Near Field Communication: Unlocking A World Of Seamless Interactions
Near Field Communication: Unlocking a World of Seamless Interactions
Related Articles: Near Field Communication: Unlocking a World of Seamless Interactions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Near Field Communication: Unlocking a World of Seamless Interactions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Near Field Communication: Unlocking a World of Seamless Interactions
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Near Field Communication: Unlocking a World of Seamless Interactions
- 3.1 The Foundation of NFC: A Deeper Dive
- 3.2 The Power of NFC: Applications Transforming Industries
- 3.3 Unveiling the Benefits of NFC: A Closer Look
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries About NFC
- 3.5 Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of NFC
- 3.6 Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Communication
- 4 Closure
Near Field Communication: Unlocking a World of Seamless Interactions
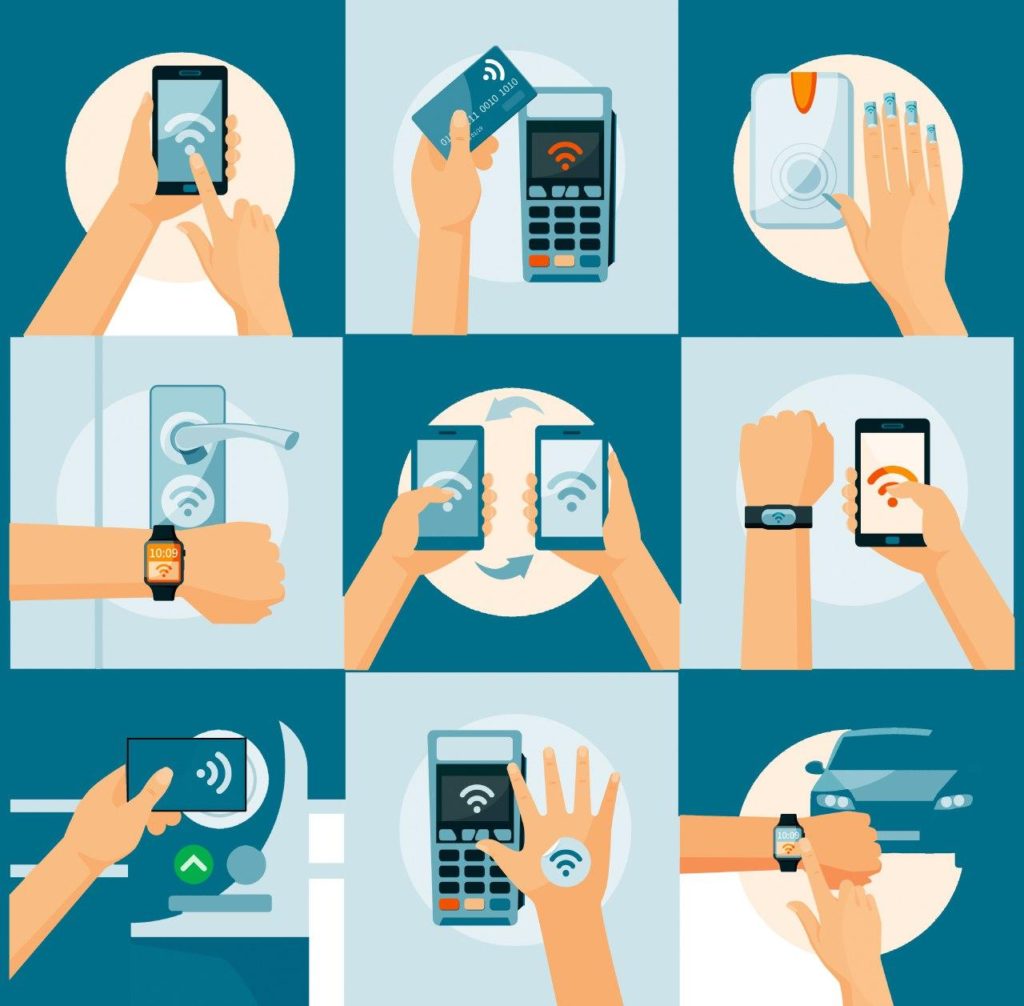

Near Field Communication (NFC) technology has emerged as a pivotal force in modern communication and data exchange, seamlessly connecting devices and facilitating a wide array of applications. This wireless communication protocol operates at short distances, typically within a few centimeters, enabling rapid and secure data transfer between NFC-enabled devices.
The core principle of NFC lies in its ability to transmit data using electromagnetic fields. When two NFC-enabled devices come into close proximity, they establish a communication channel through the exchange of electromagnetic waves. This interaction allows for a swift and secure transfer of information, paving the way for numerous applications across diverse industries.
The Foundation of NFC: A Deeper Dive
NFC technology finds its roots in the Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system, which utilizes radio waves for data identification and tracking. However, NFC goes beyond simple identification, offering a more versatile communication platform.
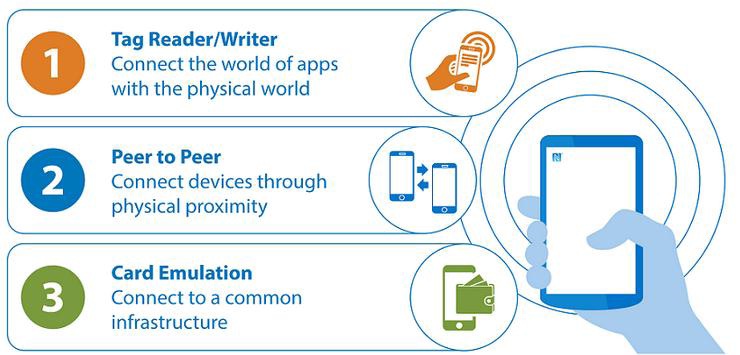
At its core, NFC operates on the 13.56 MHz frequency band, allowing for communication between two devices with NFC capabilities. This communication can be categorized into two distinct modes:
- Passive Mode: In this mode, one device acts as a reader while the other acts as a tag. The reader device initiates communication by transmitting a signal, and the tag device responds with its stored data. This mode is primarily used for applications like contactless payments and data sharing.
- Active Mode: Both devices act as both reader and tag, enabling peer-to-peer communication. This mode allows for bidirectional data exchange, making it suitable for applications like device pairing and data synchronization.
The Power of NFC: Applications Transforming Industries
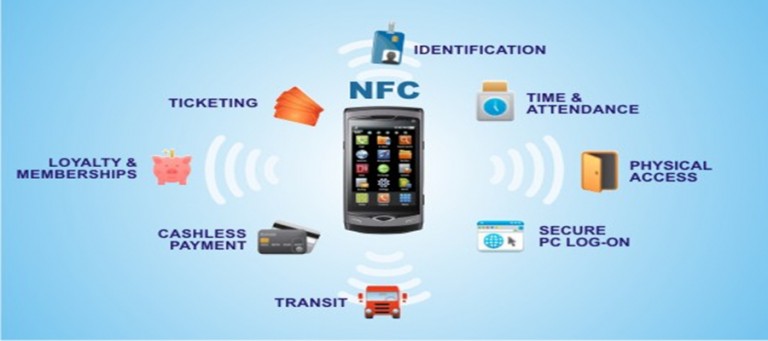
The versatility of NFC technology has opened doors to a vast spectrum of applications, transforming industries and enhancing user experiences.
1. Contactless Payments: One of the most prominent applications of NFC is contactless payments. NFC-enabled smartphones and smartwatches allow users to make secure payments at point-of-sale terminals by simply tapping their devices. This eliminates the need for physical cards and streamlines the payment process, offering convenience and security.
2. Access Control: NFC technology plays a crucial role in access control systems, enabling secure entry into buildings, offices, and restricted areas. NFC-enabled access cards or mobile devices can be used to verify identity and grant access, enhancing security and streamlining access control processes.
3. Data Sharing: NFC facilitates seamless data sharing between devices. Users can easily share contact information, photos, documents, and other digital content by simply tapping their NFC-enabled devices together. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and simplifies data exchange.
4. Device Pairing: NFC simplifies the process of pairing devices, enabling effortless connection between smartphones, smartwatches, and other NFC-enabled devices. This allows for seamless data synchronization and device control, enhancing user convenience and streamlining connectivity.
5. Transportation Ticketing: NFC is revolutionizing the transportation industry by enabling contactless ticketing solutions. Passengers can purchase and store tickets on their NFC-enabled devices, eliminating the need for physical tickets and streamlining boarding processes.
6. Healthcare: NFC finds applications in the healthcare industry, enabling secure access to patient records, medication information, and other medical data. NFC-enabled devices can be used for patient identification, medication dispensing, and remote patient monitoring, enhancing healthcare efficiency and patient safety.
7. Automotive: NFC technology is being integrated into vehicles, enabling keyless entry, remote engine start, and other vehicle control features. NFC-enabled smartphones can be used as digital keys, providing convenient and secure access to vehicles.
8. Smart Homes: NFC is playing a significant role in the development of smart homes, enabling communication between devices and appliances. NFC-enabled smart home devices can be controlled via smartphones or other NFC-enabled devices, providing users with greater control over their home environments.
9. Asset Tracking: NFC-enabled tags can be attached to assets, enabling real-time tracking and inventory management. This technology is used in various industries, including logistics, manufacturing, and retail, to track assets, optimize inventory, and improve operational efficiency.
10. Marketing and Advertising: NFC technology is being leveraged in marketing and advertising campaigns to engage consumers and deliver personalized content. NFC-enabled posters, brochures, and other marketing materials can be used to provide users with product information, promotional offers, and other interactive experiences.
Unveiling the Benefits of NFC: A Closer Look
The widespread adoption of NFC technology across diverse sectors can be attributed to its numerous benefits, making it a powerful tool for enhancing efficiency, security, and user experience.
1. Enhanced Convenience: NFC technology simplifies interactions by eliminating the need for physical cards, cables, or complex pairing processes. This convenience translates to a smoother user experience, streamlining daily tasks and reducing friction points.
2. Increased Security: NFC leverages encryption and authentication protocols to ensure secure data transmission. This robust security framework protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, mitigating the risk of fraud and data breaches.
3. Improved Efficiency: NFC technology streamlines processes by automating tasks and reducing manual interventions. This increased efficiency translates to cost savings and time optimization, boosting productivity across various industries.
4. Enhanced User Experience: NFC technology enhances user experience by providing intuitive and seamless interactions. This intuitive nature fosters user engagement and satisfaction, making NFC a valuable tool for businesses seeking to improve customer experience.
5. Wide Compatibility: NFC technology is widely supported by smartphones, tablets, and other devices, ensuring compatibility across a broad range of platforms. This wide compatibility facilitates seamless integration and interoperability, making NFC a versatile and adaptable technology.
6. Cost-Effectiveness: NFC technology offers a cost-effective solution for various applications, reducing reliance on traditional methods and minimizing operational costs. This economic advantage makes NFC an attractive option for businesses seeking to optimize resource utilization.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries About NFC
1. What is the range of NFC communication?
The effective range of NFC communication is typically within a few centimeters, typically up to 4 centimeters. This short-range nature ensures secure communication and prevents unintended data transfers.
2. Is NFC secure?
NFC technology incorporates encryption and authentication protocols to ensure secure data transmission. These security measures protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, making NFC a reliable and secure communication protocol.
3. What devices support NFC?
A wide range of devices support NFC, including smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, and other consumer electronics. To check if a device supports NFC, look for the NFC symbol, which resembles a wave with four dots, on the device’s packaging or specifications.
4. How do I enable NFC on my device?
To enable NFC on your device, navigate to the settings menu and locate the "NFC" or "Near Field Communication" option. Enable the feature, and your device will be ready to communicate with other NFC-enabled devices.
5. What are some common NFC applications?
Common NFC applications include contactless payments, access control, data sharing, device pairing, transportation ticketing, healthcare, automotive, smart homes, asset tracking, and marketing and advertising.
Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of NFC
1. Ensure Device Compatibility: Before using NFC, verify that both devices involved support NFC technology. Check the device specifications or packaging for the NFC symbol to confirm compatibility.
2. Enable NFC on Your Device: To use NFC, ensure that NFC is enabled on your device. Navigate to the settings menu and locate the "NFC" or "Near Field Communication" option to activate the feature.
3. Keep Devices Close: For NFC communication to work, the two devices must be within a few centimeters of each other. Ensure that the devices are aligned correctly and in close proximity to establish a connection.
4. Understand NFC Modes: Familiarize yourself with the two NFC modes: passive and active. Passive mode is used for reading data from a tag, while active mode enables peer-to-peer communication.
5. Explore NFC Applications: Explore the diverse range of NFC applications available to enhance your daily life. From contactless payments to access control and data sharing, NFC offers a wide range of possibilities.
6. Stay Informed About NFC Developments: Keep abreast of the latest advancements and innovations in NFC technology. As the technology continues to evolve, new applications and features will emerge, expanding the possibilities of NFC.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Communication
Near Field Communication technology has emerged as a transformative force in modern communication, seamlessly connecting devices and facilitating a wide array of applications. Its ability to enable rapid and secure data transfer at short distances has revolutionized industries, enhancing user experiences and streamlining processes. From contactless payments to access control, data sharing, and beyond, NFC is shaping the future of communication, fostering a world of seamless interactions and unlocking new possibilities for innovation and convenience. As technology continues to evolve, NFC is poised to play an even greater role in shaping the connected world, empowering individuals and businesses to embrace a future of seamless and secure interactions.
-17102022.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Near Field Communication: Unlocking a World of Seamless Interactions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply