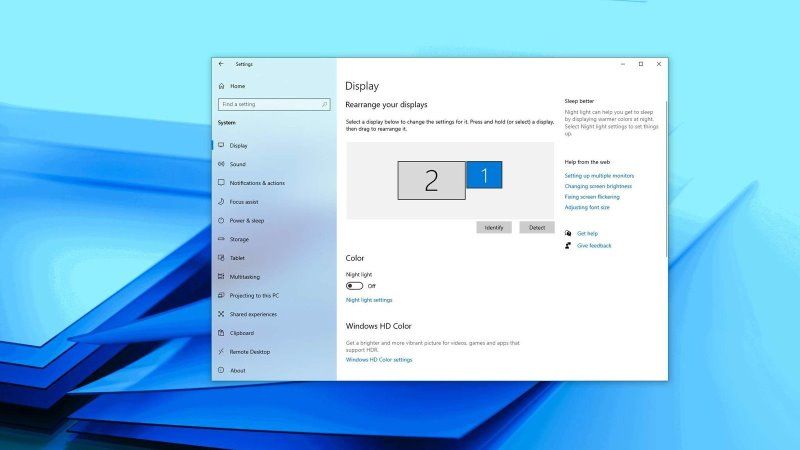
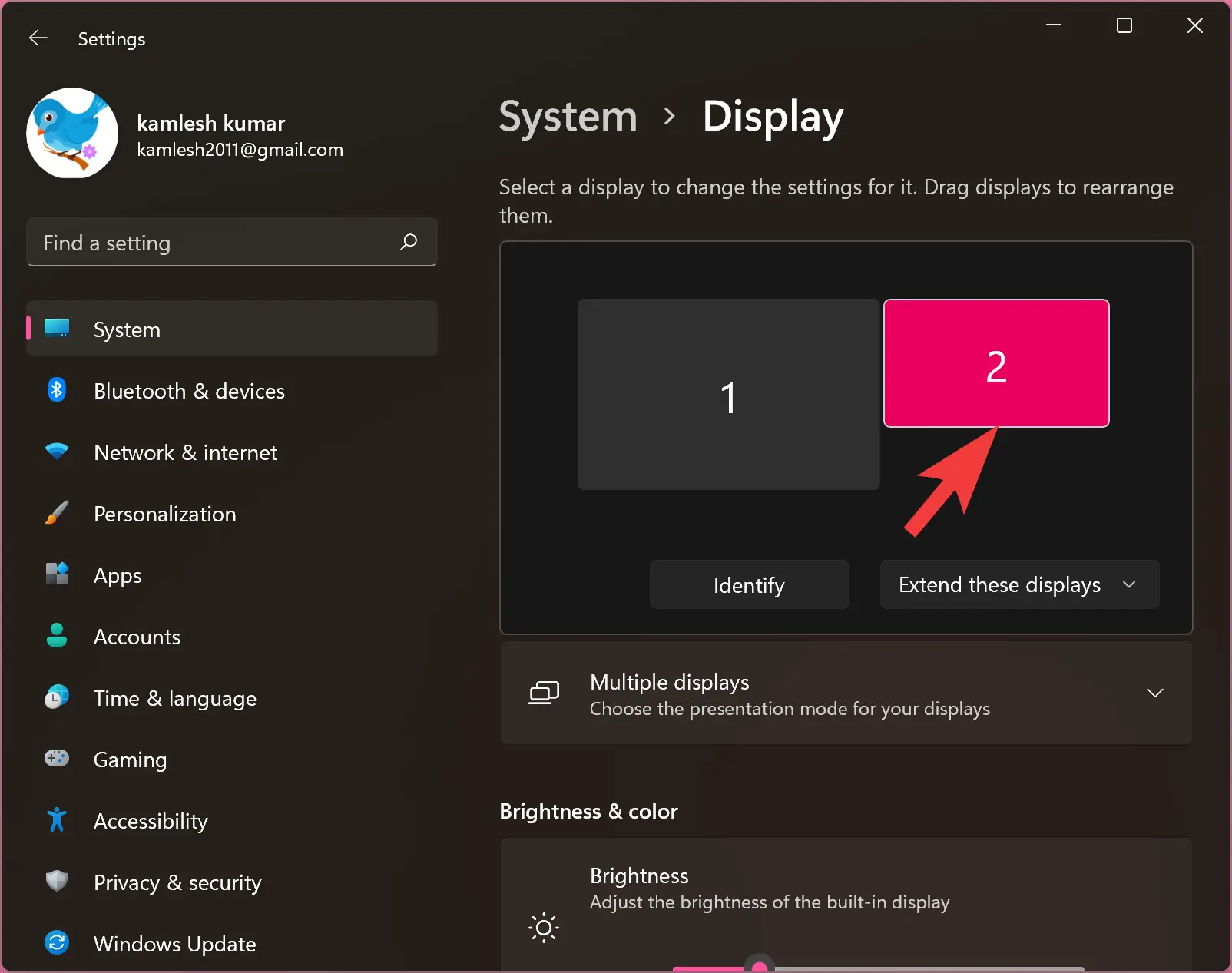
- Detect Displays: Open Settings > System > Display. Click on Detect. This will attempt to identify any connected monitors.
- Extend or Duplicate: Choose the desired display configuration. "Extend" allows you to use both monitors as one continuous workspace, while "Duplicate" mirrors the same content on both screens.
- Resolution and Refresh Rate: Adjust the resolution and refresh rate settings for each monitor to ensure optimal performance.
4. Check for System Errors
- Device Manager: Open Device Manager by searching for it in the Windows search bar. Expand the "Monitors" section. Look for any errors or exclamation marks next to the listed monitors.
- Event Viewer: Access the Event Viewer by searching for it in the Windows search bar. Check for any error messages related to display drivers or hardware.
5. Troubleshoot Compatibility Issues
- Disable Multiple Display Adapter: If your computer has multiple graphics cards, try disabling one to see if it resolves the issue.
- Compatibility Mode: If you are using an older monitor, try running the display driver in compatibility mode. Right-click on the driver in Device Manager and select "Properties". Go to the "Compatibility" tab and select a previous version of Windows.
6. Reset Display Settings
- System Settings: Navigate to Settings > System > Display. Click on "Advanced display settings" and then "Reset to default". This will revert the display settings to their original configuration.
- Graphics Driver Settings: Open the control panel for your graphics card (e.g., NVIDIA Control Panel, AMD Radeon Software). Look for options to reset display settings or revert to default configurations.
7. Perform a Clean Boot
A clean boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and programs, helping to identify software conflicts. Follow these steps:
- System Configuration: Search for "msconfig" in the Windows search bar and open the System Configuration window.
- Disable Startup Items: Navigate to the "Startup" tab and uncheck all the boxes.
- Disable Services: Go to the "Services" tab and check the box for "Hide all Microsoft services". Click on "Disable all".
- Restart: Restart the computer and see if the second monitor is detected.
8. Consider Hardware Issues
- Monitor Test: Connect the monitor to a different computer to verify its functionality.
- Cable Replacement: If the cable is suspected to be faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Graphics Card Diagnosis: If other troubleshooting steps fail, consider testing the graphics card using a different computer or contacting a computer technician for diagnosis.
FAQs
Q: What if the second monitor is detected but not displaying anything?
A: This could indicate a problem with the monitor itself, a loose connection, or an incorrect input source selected on the monitor.
Q: Can I use a USB-C to HDMI adapter to connect the second monitor?
A: Yes, if your computer and monitor support USB-C and HDMI, respectively. However, ensure the adapter is of high quality and compatible with both devices.
Q: Why is the second monitor displaying at a lower resolution than the primary monitor?
A: The resolution of the second monitor might be limited by its capabilities or by the settings in the display settings.
Q: How do I ensure that my second monitor is the primary display?
A: In the Display settings, drag the icon representing the second monitor to the top of the list.
Tips
- Check for updates: Regularly update both Windows 11 and your graphics drivers to ensure compatibility and stability.
- Use a reliable cable: Invest in a high-quality HDMI or DisplayPort cable for a stable connection.
- Monitor compatibility: Ensure the monitor is compatible with your computer’s graphics card and ports.
- Avoid overloading the system: Too many connected devices can strain the system’s resources, potentially affecting display performance.
Conclusion
Resolving the issue of a missing second monitor in Windows 11 requires a systematic approach. By carefully checking hardware connections, updating drivers, and troubleshooting software conflicts, you can often restore the functionality of your dual-monitor setup. If all else fails, seeking professional assistance from a computer technician may be necessary to diagnose and repair any underlying hardware problems.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting a Missing Second Monitor in Windows 11. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply