Near Field Communication: A Revolution In Wireless Connectivity
Near Field Communication: A Revolution in Wireless Connectivity
Related Articles: Near Field Communication: A Revolution in Wireless Connectivity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Near Field Communication: A Revolution in Wireless Connectivity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Near Field Communication: A Revolution in Wireless Connectivity
-17102022.jpg)
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a wireless communication technology that allows two devices to exchange data by bringing them within a short distance, typically a few centimeters. This technology, often described as "tap and go," has become ubiquitous, enabling a wide range of applications in various sectors, from mobile payments and data transfer to access control and contactless ticketing.
The Fundamentals of Near Field Communication:
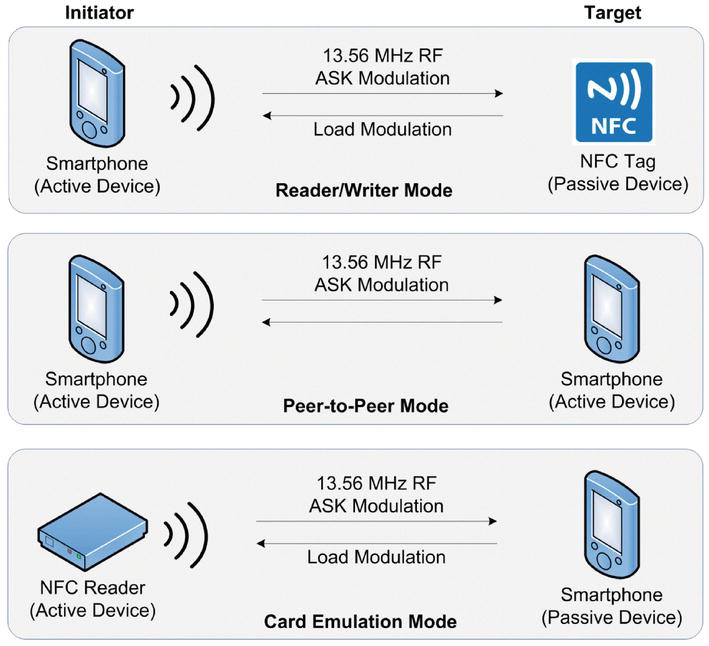
NFC operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, similar to how a transformer works. When two NFC-enabled devices are brought close together, an electromagnetic field is generated between them. This field allows the devices to exchange data wirelessly, without the need for a traditional wireless network connection.
Key Features of NFC:
- Short-Range Communication: NFC works only over very short distances, typically a few centimeters. This inherent security feature limits the range of communication, making it less susceptible to eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
- Low Power Consumption: NFC operates at low power levels, making it suitable for battery-powered devices. This feature contributes to the technology’s efficiency and extends the battery life of devices.
- Fast Data Transfer: While not as fast as other wireless technologies like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, NFC offers relatively quick data transfer rates, sufficient for most everyday applications.
- Simple and User-Friendly: NFC’s simplicity is one of its key advantages. Users can easily pair devices by simply tapping them together, eliminating the need for complex pairing processes.
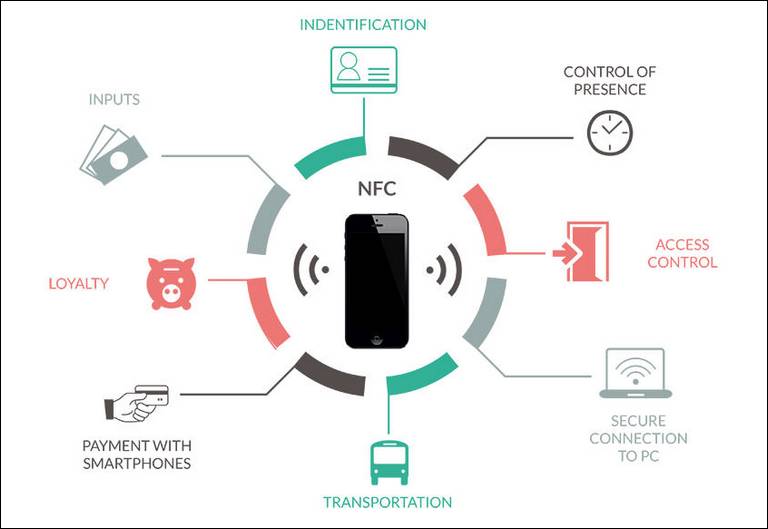
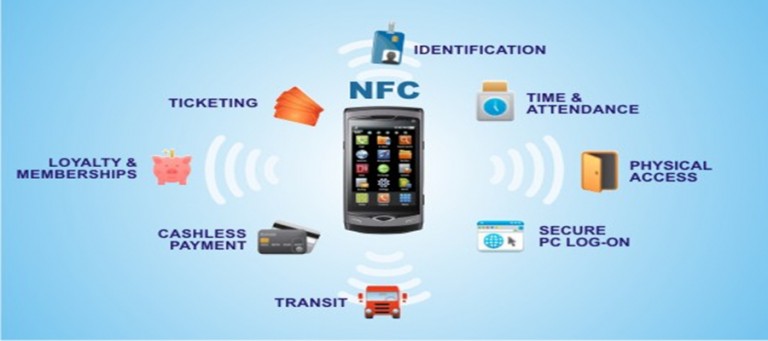
Applications of Near Field Communication:
NFC has revolutionized various aspects of our lives, finding applications in numerous sectors. Some of the most notable applications include:
1. Mobile Payments: NFC is the backbone of contactless payment systems, allowing users to make purchases by simply tapping their smartphones or other NFC-enabled devices on a payment terminal. This technology has significantly enhanced convenience and speed in retail transactions, reducing the need for cash and physical cards.
2. Data Transfer: NFC enables quick and easy data sharing between devices, facilitating file transfers, sharing contact information, and even connecting to Wi-Fi networks. This functionality has simplified data exchange for everyday tasks and business applications.
3. Access Control: NFC is widely used in access control systems, allowing individuals to access buildings, offices, or other restricted areas by tapping their NFC-enabled devices on a reader. This technology enhances security and streamlines access control processes.
4. Contactless Ticketing: NFC has revolutionized ticketing systems, enabling users to purchase and use tickets for public transportation, events, and other services through their smartphones or other NFC-enabled devices. This contactless approach provides convenience, reduces fraud, and improves efficiency.
5. Digital Identity and Authentication: NFC can be used for digital identity verification and authentication, allowing users to access services, confirm their identity, or gain access to secure areas using their NFC-enabled devices.
6. Healthcare: NFC is finding applications in healthcare, enabling patients to store and share their medical records securely, facilitating communication between healthcare providers and patients.
7. Industrial Automation: NFC is being incorporated into industrial automation systems, allowing for communication between machines and control systems, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
8. Smart Home Integration: NFC is increasingly used in smart homes, allowing users to control appliances, lighting, and other devices through their smartphones or other NFC-enabled devices.
Benefits of Near Field Communication:
- Convenience and Simplicity: NFC’s ease of use and intuitive interface have made it a popular technology, simplifying various tasks and enhancing user experience.
- Enhanced Security: The short-range nature of NFC and the use of encryption protocols make it a secure technology, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Efficiency and Speed: NFC offers fast data transfer rates and streamlined processes, improving efficiency in various applications, from mobile payments to access control.
- Cost-Effectiveness: NFC technology is relatively inexpensive, making it a viable option for businesses and individuals alike.
- Wide Compatibility: NFC is supported by a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, and even some payment cards, ensuring broad compatibility and accessibility.
Frequently Asked Questions about Near Field Communication:
1. Is NFC Secure?
Yes, NFC is generally considered secure due to its short-range communication and the use of encryption protocols. However, it is important to use NFC-enabled devices from reputable manufacturers and to ensure that your device’s operating system is up-to-date with the latest security patches.
2. How Does NFC Work with Mobile Payments?
When you make a contactless payment using NFC, your device sends your payment information securely to the payment terminal. This information is encrypted and verified by the payment network, ensuring secure and authorized transactions.
3. What are the Differences Between NFC, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi?
NFC, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi are all wireless technologies, but they differ in their range, data transfer rates, and applications. NFC is short-range, Bluetooth has a longer range, and Wi-Fi has the longest range. NFC is best suited for short-distance communication, while Bluetooth is used for device pairing and data transfer, and Wi-Fi is used for internet connectivity.
4. Can I Use NFC with Any Device?
Not all devices are equipped with NFC. To use NFC, you need a device that has an NFC chip and supports NFC functionality. You can check your device’s specifications to determine if it supports NFC.
5. Is NFC Safe to Use?
NFC is generally safe to use when used with reputable devices and services. However, it is important to be aware of potential security risks and to take precautions to protect your data.
Tips for Using Near Field Communication:
- Ensure Your Device Supports NFC: Before attempting to use NFC, verify that your device has NFC capabilities.
- Enable NFC on Your Device: Activate NFC functionality on your device through the settings menu.
- Keep Devices Close Together: For successful NFC communication, ensure that the two devices are within a few centimeters of each other.
- Use Reputable Apps and Services: When using NFC for mobile payments or other applications, choose reputable apps and services to minimize security risks.
- Keep Your Devices Up-to-Date: Regularly update your device’s operating system and apps to ensure the latest security patches are installed.
Conclusion:
Near Field Communication has become an indispensable part of our modern world, revolutionizing various aspects of our lives, from mobile payments and data transfer to access control and contactless ticketing. Its convenience, simplicity, security, and wide compatibility have made it a technology with immense potential for future advancements and applications. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative and transformative uses of NFC in the years to come.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Near Field Communication: A Revolution in Wireless Connectivity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply