Protecting Your PC: Understanding And Configuring Overheat Protection In Windows 10
Protecting Your PC: Understanding and Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10
Related Articles: Protecting Your PC: Understanding and Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Protecting Your PC: Understanding and Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Protecting Your PC: Understanding and Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Protecting Your PC: Understanding and Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10
- 3.1 Understanding Overheat Protection in Windows 10
- 3.2 The Importance of Overheat Protection
- 3.3 Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Tips for Maintaining Optimal System Temperature
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Protecting Your PC: Understanding and Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10

Modern computers are marvels of engineering, capable of handling complex tasks with remarkable speed and efficiency. However, these powerful machines are not immune to the effects of excessive heat. Overheating can lead to a range of issues, from performance degradation and system instability to permanent hardware damage. To safeguard your PC, Windows 10 incorporates a robust overheat protection system that monitors crucial components and takes corrective action when necessary. This article delves into the intricacies of this protective mechanism, outlining its importance, configuration options, and best practices for ensuring optimal system health.
Understanding Overheat Protection in Windows 10
Windows 10’s overheat protection system is a multifaceted approach that combines hardware monitoring with software-based responses. The primary goal is to prevent catastrophic failures by identifying and mitigating potential heat-related issues. This system actively monitors various components, including the CPU, GPU, and system memory, constantly assessing their operating temperatures.
The core components of Windows 10’s overheat protection system include:
- Hardware Monitoring: The system relies on sensors embedded within hardware components, such as the CPU and GPU, to gather real-time temperature readings. These readings are constantly relayed to the operating system.
- Software-Based Thresholds: Windows 10 defines predefined temperature thresholds for various components. When these thresholds are breached, the system triggers a series of actions to mitigate the overheating situation.
- Automatic Throttling: As a primary defense mechanism, Windows 10 can automatically throttle the performance of the CPU or GPU when temperatures exceed predefined limits. This reduces the heat generated by these components, preventing further escalation.
- System Warnings: Windows 10 displays visual warnings and alerts when overheating is detected. These alerts inform the user of the issue and recommend potential solutions, such as closing resource-intensive applications or ensuring proper cooling.
- Automatic Shutdowns: In severe cases, where overheating persists despite throttling and warnings, Windows 10 may automatically shut down the system to prevent permanent hardware damage.
The Importance of Overheat Protection
The presence of a robust overheat protection system in Windows 10 is crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Hardware Damage: Overheating can lead to irreparable damage to sensitive components like the CPU, GPU, and motherboard. Windows 10’s overheat protection mitigates this risk by proactively identifying and addressing overheating situations.
- Maintaining System Stability: Excessive heat can cause system instability, leading to crashes, freezes, and data loss. Overheat protection ensures that the system operates within safe temperature ranges, minimizing these issues.
- Optimizing Performance: While throttling may temporarily reduce performance, it prevents more severe consequences such as system crashes or hardware damage. This ensures that the system continues to function reliably, albeit at a slightly reduced performance level.
- Enhancing User Experience: By providing timely warnings and alerts, Windows 10’s overheat protection system empowers users to take appropriate actions to prevent overheating and maintain optimal system performance.
Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10
While Windows 10’s overheat protection system operates automatically, users can fine-tune its behavior to meet specific needs. Here’s a guide to configuring key settings:
1. Managing Power Options:
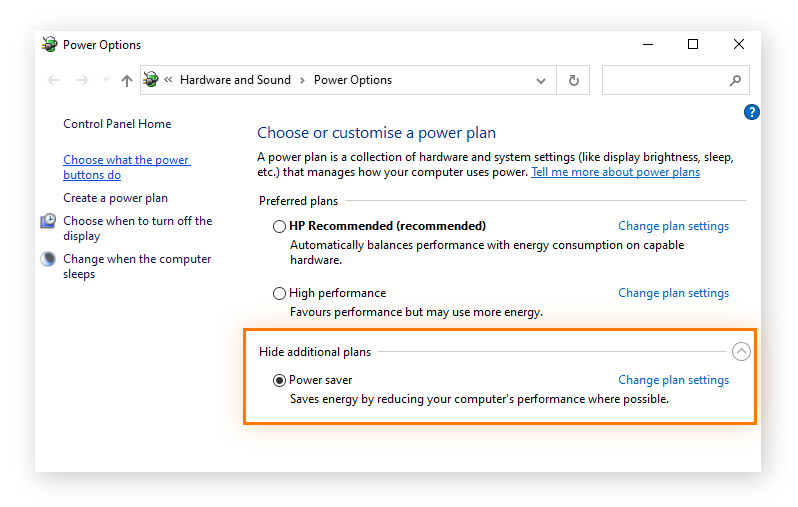
- Accessing Power Options: Navigate to the "Control Panel" and select "Power Options." This section allows users to adjust power-related settings, including those affecting system behavior during overheating.
- Power Plans: Windows 10 offers various power plans (Balanced, High Performance, Power Saver) that influence system performance and energy consumption. Selecting a power plan that prioritizes energy efficiency may help reduce heat generation.
- Advanced Power Settings: Click on "Change plan settings" and then "Change advanced power settings" to access a comprehensive range of power-related options. Here, you can customize how the system reacts to overheating events, such as the level of CPU throttling and the shutdown behavior.
2. Utilizing the Performance Monitor:
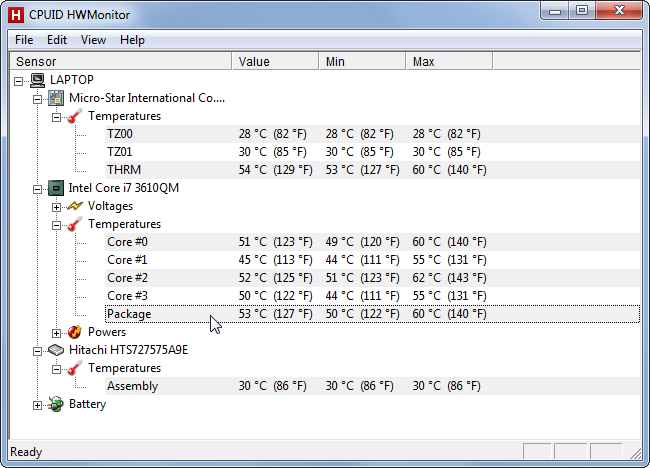
- Monitoring System Temperatures: The Performance Monitor provides detailed information about system resources, including component temperatures. To access it, search for "Performance Monitor" in the Windows search bar.
- Customizing Monitoring: Within the Performance Monitor, users can add counters to track specific components’ temperatures. This allows for real-time monitoring and identification of potential overheating issues.
3. Examining System Logs:
- Event Viewer: Windows 10 keeps a record of system events in the Event Viewer. This tool can be accessed by searching for "Event Viewer" in the Windows search bar.
- Overheating Events: By reviewing the system logs, users can identify instances of overheating and the corresponding actions taken by the system. This information can help diagnose potential issues and adjust settings accordingly.
4. Updating Drivers and BIOS:
- Driver Updates: Outdated device drivers can sometimes contribute to overheating issues. Regularly updating drivers ensures compatibility and optimal performance.
- BIOS Updates: The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) controls the system’s hardware at a fundamental level. Updating the BIOS can sometimes improve thermal management and enhance the overall efficiency of the system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can I tell if my PC is overheating?
Several indicators suggest potential overheating, including:
- System Slowdowns: A noticeable drop in performance, especially during demanding tasks, can indicate overheating.
- Unusual Noise: Fans running at high speeds or making unusual noises can be a sign of the system attempting to cool down.
- Automatic Shutdowns: If your computer shuts down unexpectedly, especially during intensive tasks, overheating is a likely culprit.
- Error Messages: Windows 10 may display error messages related to overheating, such as "System Overheating" or "CPU Throttling."
2. What are the common causes of overheating?
- Dust Accumulation: Dust buildup inside the PC can impede airflow and hinder cooling.
- Insufficient Cooling: A poorly ventilated case or inadequate cooling solutions, such as insufficient fans or a malfunctioning heatsink, can contribute to overheating.
- Overclocking: Pushing hardware beyond its default limits can increase heat generation.
- Resource-Intensive Applications: Running demanding software or games can strain the system and generate excessive heat.
3. What can I do to prevent overheating?
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the inside of your PC regularly to remove dust and debris.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow by positioning the PC in a well-ventilated area and avoiding obstructions.
- Use a Cooling Pad: Consider using a cooling pad to enhance airflow and reduce component temperatures.
- Monitor System Temperatures: Use the Performance Monitor or other monitoring tools to track component temperatures and identify potential overheating issues.
- Close Unnecessary Applications: Exit programs that you are not actively using to reduce system load and heat generation.
Tips for Maintaining Optimal System Temperature
- Invest in Quality Cooling Solutions: Consider upgrading to a higher-quality heatsink or adding additional fans for better cooling.
- Utilize Under-Voltage Settings: If you are familiar with BIOS settings, you can explore under-voltage options to reduce the power consumption and heat generation of your CPU.
- Monitor System Temperatures Regularly: Use monitoring tools to keep an eye on component temperatures and make adjustments as needed.
- Consider Liquid Cooling: For extreme performance and cooling needs, liquid cooling systems can offer significant temperature reductions.
Conclusion
Windows 10’s overheat protection system is an essential safeguard for your PC’s health. By monitoring component temperatures, triggering performance throttling, and issuing warnings when necessary, this system effectively prevents catastrophic failures and maintains optimal system stability. Understanding the intricacies of overheat protection, configuring settings appropriately, and following best practices for thermal management will ensure your PC operates reliably and efficiently for years to come.

![[Guide] Enable System Protection in Windows 10](http://www.filecluster.com/howto/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Enable-System-Protection-in-Windows-10.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Protecting Your PC: Understanding and Configuring Overheat Protection in Windows 10. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply