Power Management In Windows 10: Balancing Performance And Efficiency
Power Management in Windows 10: Balancing Performance and Efficiency
Related Articles: Power Management in Windows 10: Balancing Performance and Efficiency
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Power Management in Windows 10: Balancing Performance and Efficiency. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Power Management in Windows 10: Balancing Performance and Efficiency

Windows 10, a ubiquitous operating system, constantly strives to strike a delicate balance between performance and energy efficiency. This is achieved through a sophisticated system of power management features, collectively known as "power throttling." This mechanism dynamically adjusts the system’s performance based on factors like battery life, workload, and user preferences, ensuring optimal operation across various scenarios.
Understanding Power Management in Windows 10
Power throttling in Windows 10 is not a singular action, but rather a comprehensive approach encompassing various techniques and technologies. It aims to manage the system’s energy consumption by dynamically adjusting the CPU clock speed, voltage, and other hardware components. This dynamic adjustment is critical for:
- Extending Battery Life: In portable devices, power management plays a vital role in maximizing battery life. By reducing the power consumption of components, Windows 10 ensures longer usage time between charges.
- Reducing Heat Generation: Excessive processing power can lead to increased heat generation, potentially causing performance degradation and even hardware damage. Power management helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing thermal throttling and ensuring stable performance.
- Improving Performance in Specific Scenarios: While often associated with reducing power consumption, power management can also enhance performance in certain situations. By prioritizing the allocation of power to critical processes, Windows 10 can deliver smoother and faster operation when needed.
How Windows 10 Manages Power Consumption
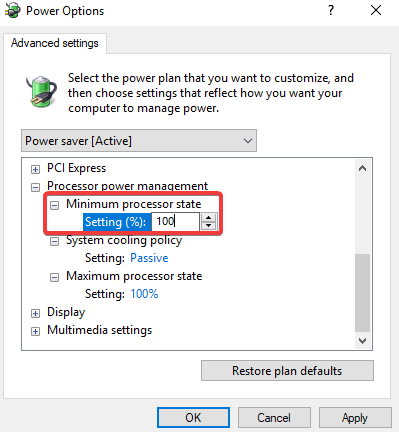
The foundation of power management in Windows 10 lies in the "Power Options" settings, accessible through the Control Panel. These settings allow users to customize the system’s power behavior based on their preferences and usage patterns. The key components of power management in Windows 10 include:
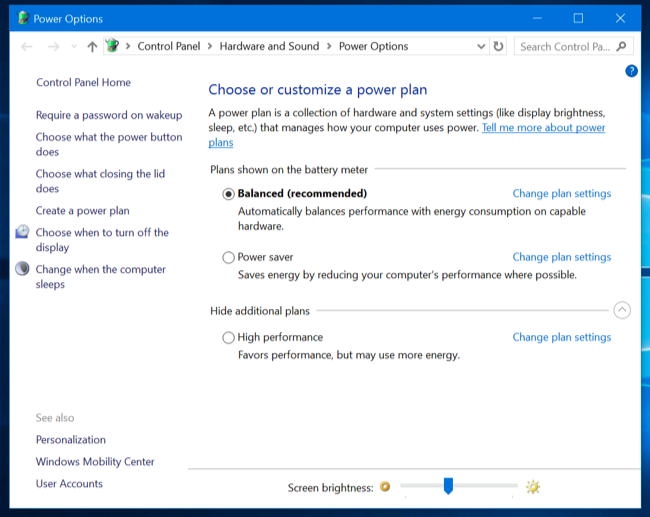
1. Power Plans: Windows 10 offers pre-configured power plans that cater to different usage scenarios. These plans define the system’s power behavior, including the CPU’s maximum frequency, screen brightness, and other settings. The available power plans typically include:
- Balanced: A well-rounded plan that prioritizes both performance and power efficiency, suitable for general-purpose computing.
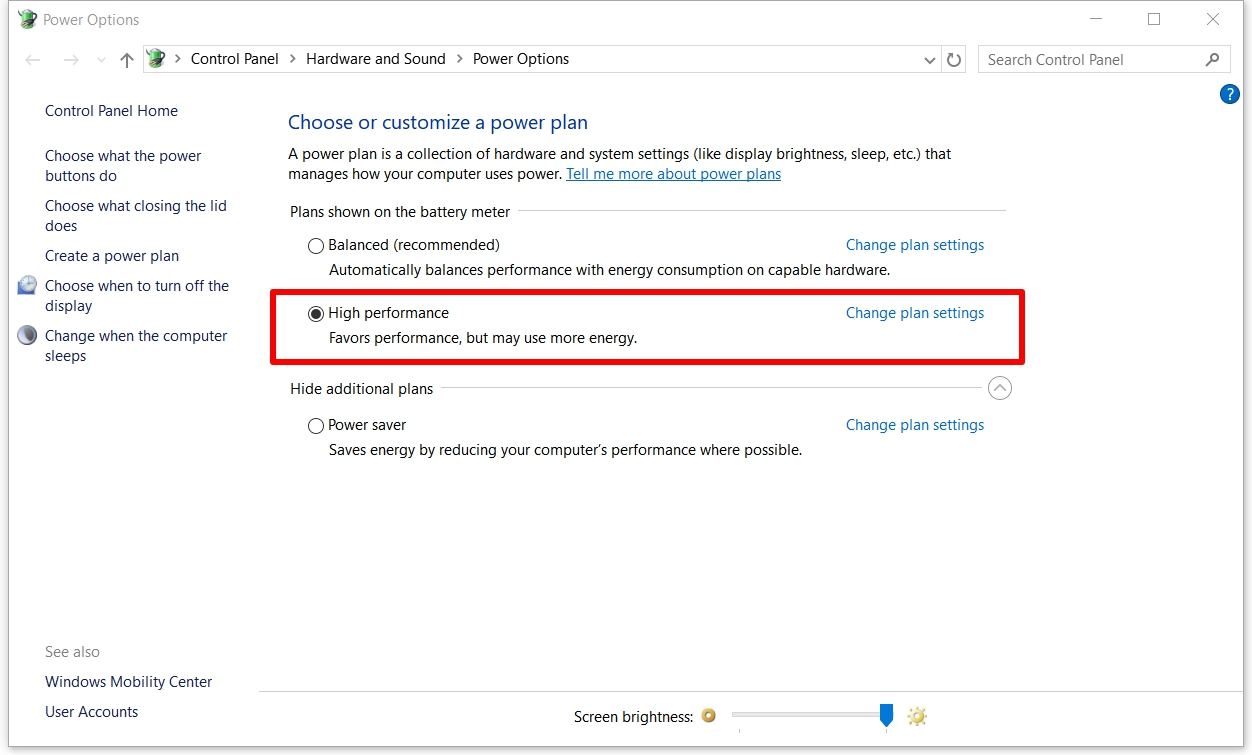
- High Performance: A plan that emphasizes maximum performance, often at the expense of battery life.
- Power Saver: A plan focused on maximizing battery life, potentially sacrificing some performance.
Users can create custom power plans, tailoring them to their specific needs.
2. CPU Throttling: The CPU, the brain of the computer, consumes a significant amount of power. Windows 10 employs dynamic CPU throttling, adjusting the CPU’s clock speed and voltage based on the workload and power settings. This ensures that the CPU operates at the optimal performance level while minimizing power consumption.
3. GPU Throttling: Similar to the CPU, the GPU, responsible for graphics processing, can also be throttled. Windows 10 dynamically adjusts the GPU’s performance based on the graphical demands of the running applications and the power settings. This ensures efficient utilization of the GPU while conserving energy.
4. Device Sleep States: When idle, various hardware components, such as hard drives, network adapters, and USB devices, can enter sleep states to minimize power consumption. Windows 10 manages these sleep states, activating components when needed and returning them to sleep when idle, contributing to overall power efficiency.
5. Display Power Management: The display is another significant energy consumer. Windows 10 incorporates features like automatic brightness adjustment, screen timeout, and sleep states for the display to reduce power consumption.
6. Power Management Policies: Windows 10 allows administrators to define power management policies, enforcing specific power settings across the network. These policies can be used to optimize power consumption and ensure compliance with organizational guidelines.
Benefits of Power Management in Windows 10
Power management in Windows 10 offers numerous benefits, extending beyond just prolonging battery life. These benefits include:
- Increased Battery Life: This is the most direct and obvious benefit, especially for users relying on portable devices. Efficient power management allows for longer usage time between charges, enhancing productivity and convenience.
- Reduced Heat Generation: By dynamically adjusting component performance, power management prevents excessive heat generation, reducing the risk of thermal throttling and ensuring stable system operation.
- Improved Performance in Specific Scenarios: By prioritizing power allocation to critical processes, power management can enhance performance in demanding tasks, ensuring a smoother and faster user experience.
- Extended Hardware Lifespan: Lower operating temperatures due to efficient power management can contribute to a longer lifespan for hardware components, reducing the risk of premature failure.
- Reduced Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact: Efficient power management translates to lower energy consumption, reducing the environmental impact of computing devices.
FAQs on Power Management in Windows 10
1. Does Power Management Affect Performance?
While power management primarily focuses on reducing power consumption, it can also impact performance, particularly in resource-intensive tasks. However, Windows 10 intelligently adjusts performance based on the workload and power settings, ensuring a balance between efficiency and responsiveness.
2. Can I Disable Power Management?
It’s generally not recommended to disable power management entirely. Doing so can lead to excessive heat generation, reduced battery life, and potentially decreased hardware lifespan. However, users can fine-tune the power settings to suit their individual needs and preferences.
3. How Can I Optimize Power Management for My Device?
Optimizing power management for a specific device involves understanding its usage patterns and adjusting the power settings accordingly. Users can:
- Choose the appropriate power plan: Select the plan that best suits the device’s usage, considering factors like battery life, performance, and heat generation.
- Customize power settings: Fine-tune the power settings to control specific aspects like screen brightness, sleep states, and CPU performance.
- Use power-saving features: Utilize built-in power-saving features like automatic brightness adjustment, screen timeout, and device sleep states.
- Monitor power consumption: Use system monitoring tools to track power usage and identify areas for optimization.
4. Is Power Management Relevant for Desktop Computers?
While power management is often associated with portable devices, it’s equally relevant for desktop computers. It helps reduce energy consumption, minimize heat generation, and extend the lifespan of hardware components.
Tips for Optimizing Power Management in Windows 10
- Monitor Battery Usage: Regularly monitor battery usage to identify areas for optimization. Utilize built-in tools or third-party applications to track power consumption patterns.
- Adjust Power Settings: Experiment with different power plans and customize settings to find the ideal balance between performance and power efficiency.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Identify and disable services that are not actively used, as they can consume unnecessary power.
- Update Drivers: Regularly update device drivers to ensure optimal power management and performance.
- Use Power-Saving Features: Enable power-saving features like automatic brightness adjustment, screen timeout, and device sleep states to conserve energy.
- Avoid Overheating: Ensure proper ventilation and cooling to prevent overheating, which can lead to performance throttling and reduced battery life.
Conclusion
Power management in Windows 10 is an essential aspect of ensuring optimal system performance while maximizing efficiency. By dynamically adjusting component performance based on various factors, it strikes a balance between power consumption and user experience. Understanding and optimizing power management settings can significantly enhance battery life, reduce heat generation, and prolong hardware lifespan. Utilizing the available tools and techniques empowers users to tailor their system’s power behavior to their specific needs, maximizing efficiency and performance across various usage scenarios.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Power Management in Windows 10: Balancing Performance and Efficiency. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply