The Absence Of Windows Defender In Windows 10: A Comprehensive Exploration
The Absence of Windows Defender in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Absence of Windows Defender in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Absence of Windows Defender in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Absence of Windows Defender in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Exploration
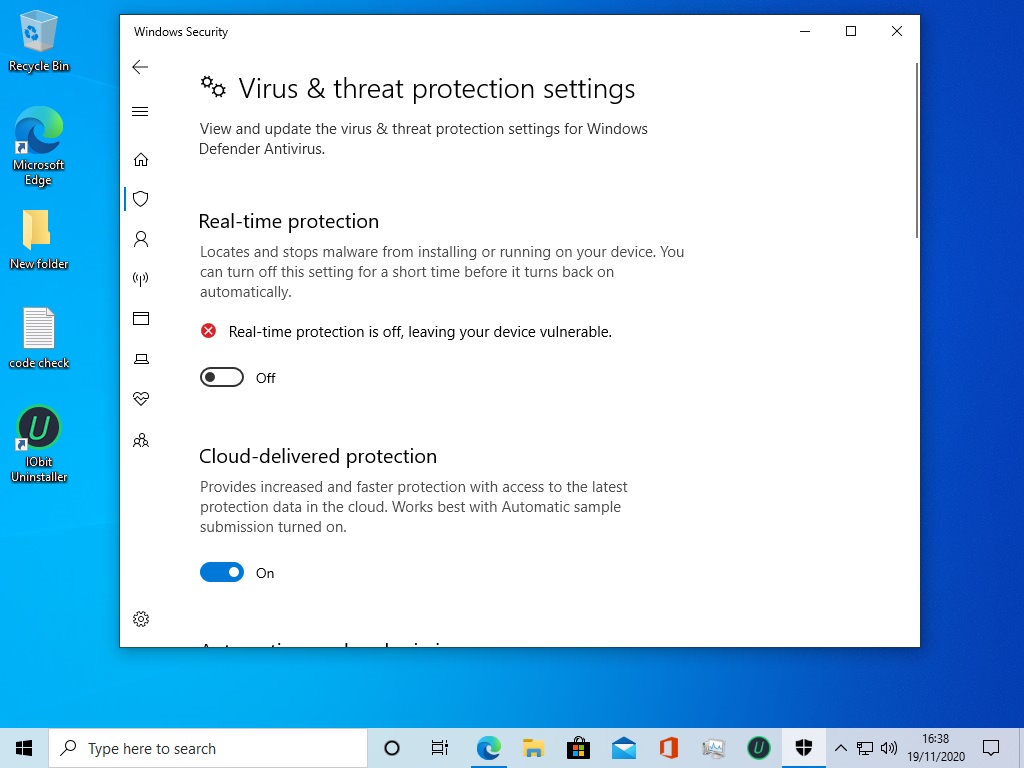
Windows Defender, a robust and comprehensive security solution, is a cornerstone of Windows 10’s security infrastructure. Its absence, while seemingly improbable, can arise from various factors, each demanding a distinct approach to remediation. This article will delve into the potential scenarios leading to the non-appearance of Windows Defender in Windows 10, exploring the implications and offering solutions for each scenario.
Understanding Windows Defender’s Role
Windows Defender serves as the built-in antivirus and anti-malware protection for Windows 10. It operates in real-time, constantly monitoring the system for malicious threats, including viruses, spyware, ransomware, and other forms of malware. Its functionalities extend beyond basic threat detection, encompassing:
- Real-time Protection: This feature scans files and applications as they are downloaded, opened, or executed, preventing potentially harmful programs from accessing the system.
- Scheduled Scans: Regular scans ensure that the system is consistently checked for threats, even when not actively downloading or opening files.
- Firewall: Windows Defender Firewall acts as a barrier between the system and the internet, blocking unauthorized connections and preventing potential attacks.
- Exploit Protection: This feature helps mitigate vulnerabilities in the system, preventing attackers from exploiting weaknesses to gain unauthorized access.
- Cloud-based Protection: Leveraging Microsoft’s vast cloud infrastructure, Windows Defender can access real-time threat intelligence, enhancing its ability to identify and neutralize emerging threats.
Scenarios Leading to the Absence of Windows Defender
The absence of Windows Defender in Windows 10 can be attributed to several factors, each requiring a unique approach to resolution. These scenarios include:
1. Accidental Deactivation or Removal:
Windows Defender, like many other system components, can be inadvertently disabled or removed. This might occur due to:
- Third-party security software: Installing another antivirus program might automatically disable Windows Defender to avoid conflicts.
- System configuration changes: Accidental modifications to system settings, particularly those related to security, could disable Windows Defender.
- Manual removal: Users might mistakenly remove Windows Defender components, believing them to be unnecessary or redundant.
2. System Corruption or Errors:
Windows Defender, like any software, can be affected by system corruption or errors. These problems might arise from:
- Malware infections: Malicious programs can deliberately disable or corrupt Windows Defender to evade detection and gain control over the system.
- System updates or installations: Faulty updates or installations can introduce errors that interfere with Windows Defender’s functionality.
- Hardware failures: Malfunctioning hard drives or other hardware components can lead to data corruption, affecting system files, including those associated with Windows Defender.
3. Specific Windows 10 Versions or Settings:
Certain versions or configurations of Windows 10 might not include Windows Defender by default or might have it disabled by design. This might occur in:
- Enterprise editions: Some enterprise editions of Windows 10 might allow administrators to disable Windows Defender and rely on alternative security solutions.
- Specific system configurations: Advanced system configurations or policies might restrict or disable certain system components, including Windows Defender.
4. System Limitations:
Windows Defender’s presence and functionality might be limited or unavailable in specific scenarios, including:
- Limited hardware resources: Older or low-powered devices might not meet the minimum requirements for Windows Defender to function effectively.
- Virtual machines: Virtualized environments might require specific configurations to enable Windows Defender functionality.
Solutions and Troubleshooting Steps
Addressing the absence of Windows Defender requires a systematic approach, focusing on identifying the underlying cause and implementing appropriate solutions. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Check for Accidental Deactivation:
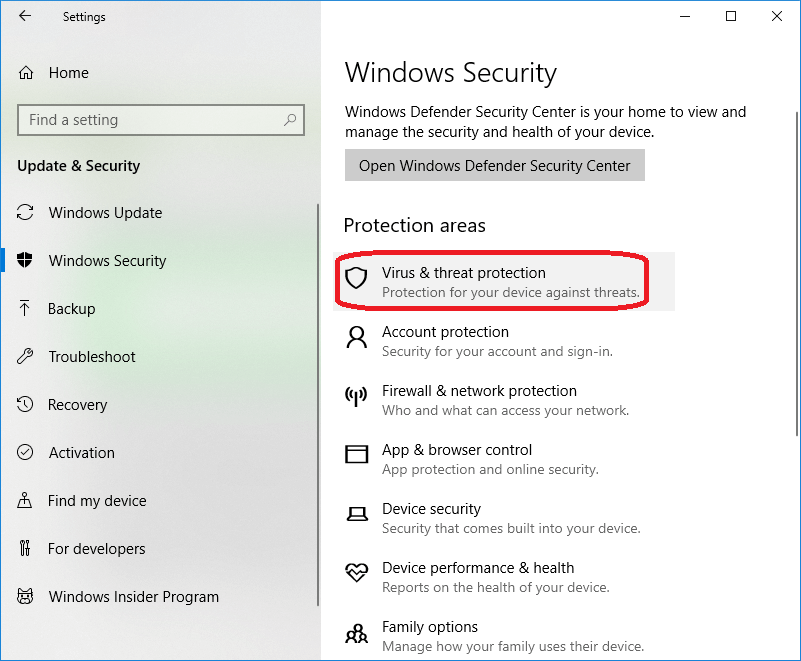
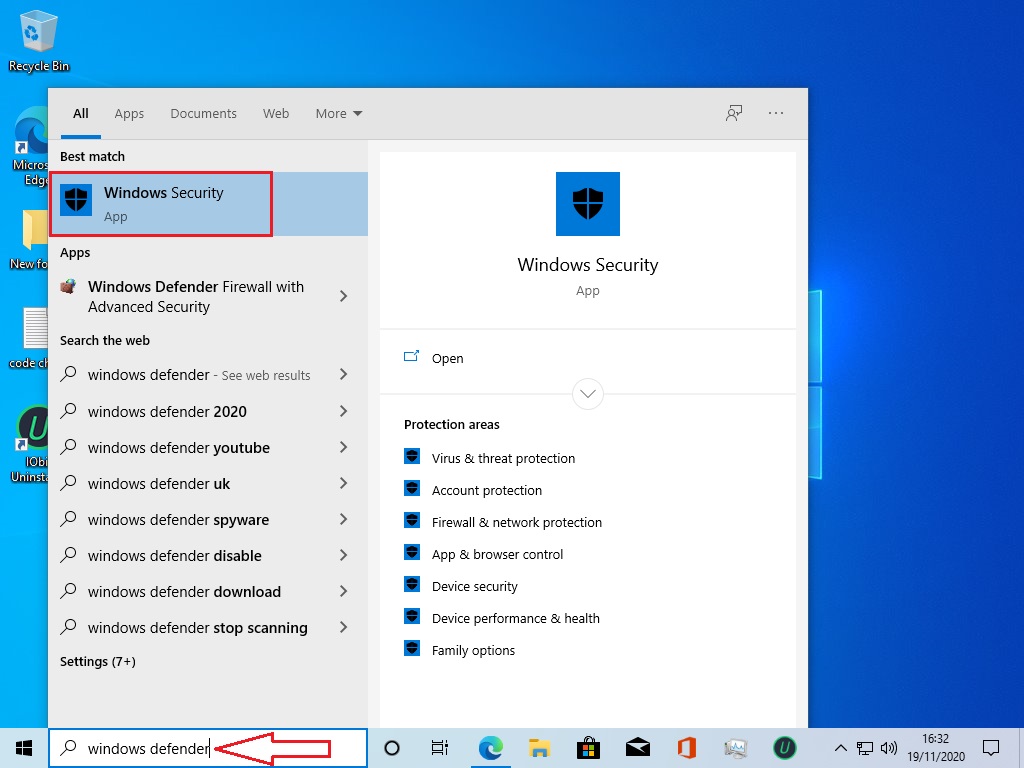
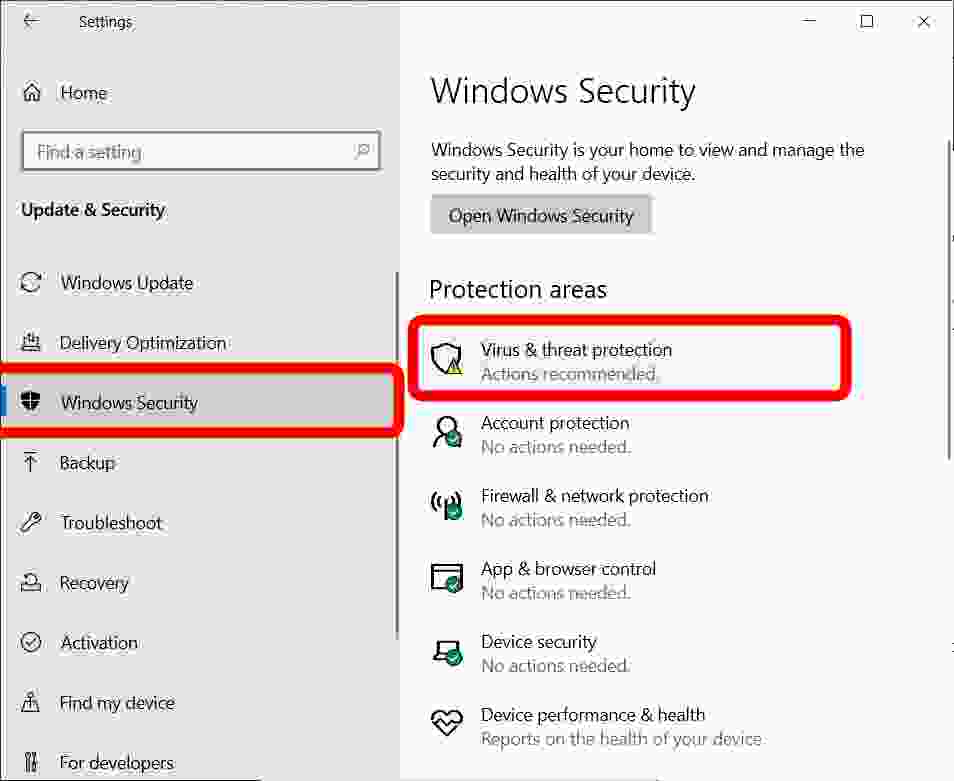
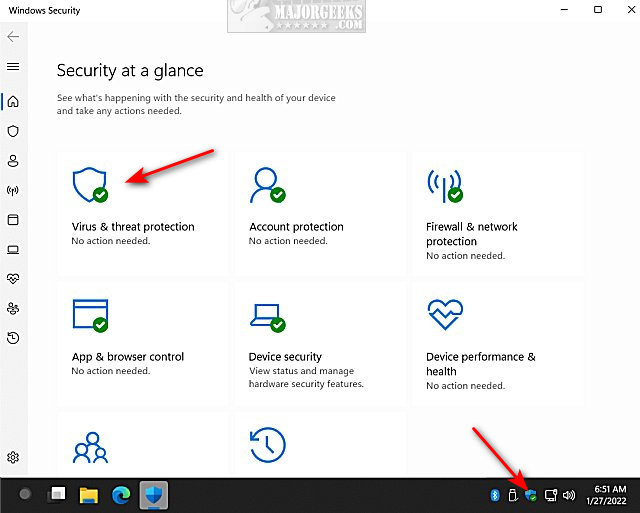
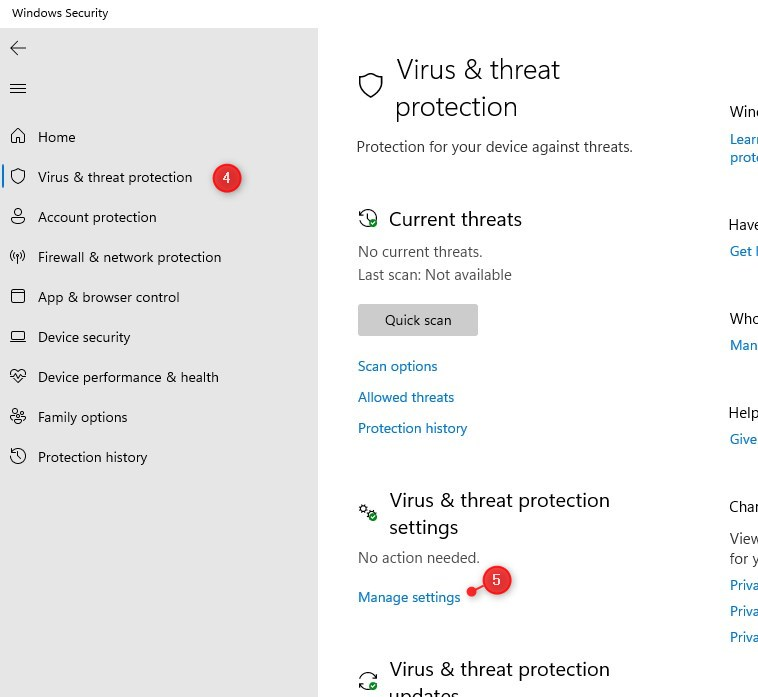
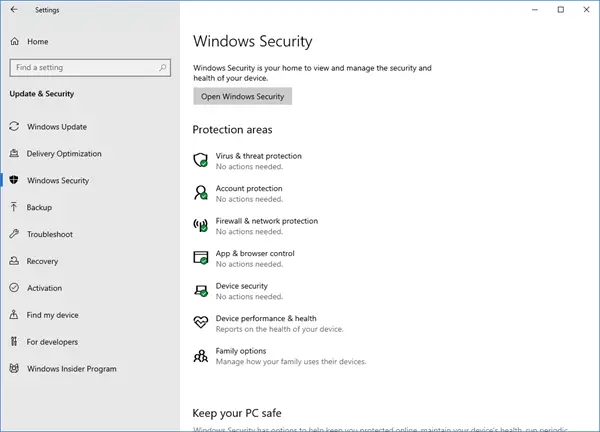
- Verify Windows Defender status: Navigate to Windows Security (previously known as Windows Defender Security Center) in the Start Menu and check the status of real-time protection, scheduled scans, and firewall.
- Review third-party security software: If another antivirus program is installed, check its settings to see if it’s disabling Windows Defender. You might need to adjust the settings or temporarily disable the third-party software to re-enable Windows Defender.
- Restore system settings: If recent changes were made to system settings, consider restoring the system to a previous restore point.
2. Troubleshoot System Corruption or Errors:
- Run System File Checker (SFC): This tool scans system files for corruption and attempts to repair them. Open Command Prompt as administrator and run the command: sfc /scannow.
- Run DISM tool: The Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool can repair corrupted system images. Open Command Prompt as administrator and run the command: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth.
- Perform a clean boot: This isolates the problem by starting the system with minimal programs and services running. This can help identify if a third-party program is interfering with Windows Defender.
- Run a full system scan: Use Windows Defender to perform a full system scan to detect and remove any malware that might be interfering with its functionality.
- Update Windows: Ensure the system is running the latest Windows updates, as they often include security patches and fixes that can address issues with Windows Defender.
3. Review Windows 10 Version and Settings:
- Verify Windows 10 edition: If using an enterprise edition, check with your system administrator to confirm if Windows Defender is enabled or if alternative security solutions are in place.
- Review Group Policy settings: If using a domain-joined computer, check the Group Policy settings to see if they are restricting or disabling Windows Defender.
4. Address System Limitations:
- Upgrade hardware: If the system’s hardware resources are insufficient, consider upgrading to a more powerful device.
- Optimize virtual machine settings: If running in a virtualized environment, ensure that the virtual machine’s settings are configured to support Windows Defender.
FAQs on the Absence of Windows Defender in Windows 10
Q: Is it safe to use Windows 10 without Windows Defender?
A: It is strongly recommended to use Windows Defender or a comparable security solution to protect your system from threats. Operating without a robust security program significantly increases the risk of malware infections, data loss, and other security breaches.
Q: Can I use another antivirus program alongside Windows Defender?
A: While technically possible, it’s generally not recommended to run multiple antivirus programs simultaneously. This can lead to conflicts, performance issues, and potentially reduce the effectiveness of both programs.
Q: How do I know if my system is protected without Windows Defender?
A: If Windows Defender is not present or disabled, you can check if another antivirus program is installed and active. Look for its icon in the system tray or within the Windows Security app. You can also verify the status of the firewall and other security features.
Tips for Maintaining Windows Defender Functionality
- Keep Windows Defender updated: Ensure that Windows Defender is regularly updated to benefit from the latest threat definitions and security enhancements.
- Perform regular scans: Schedule regular scans to proactively identify and remove threats before they can compromise your system.
- Enable real-time protection: Real-time protection provides continuous monitoring for threats, ensuring that your system is protected at all times.
- Review security settings: Periodically review and adjust your security settings to ensure they meet your specific needs and security requirements.
Conclusion
The absence of Windows Defender in Windows 10 can be a cause for concern, leaving your system vulnerable to various threats. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for implementing the appropriate solutions. Whether it’s accidental deactivation, system corruption, specific Windows 10 configurations, or system limitations, understanding the root of the problem allows for targeted troubleshooting and remediation. By addressing the issue promptly and diligently, you can restore Windows Defender’s crucial role in protecting your system from malware and other cyber threats, ensuring a secure and reliable computing experience.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Absence of Windows Defender in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply