Near Field Communication: The Invisible Power Of Proximity
Near Field Communication: The Invisible Power of Proximity
Related Articles: Near Field Communication: The Invisible Power of Proximity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Near Field Communication: The Invisible Power of Proximity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Near Field Communication: The Invisible Power of Proximity
-17102022.jpg)
Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, often described as a wireless communication protocol operating at short distances, has become a ubiquitous presence in our everyday lives. While its operation may be invisible to the naked eye, its impact on the way we interact with devices, make payments, and access information is undeniable. This article delves into the intricacies of NFC, exploring its underlying principles, practical applications, and the transformative potential it holds for the future.
Understanding the Fundamentals:
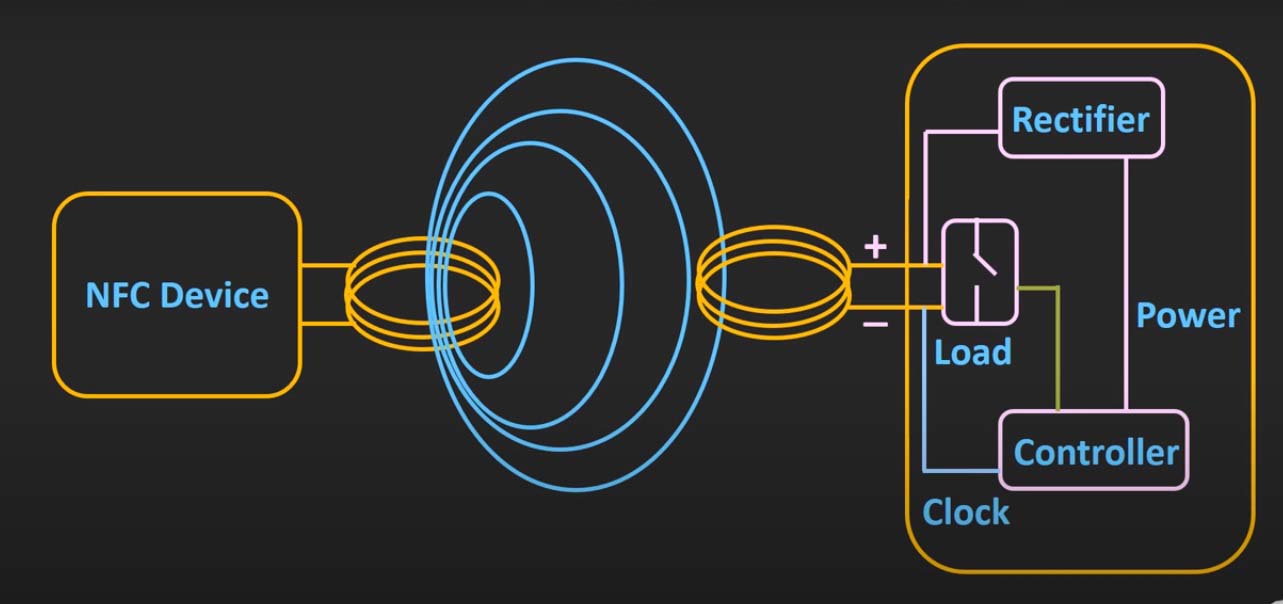
NFC operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, a phenomenon where a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a nearby conductor. This interaction occurs within a very short range, typically a few centimeters, making NFC a highly secure and efficient communication method.
At its core, NFC relies on two key components:
- The Transmitter: This component generates a fluctuating magnetic field, transmitting data to the receiver.
- The Receiver: This component captures the magnetic field generated by the transmitter, converting it back into an electrical signal and extracting the data.
Both the transmitter and receiver must be in close proximity for communication to occur. This proximity requirement ensures that data exchange is limited to authorized devices, enhancing security and privacy.
Types of NFC Communication:
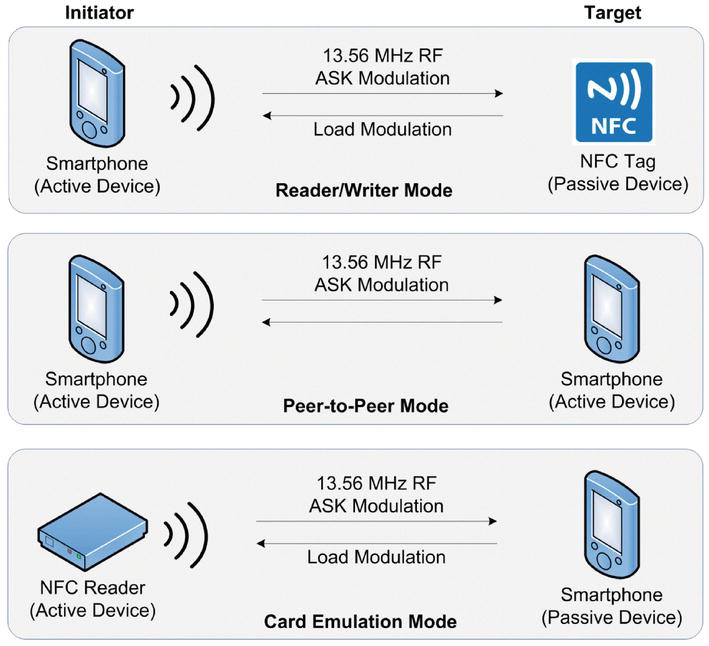
NFC communication can be categorized into two distinct modes:
- Passive Mode: In this mode, one device acts as a passive tag, relying solely on the energy provided by the other device, known as the reader, to power its communication. This mode is commonly used for applications like contactless payment, data transfer, and access control.
- Active Mode: Both devices in this mode operate actively, each possessing its own power source and transmitting data. This mode is typically used for peer-to-peer communication between two NFC-enabled devices, facilitating data exchange, file sharing, and device pairing.
The Evolution of NFC: From Niche Technology to Mainstream Adoption:
The origins of NFC can be traced back to the early 2000s, when it emerged as a promising technology for mobile payments and data transfer. However, its initial adoption was limited by factors such as high implementation costs and a lack of widespread device compatibility.
A turning point occurred in the late 2000s and early 2010s, with the introduction of NFC-enabled smartphones and the increasing popularity of contactless payment systems. This surge in adoption propelled NFC into the mainstream, making it an integral part of our modern technological landscape.
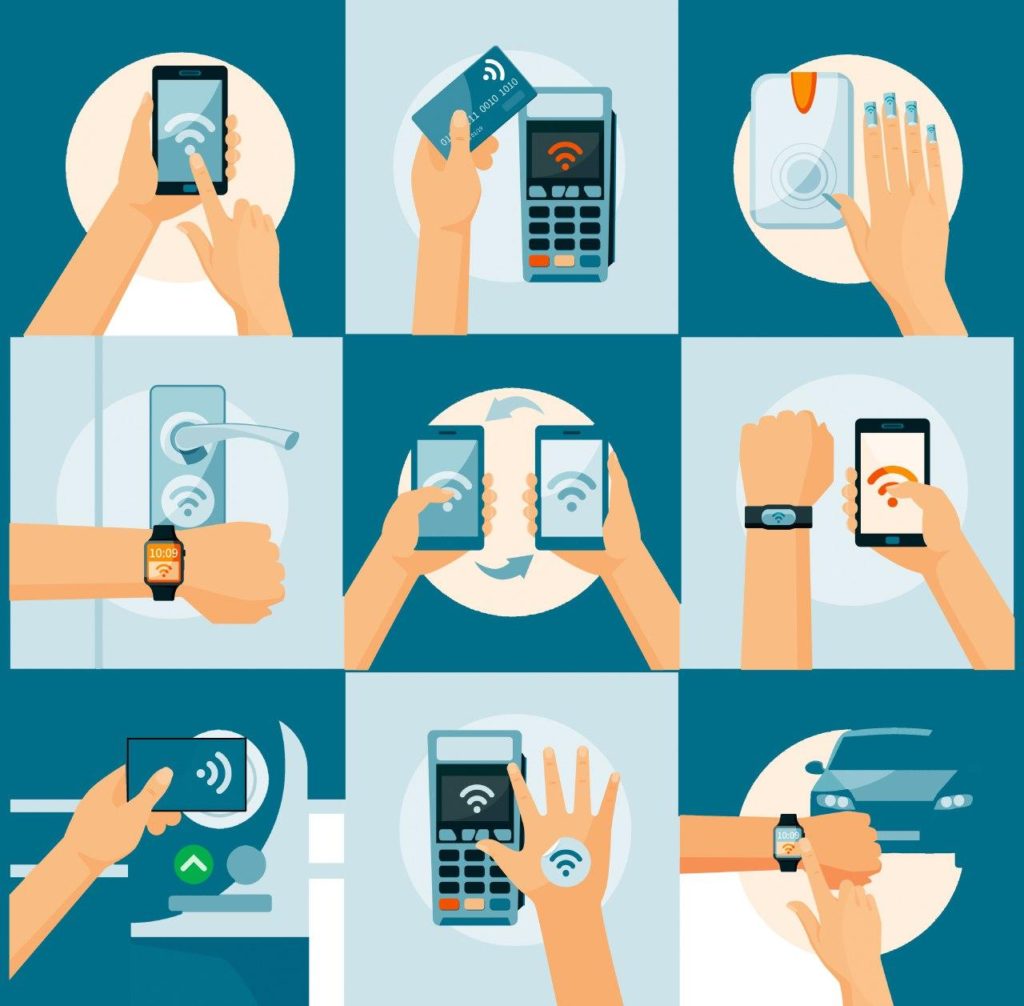
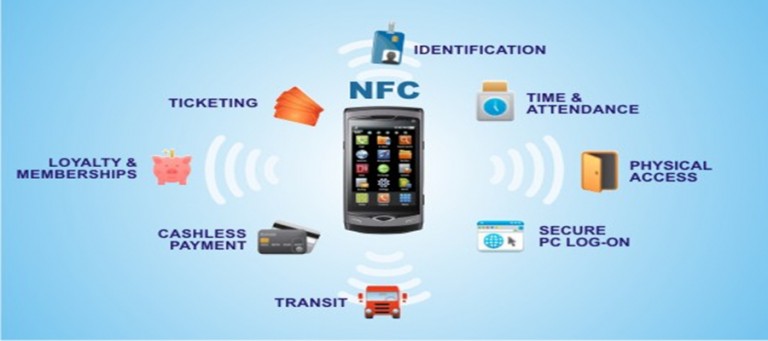
Applications of NFC: Transforming Everyday Experiences:
NFC has permeated various aspects of our lives, revolutionizing how we interact with our environment and devices. Some of its most prominent applications include:
-
Contactless Payment: NFC has transformed the way we pay for goods and services, enabling secure and convenient transactions without the need for physical cards. By simply tapping an NFC-enabled smartphone or wearable device on a payment terminal, users can quickly and securely complete their purchases.
-
Data Transfer: NFC facilitates seamless data exchange between devices, enabling users to share files, contacts, and other information effortlessly. This feature is particularly useful for transferring data between smartphones, tablets, and other NFC-enabled devices.
-
Access Control: NFC is widely used for access control systems, granting authorized individuals access to buildings, rooms, and other restricted areas. By simply presenting an NFC-enabled card or device to a reader, users can gain entry, eliminating the need for physical keys or traditional access cards.
-
Mobile Ticketing: NFC has revolutionized ticketing systems, enabling users to purchase, store, and present tickets directly on their smartphones. This eliminates the need for paper tickets and facilitates a more efficient and convenient ticketing experience.
-
Device Pairing: NFC enables effortless pairing of devices, simplifying the process of connecting smartphones, headphones, and other accessories. By simply tapping two NFC-enabled devices together, users can establish a connection and begin using the devices seamlessly.
-
Interactive Marketing: NFC is increasingly being employed in interactive marketing campaigns, allowing businesses to engage customers through immersive experiences. By tapping an NFC-enabled poster or product, users can access additional information, videos, and promotional offers, enhancing their brand interaction.
Benefits of NFC: Enhancing Convenience, Security, and Efficiency:
NFC technology offers a plethora of benefits, contributing to a more convenient, secure, and efficient user experience:
-
Convenience: NFC eliminates the need for physical cards, keys, and tickets, streamlining everyday tasks and reducing the hassle associated with traditional methods.
-
Security: NFC operates within a very short range, limiting communication to authorized devices and minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. This inherent security feature makes NFC a highly secure communication method.
-
Efficiency: NFC enables quick and easy transactions, data transfers, and device pairing, enhancing efficiency and saving time.
-
Versatility: NFC is a versatile technology, adaptable to a wide range of applications, from mobile payments and data transfer to access control and interactive marketing.
Addressing Concerns and Challenges:
While NFC technology offers numerous advantages, it also faces certain challenges and concerns:
-
Security Concerns: Despite its inherent security features, NFC can be vulnerable to certain security threats, such as cloning or spoofing attacks. Robust security measures and user education are crucial to mitigate these risks.
-
Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between different NFC devices and platforms remains a challenge. Standardization efforts and industry collaboration are essential to promote seamless communication across diverse ecosystems.
-
Privacy Concerns: As NFC technology collects and transmits data, concerns regarding user privacy arise. Ensuring data privacy and implementing appropriate security protocols are paramount to address these concerns.
Future of NFC: Expanding Horizons and Possibilities:
NFC technology continues to evolve, with exciting developments on the horizon:
-
Integration with IoT: NFC is poised to play a crucial role in the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling seamless communication between devices and the surrounding environment.
-
Enhanced Security Features: Ongoing research and development are focused on enhancing NFC security measures, further protecting user data and preventing unauthorized access.
-
New Applications: NFC is expected to find new and innovative applications in various industries, from healthcare and transportation to education and entertainment.
FAQs:
Q: What is the range of NFC communication?
A: NFC communication typically occurs within a range of a few centimeters, making it a short-range wireless technology.
Q: Is NFC secure?
A: NFC is considered a highly secure technology due to its short-range communication and encryption capabilities. However, it’s essential to implement appropriate security measures and stay informed about potential vulnerabilities.
Q: What devices support NFC?
A: Many modern smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices support NFC. Check the device specifications or manufacturer’s website for NFC compatibility.
Q: How can I use NFC for mobile payments?
A: To use NFC for mobile payments, your device must be NFC-enabled and linked to a compatible payment service. Simply tap your device on a payment terminal to complete the transaction.
Q: Can I transfer files using NFC?
A: Yes, NFC enables data transfer between devices, allowing you to share files, contacts, and other information seamlessly.
Q: Is NFC used in other industries besides mobile payments?
A: Yes, NFC is used in a wide range of industries, including access control, ticketing, transportation, healthcare, and interactive marketing.
Tips:
-
Check Device Compatibility: Ensure your device supports NFC before attempting to use it.
-
Enable NFC on Your Device: Activate NFC settings on your device to enable communication.
-
Keep Devices Close: NFC requires close proximity between devices for communication to occur.
-
Use Reputable Payment Services: Choose trusted and secure payment services for NFC transactions.
-
Be Aware of Security Risks: Stay informed about potential security threats and implement appropriate security measures.
Conclusion:
NFC technology has emerged as a powerful and versatile communication method, transforming the way we interact with devices, make payments, and access information. Its convenience, security, and efficiency have made it an integral part of our modern technological landscape. As NFC continues to evolve and find new applications, its transformative potential promises to shape the future of communication and enhance our everyday experiences.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Near Field Communication: The Invisible Power of Proximity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply