Shielding Your Windows From Ransomware: A Comprehensive Guide
Shielding Your Windows from Ransomware: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Shielding Your Windows from Ransomware: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Shielding Your Windows from Ransomware: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shielding Your Windows from Ransomware: A Comprehensive Guide

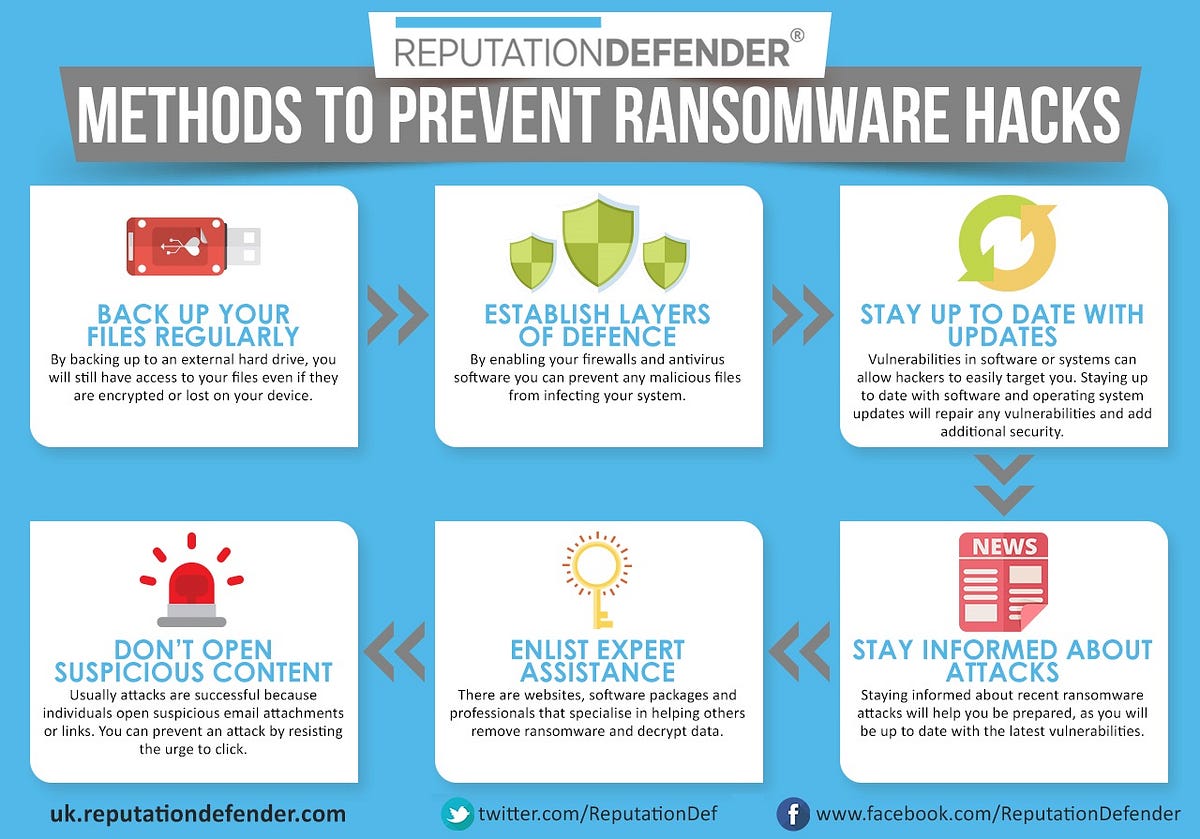
Ransomware, a type of malicious software, poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. It encrypts data, rendering it inaccessible, and demands payment for its decryption. The consequences of a successful ransomware attack can be devastating, ranging from lost productivity and financial losses to irreparable damage to reputation and data integrity. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ransomware protection strategies within the Windows environment, equipping users with the knowledge and tools to mitigate the risk of such attacks.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
Ransomware has evolved from simple encryption tools to sophisticated, multi-layered attacks. Understanding the methods employed by these threats is crucial for effective protection:
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Ransomware frequently leverages known vulnerabilities in software, including operating systems and applications, to gain unauthorized access to systems. These vulnerabilities often arise from outdated software, neglected security updates, and insecure configurations.
- Social Engineering: Ransomware attacks often rely on social engineering techniques to trick users into granting access to their systems. This can involve phishing emails, malicious links, or attachments disguised as legitimate communications.
- Malware Distribution: Ransomware can be disseminated through various channels, including infected websites, malicious downloads, and compromised software.
Layered Defense: A Multi-faceted Approach
Effective ransomware protection requires a layered approach, encompassing multiple security measures to create a robust defense against these evolving threats.
1. Operating System Security:
- Windows Updates: Regularly updating the Windows operating system is essential for patching vulnerabilities and enhancing security. Automatic updates should be enabled to ensure timely delivery of critical security patches.
- Firewall: Windows Firewall acts as a barrier between your system and the external network, blocking unauthorized access attempts. Configuring the firewall to block unnecessary ports and connections can further strengthen security.
- User Account Control (UAC): UAC prompts users for confirmation before allowing applications to make changes to the system. This feature helps prevent unauthorized modifications and potential malware installation.
2. Application Security:
- Software Updates: Keeping applications up-to-date is crucial for addressing security vulnerabilities. Regularly checking for and installing software updates is a fundamental practice for maintaining system security.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: Robust antivirus and anti-malware solutions provide real-time protection against known threats, including ransomware. These programs monitor system activity, detect suspicious files, and block malicious attempts.
- Sandboxing: Sandboxing tools isolate potentially unsafe applications and files from the main system. This prevents malicious code from accessing critical system files or data, limiting the impact of a ransomware attack.
3. Data Backup and Recovery:
- Regular Backups: Implementing a regular data backup strategy is essential for recovering data in the event of a ransomware attack. Backups should be stored offline, ensuring that they are not accessible to ransomware.
- Data Recovery Tools: Specialized data recovery tools can help recover encrypted files even after a ransomware attack. These tools utilize various techniques to bypass encryption and restore data.
4. User Education and Awareness:
- Phishing Awareness: Educating users about phishing techniques is crucial for preventing social engineering attacks. Users should be trained to identify suspicious emails, links, and attachments, and to report them to appropriate authorities.
- Password Management: Strong passwords and password management tools are essential for protecting accounts from unauthorized access. Using unique, complex passwords for each account minimizes the risk of compromised credentials.
- Secure Browsing Practices: Users should be aware of the risks associated with visiting untrusted websites and downloading files from unknown sources. Employing secure browsing practices, such as using reputable browsers and avoiding suspicious links, is crucial for preventing malware infections.
5. Network Security:
- Network Segmentation: Dividing the network into isolated segments can limit the spread of ransomware within an organization. This helps prevent an attack from compromising multiple systems.
- Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can block or alert on potential ransomware attacks.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA for sensitive accounts requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as passwords and one-time codes, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the signs of a ransomware attack?
A: Signs of a ransomware attack include:
- Data inaccessibility: Files become inaccessible or open with an error message.
- Ransom demands: A ransom note or message appears on the screen demanding payment for decryption.
- Unusual file extensions: File extensions are changed to unusual or unfamiliar formats.
- System performance issues: The system becomes slow, unresponsive, or crashes frequently.
Q: How do I prevent ransomware from infecting my computer?
A: Preventing ransomware infection involves a multi-pronged approach:
- Keep your software updated: Regularly install software updates to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication: Protect accounts from unauthorized access.
- Be cautious of suspicious emails and links: Avoid clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown sources.
- Use reputable antivirus and anti-malware software: Install and maintain a reliable security solution.
- Back up your data regularly: Create backups of important files and store them offline.
Q: What should I do if I suspect my computer has been infected with ransomware?
A: If you suspect a ransomware attack, take the following steps:
- Disconnect from the network: Isolate the infected system from the network to prevent further spread.
- Do not pay the ransom: Paying the ransom does not guarantee data recovery and often encourages further attacks.
- Contact security professionals: Consult with cybersecurity experts or IT support for assistance.
- Restore data from backups: Attempt to restore data from recent backups.
- Report the incident: Report the attack to law enforcement authorities.
Tips for Enhanced Ransomware Protection:
- Limit administrative privileges: Restrict user accounts to standard privileges, minimizing the potential for unauthorized actions.
- Implement a robust data loss prevention (DLP) system: DLP solutions can prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network, mitigating the impact of a ransomware attack.
- Train employees on cybersecurity best practices: Regularly educate users about ransomware threats and proper security measures.
- Conduct regular security audits: Periodically assess system security and identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Implement a comprehensive incident response plan: Develop a plan for responding to ransomware attacks, including steps for containment, recovery, and reporting.
Conclusion
Ransomware presents a persistent and evolving threat to individuals and organizations. By implementing a layered defense strategy, encompassing operating system security, application security, data backup and recovery, user education, network security, and ongoing vigilance, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to these attacks. Proactive measures, regular updates, and informed decision-making are essential for protecting data and systems from the devastating consequences of ransomware. Ultimately, a collaborative approach, involving users, administrators, and security professionals, is crucial for building a resilient defense against this ever-present threat.
![Ransomware: How to Protection from Ransomware In Windows 10 Windows 10 [January 2020] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gSakNFc0lWY/maxresdefault.jpg)






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shielding Your Windows from Ransomware: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply