Near-Field Communication: A Tutorial Review
Near-Field Communication: A Tutorial Review
Related Articles: Near-Field Communication: A Tutorial Review
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Near-Field Communication: A Tutorial Review. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Near-Field Communication: A Tutorial Review

Near-field communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that enables two devices to communicate by bringing them within a few centimeters of each other. It has become ubiquitous in modern life, powering a wide range of applications, from contactless payments and data transfer to access control and device pairing. This tutorial review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of NFC technology, exploring its principles, functionalities, and applications, while highlighting its significance in the evolving technological landscape.
1. Introduction to NFC Technology
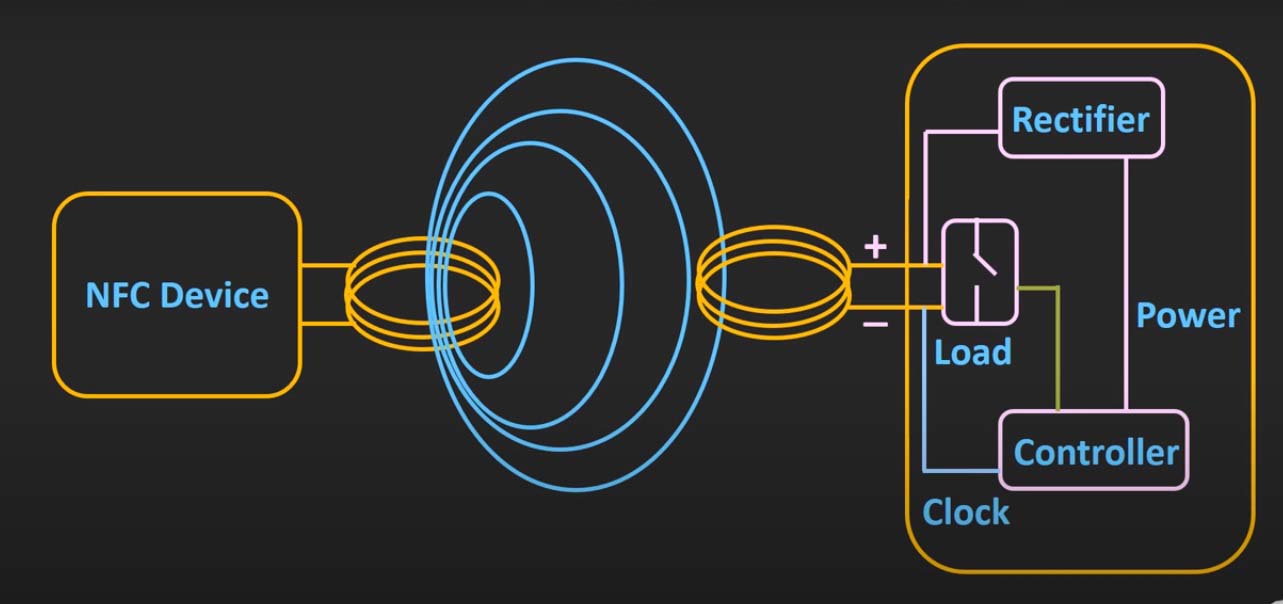
NFC technology is built upon the principles of electromagnetic induction, where energy is transferred wirelessly between two devices through a magnetic field. This process is facilitated by two key components:
- Transmitter: The device transmitting the signal, typically containing a coil that generates a magnetic field.
- Receiver: The device receiving the signal, containing a coil that picks up the magnetic field and converts it into an electrical signal.
The transfer of data occurs within a very short range, typically less than 10 centimeters. This short-range communication is what distinguishes NFC from other wireless technologies like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, which can operate over longer distances.
2. NFC Standards and Protocols
NFC technology adheres to a standardized framework to ensure interoperability between devices from different manufacturers. The primary standards governing NFC are:
- ISO/IEC 14443: This standard defines the communication protocols for passive NFC devices, which are powered by the electromagnetic field generated by the active device.
- ISO/IEC 18092: This standard defines the communication protocols for active NFC devices, which have their own power source and can initiate communication with passive devices.
- NFC Forum: This organization promotes the adoption and development of NFC technology, defining specifications and certification programs to ensure compatibility and security.
These standards ensure that NFC-enabled devices can communicate seamlessly, regardless of their manufacturer or operating system.
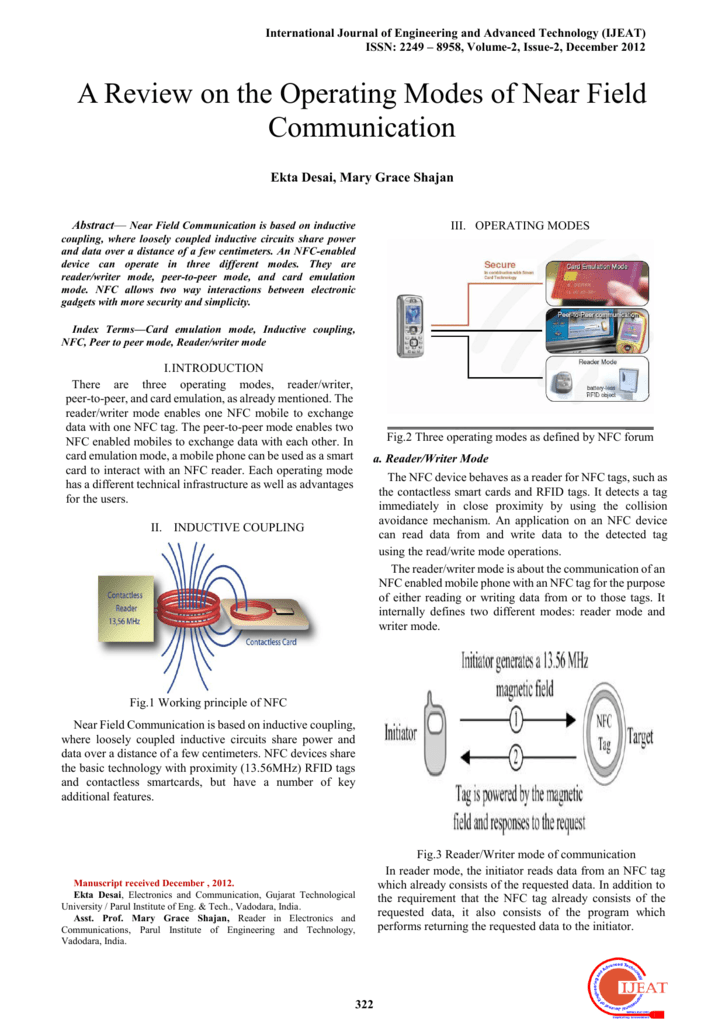
3. NFC Modes of Operation
NFC technology supports three distinct modes of operation, each tailored to specific applications:
- Passive Mode: The passive device is powered by the active device and only transmits data when prompted. This mode is commonly used for contactless payments, where the payment terminal acts as the active device and the card or phone acts as the passive device.
- Active Mode: Both devices have their own power source and can initiate communication. This mode is suitable for data transfer applications between two NFC-enabled devices, such as exchanging contact information or transferring files.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Mode: This mode allows two active NFC devices to communicate directly with each other. It is used for applications like device pairing, file sharing, and wireless printing.
The choice of mode depends on the specific application and the capabilities of the participating devices.
4. NFC Applications
NFC technology has permeated various aspects of modern life, enabling a wide range of applications:
- Contactless Payments: NFC-enabled cards and mobile devices have revolutionized payment systems, allowing for quick and secure transactions without the need for physical contact.
- Data Transfer: NFC allows for the transfer of small amounts of data between devices, such as contact information, website URLs, and digital business cards.
- Access Control: NFC technology is used for access control systems in various settings, including buildings, offices, and public transport.
- Device Pairing: NFC simplifies the process of pairing devices, such as connecting a Bluetooth speaker to a smartphone or setting up a wireless headset.
- Mobile Ticketing: NFC enables contactless ticketing for public transport, eliminating the need for physical tickets and streamlining the boarding process.
- Near-Field Communication Tag (NFC Tag) Applications: NFC tags are passive devices containing information that can be read by NFC-enabled devices. These tags are used in various applications, including product information, asset tracking, and interactive advertising.
The versatility of NFC technology has led to its widespread adoption in diverse industries, from retail and finance to transportation and healthcare.
5. Advantages of NFC Technology
NFC technology offers several advantages over other wireless communication technologies:
- Short Range and Security: The short-range nature of NFC communication inherently limits the range of potential eavesdroppers, enhancing security.
- Low Power Consumption: NFC devices consume minimal power, making them suitable for battery-powered devices.
- Ease of Use: NFC technology is simple to use, requiring minimal user interaction.
- Interoperability: NFC standards ensure interoperability between devices from different manufacturers, facilitating seamless communication.
- Cost-Effectiveness: NFC technology is relatively inexpensive to implement, making it accessible for a wide range of applications.
These advantages have contributed to the rapid adoption of NFC technology across various sectors.
6. Challenges and Limitations of NFC Technology
Despite its numerous advantages, NFC technology also faces certain challenges and limitations:
- Limited Data Transfer Rate: NFC has a relatively low data transfer rate, making it unsuitable for large file transfers or streaming applications.
- Short Range: The short communication range limits its applicability in scenarios requiring long-distance communication.
- Interference: NFC signals can be affected by electromagnetic interference from other devices, potentially causing communication disruptions.
- Security Concerns: While NFC provides inherent security benefits, vulnerabilities still exist, requiring robust security protocols and implementation.
These challenges are being addressed through ongoing research and development efforts to enhance the capabilities and security of NFC technology.
7. Future Trends in NFC Technology
The future of NFC technology is promising, with ongoing advancements and emerging applications:
- Integration with Other Technologies: NFC is increasingly being integrated with other technologies, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, to enhance functionality and expand its application scope.
- Enhanced Security Features: Research is focused on developing more robust security protocols to address potential vulnerabilities and ensure secure data transmission.
- New Applications: Emerging applications of NFC technology include contactless payments in emerging markets, smart home automation, and healthcare monitoring.
As technology continues to evolve, NFC technology is poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of wireless communication and mobile technology.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about NFC
Q1: What is the difference between NFC and Bluetooth?
A: NFC is a short-range wireless communication technology that operates within a few centimeters, while Bluetooth is a longer-range technology that can operate over distances of up to 10 meters. NFC is designed for quick and easy communication, while Bluetooth is more suitable for continuous communication and data transfer.
Q2: Is NFC secure?
A: NFC technology is inherently secure due to its short range and limited communication capabilities. However, vulnerabilities exist, and robust security protocols are essential to protect sensitive data.
Q3: How do I enable NFC on my smartphone?
A: The method for enabling NFC on a smartphone varies depending on the device and operating system. Typically, you can find the NFC settings within the device’s wireless or connectivity settings.
Q4: Can I use NFC to transfer large files?
A: NFC is not suitable for transferring large files due to its limited data transfer rate. Other technologies, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, are more appropriate for large file transfers.
Q5: What is the future of NFC technology?
A: NFC technology is expected to continue evolving with advancements in security, integration with other technologies, and new applications in diverse sectors.
9. Tips for Using NFC Technology
- Ensure your device supports NFC: Check the specifications of your device to confirm NFC compatibility.
- Enable NFC on your device: Locate and enable the NFC setting within your device’s settings.
- Bring devices close together: For successful communication, ensure the two NFC-enabled devices are within a few centimeters of each other.
- Use NFC-enabled apps: Utilize NFC-compatible apps to access various NFC functionalities, such as contactless payments and data transfer.
- Be mindful of security: Ensure you are using reputable apps and services to protect your data from unauthorized access.
10. Conclusion
Near-field communication (NFC) technology has emerged as a transformative wireless communication technology, enabling a wide range of applications that have revolutionized how we interact with devices and our surroundings. Its short range, low power consumption, and ease of use have made it a ubiquitous technology, powering contactless payments, data transfer, access control, and device pairing. As technology continues to evolve, NFC is poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of wireless communication and mobile technology, with ongoing advancements in security, integration with other technologies, and the development of new and innovative applications.




-17102022.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Near-Field Communication: A Tutorial Review. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply