Near Field Communication: A Technological Revolution In Our Pockets
Near Field Communication: A Technological Revolution in Our Pockets
Related Articles: Near Field Communication: A Technological Revolution in Our Pockets
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Near Field Communication: A Technological Revolution in Our Pockets. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Near Field Communication: A Technological Revolution in Our Pockets
-17102022.jpg)
Near field communication (NFC) technology has quietly become an integral part of our daily lives. This wireless communication protocol, operating over short distances, has revolutionized how we interact with devices and services, making it possible to transfer data, make payments, and access information seamlessly. Its widespread adoption across various industries, from mobile payments to transportation and healthcare, highlights its transformative potential. This article delves into the intricacies of NFC technology, exploring its applications, benefits, and future prospects.
Understanding the Fundamentals of NFC
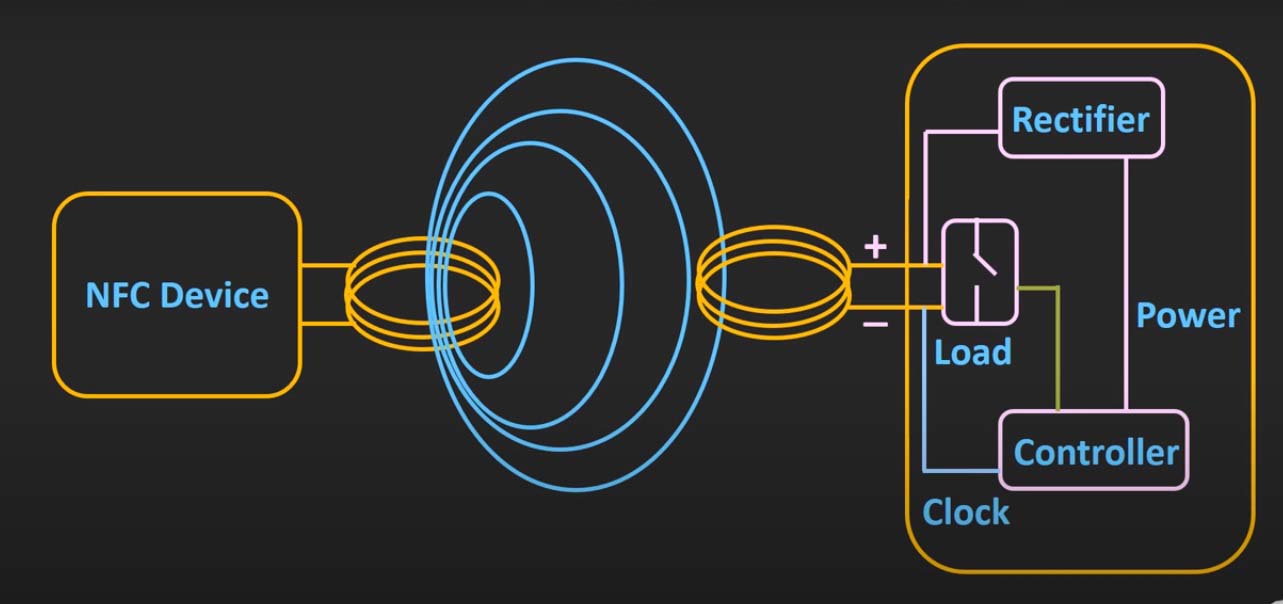
NFC, at its core, is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows two devices to exchange data when they are within a few centimeters of each other. This communication occurs through electromagnetic fields, eliminating the need for line-of-sight visibility. NFC operates on the 13.56 MHz radio frequency band, enabling data transfer rates ranging from 106 kbit/s to 424 kbit/s.
NFC: A Closer Look at the Technology
The foundation of NFC lies in the principles of electromagnetic induction. When two NFC-enabled devices are brought close together, one device acts as a transmitter, generating a magnetic field. This field induces an electric current in the receiving device, enabling the transfer of data.
Two Modes of Operation
NFC operates in two distinct modes:
- Passive Mode: In this mode, one device acts as a passive tag, drawing power from the electromagnetic field generated by the other device, which acts as an active reader. This mode is commonly used in applications like contactless payment cards and RFID tags.
- Active Mode: Both devices actively transmit and receive data, allowing for peer-to-peer communication. This mode is employed in applications like NFC-enabled mobile payments and data sharing between devices.
The Benefits of NFC Technology
NFC’s versatility and convenience have made it a preferred choice for a wide range of applications. Its key benefits include:
- Simplicity: NFC communication is inherently user-friendly, requiring minimal setup and interaction. Users can simply tap their NFC-enabled devices together to initiate data transfer or complete transactions.
- Security: NFC transactions are typically secure, utilizing encryption protocols to protect sensitive data during transmission. This enhanced security is crucial for sensitive applications like mobile payments and data sharing.
- Versatility: NFC technology is highly adaptable, supporting various applications across diverse industries. From contactless payments and data transfer to access control and mobile ticketing, NFC’s versatility makes it a valuable tool for businesses and consumers alike.
- Energy Efficiency: NFC communication consumes minimal power, making it suitable for battery-powered devices. This energy efficiency is particularly advantageous for mobile devices and wearables.
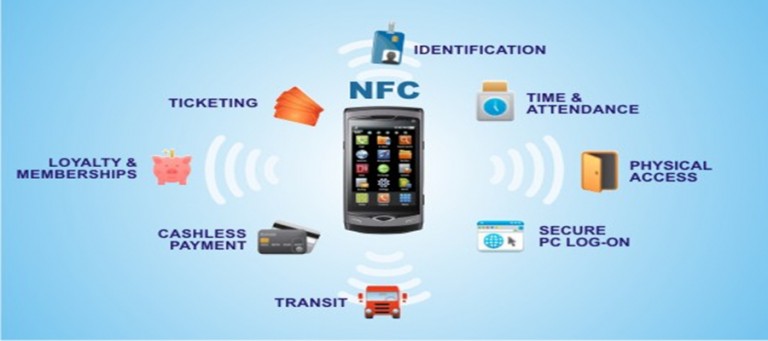
Exploring the Applications of NFC
NFC technology has made its mark across various industries, revolutionizing how we interact with our surroundings and manage our daily activities. Here are some prominent examples:
1. Contactless Payments:
NFC has become synonymous with contactless payments. Smartphones, smartwatches, and even payment cards equipped with NFC chips allow users to make secure and convenient payments by simply tapping their devices at NFC-enabled terminals. This technology has transformed the retail landscape, providing a faster and more secure alternative to traditional payment methods.
2. Mobile Ticketing:
NFC technology has revolutionized the way we access and manage transportation tickets. Mobile ticketing applications utilize NFC to store and display tickets on smartphones, eliminating the need for physical tickets. Users can simply tap their phones at NFC readers to validate their tickets and gain access to public transportation.
3. Data Sharing and File Transfer:
NFC facilitates seamless data sharing between devices. Users can easily exchange contact information, photos, videos, and other files by simply tapping their NFC-enabled devices together. This feature eliminates the need for cumbersome Bluetooth pairing or data cables, streamlining the file transfer process.
4. Access Control and Security:
NFC technology plays a crucial role in enhancing security and access control systems. NFC-enabled keycards or mobile devices can be used to grant access to buildings, offices, and other restricted areas. This technology eliminates the need for traditional keys or physical access cards, providing a more secure and convenient way to manage access control.
5. Healthcare and Medical Applications:
NFC is increasingly being integrated into healthcare applications, enabling secure and efficient data exchange between patients and healthcare providers. For instance, NFC-enabled medical devices can transmit patient data, such as vital signs and medication records, to healthcare professionals, facilitating better patient care and remote monitoring.
6. NFC in the Automotive Industry:
NFC technology is being adopted in the automotive industry for various applications. Car keyless entry systems utilize NFC to unlock and start vehicles, while NFC-enabled infotainment systems allow drivers to connect their smartphones to their car’s entertainment systems.
7. NFC in the Retail Industry:
NFC technology is transforming the retail experience by enabling contactless payments, inventory management, and customer engagement. NFC-enabled point-of-sale terminals allow customers to make quick and secure payments, while NFC tags can be used to track inventory and provide customers with product information.
8. NFC in the IoT (Internet of Things):
NFC is a key enabling technology for the Internet of Things (IoT), facilitating communication and data exchange between various connected devices. For example, NFC tags can be used to identify and track objects in the supply chain, while NFC-enabled smart home devices can interact with each other seamlessly.
FAQs on NFC Technology
1. What are the security concerns associated with NFC technology?
While NFC transactions are generally secure, potential security risks include:
- Data Breaches: If an NFC-enabled device is compromised, sensitive data stored on the device could be accessed by unauthorized individuals.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Attackers can intercept communication between two NFC devices, potentially stealing data or altering transactions.
2. How can I protect myself from NFC security risks?
To mitigate security risks associated with NFC technology, consider these measures:
- Use Strong Passwords: Set strong passwords for your NFC-enabled devices and payment accounts.
- Enable Device Security Features: Utilize device security features such as PIN codes, biometrics, and screen locks to protect your device from unauthorized access.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure that your device’s operating system and NFC-related apps are updated to the latest versions, which typically include security patches.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Be mindful of your surroundings when using NFC-enabled devices, particularly in crowded or unfamiliar areas.
3. What are the limitations of NFC technology?
Despite its numerous benefits, NFC technology has certain limitations:
- Short Range: NFC communication is restricted to short distances, typically a few centimeters.
- Limited Data Transfer Speed: NFC data transfer speeds are relatively slow compared to other wireless technologies like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Device Compatibility: Not all devices are equipped with NFC capabilities, limiting its applicability in certain scenarios.
4. How is NFC different from Bluetooth or Wi-Fi?
NFC, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi are all wireless communication technologies, but they differ in their operating principles, range, and applications:
- NFC: Short-range, operates on electromagnetic induction, primarily used for contactless payments, data sharing, and access control.
- Bluetooth: Medium-range, uses radio waves, primarily used for wireless audio streaming, data transfer, and device connectivity.
- Wi-Fi: Long-range, uses radio waves, primarily used for internet access, data transfer, and device connectivity.
5. What is the future of NFC technology?
NFC technology is expected to continue evolving and expanding its reach in various industries. Some key trends include:
- Integration with Other Technologies: NFC is likely to be integrated with other technologies, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, to enhance functionality and expand its applications.
- Increased Security Measures: Advancements in encryption and security protocols will further enhance the security of NFC transactions.
- New Applications: NFC technology is expected to find new applications in areas like smart cities, industrial automation, and wearable technology.
Tips for Using NFC Technology
- Ensure Device Compatibility: Before using NFC, verify that both your device and the receiving device are NFC-enabled.
- Enable NFC Functionality: Activate NFC functionality on your device by going to the settings menu and enabling NFC.
- Keep Devices Close Together: For successful NFC communication, ensure that the two devices are within a few centimeters of each other.
- Be Mindful of Security: Use strong passwords and enable device security features to protect your data.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your device’s operating system and NFC-related apps to ensure optimal performance and security.
Conclusion
Near field communication technology has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing the way we interact with devices, services, and our surroundings. Its versatility, convenience, and security have made it an integral part of our daily lives, enabling contactless payments, mobile ticketing, data sharing, and access control. As NFC technology continues to evolve and integrate with other technologies, its impact on various industries is expected to grow, shaping the future of communication and interaction. From simplifying everyday transactions to enhancing security and enabling new applications, NFC’s potential is vast and promising, making it a technology poised to play a significant role in the future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Near Field Communication: A Technological Revolution in Our Pockets. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply