Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide
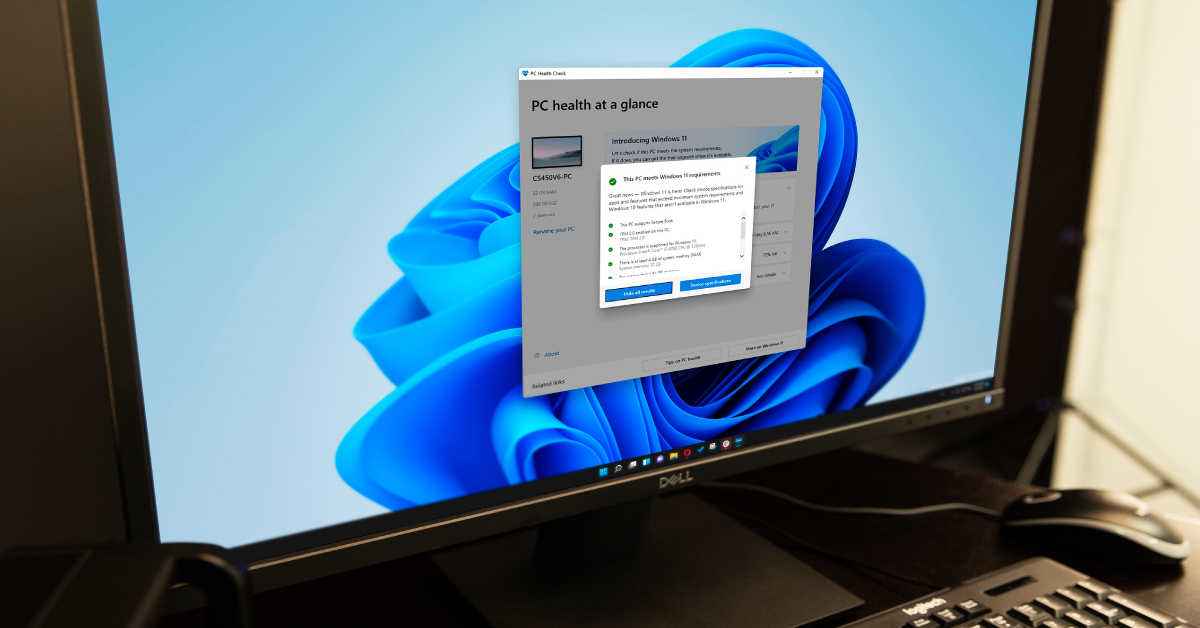
Windows 11, Microsoft’s latest operating system, promises a modern, streamlined experience. However, its compatibility requirements can be a hurdle for some users. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Windows 11 compatibility, outlining the key factors, potential issues, and solutions to ensure a smooth transition.
Understanding the Compatibility Requirements
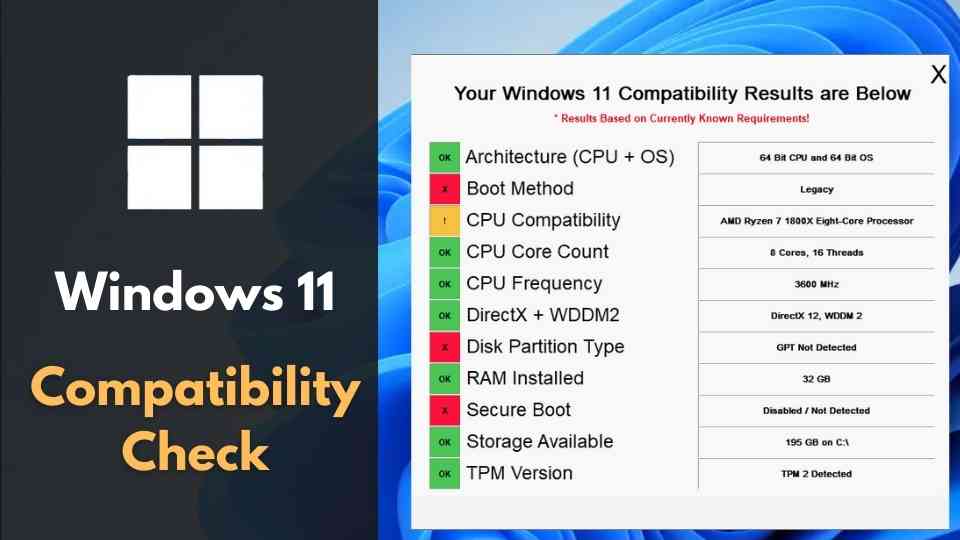
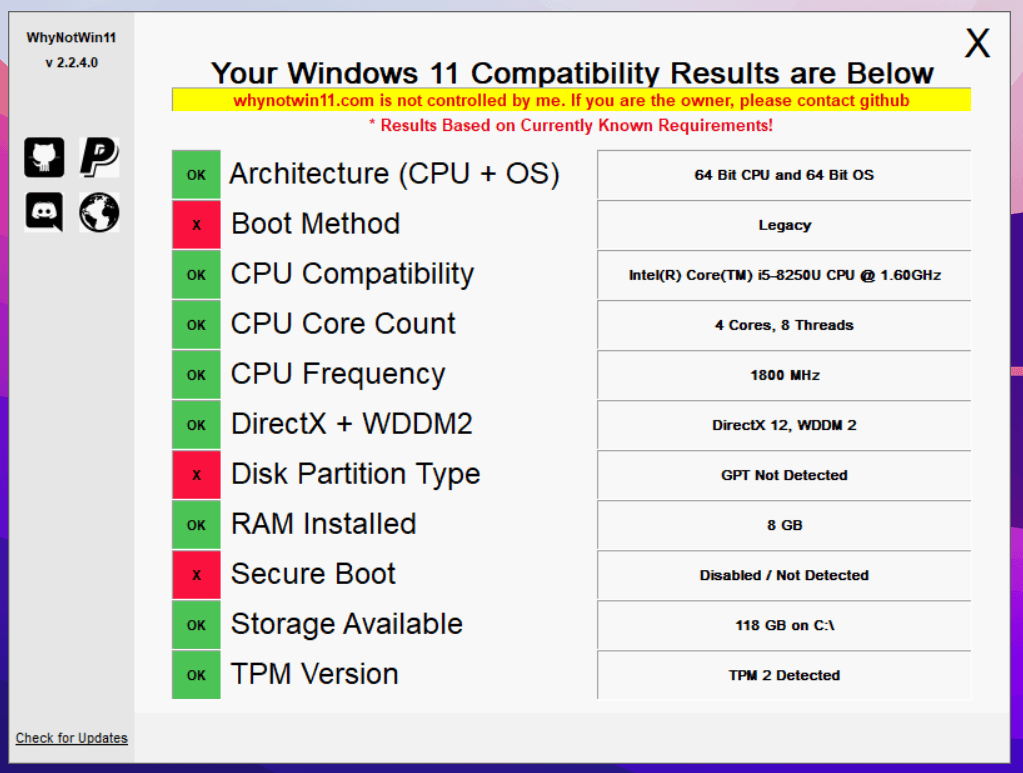
Microsoft has established specific hardware and software requirements for Windows 11 to guarantee optimal performance and security. These requirements are designed to ensure that the operating system can leverage the latest technologies and deliver the intended user experience.
Hardware Requirements:
- Processor: A 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster, with 2 or more cores, compatible with 64-bit architecture. This ensures sufficient processing power for demanding tasks and multitasking.
- RAM: At least 4 GB of RAM is required for basic functionality. 8 GB or more is recommended for a smoother experience with multiple applications running concurrently.
- Storage: A minimum of 64 GB of storage is needed, with at least 8 GB of free space for Windows 11 installation.
- TPM (Trusted Platform Module): A TPM 2.0 chip is mandatory for security purposes. This chip enhances system security by storing encryption keys and protecting against unauthorized access.
- Secure Boot: This feature must be enabled in the BIOS/UEFI settings. It prevents malicious software from loading before the operating system starts.
- Display: A display with a minimum resolution of 1366 x 768 pixels is required. This ensures that the user interface elements are displayed correctly.
Software Requirements:
- Windows 10 Version 2004 or later: This ensures that the system meets the minimum software prerequisites for a seamless upgrade.
- Microsoft Account: A Microsoft account is required for initial setup and system activation.
Identifying Compatibility Issues
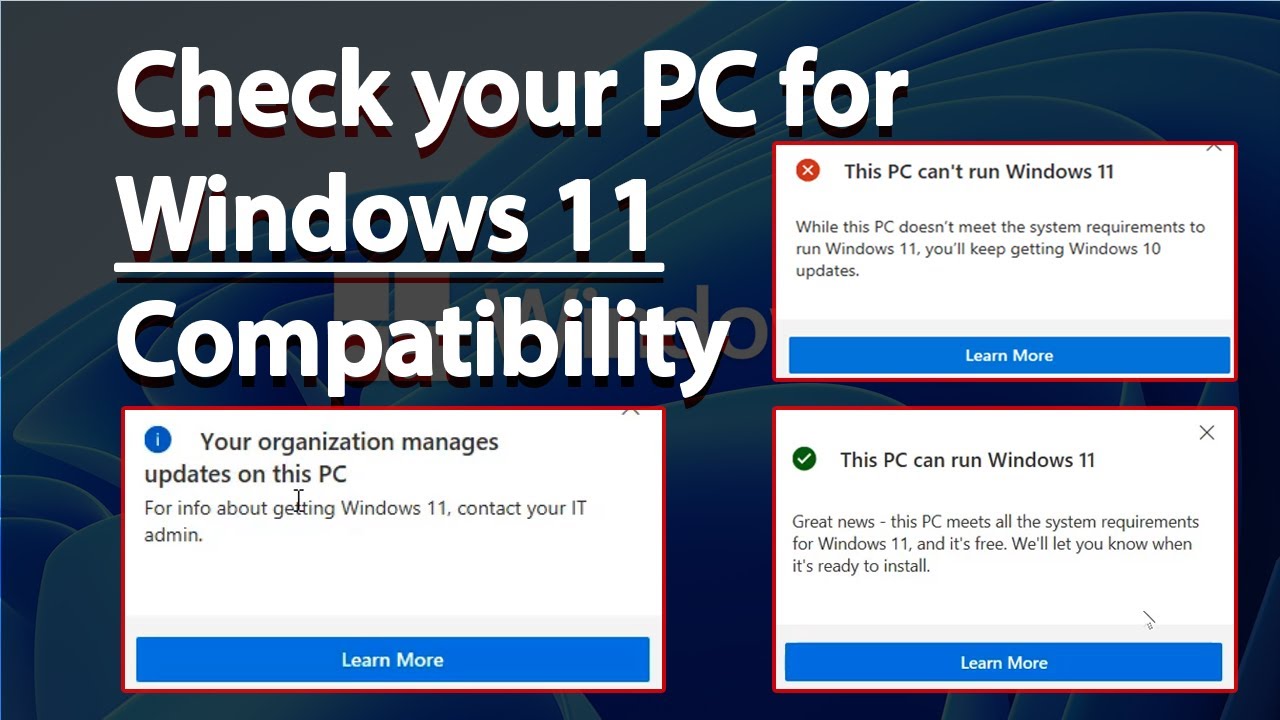
If your current system does not meet the minimum requirements, you may encounter various issues during installation or after upgrading to Windows 11. These issues can range from incompatibility errors to performance degradation.
- Installation Errors: The installation process might fail if the hardware or software requirements are not met. Error messages indicating incompatibility will be displayed.
- Performance Issues: A system that does not meet the minimum requirements may experience slow performance, lagging applications, and frequent crashes.
- Feature Limitations: Certain features of Windows 11 might not function correctly or be unavailable on systems that do not meet the requirements.
Troubleshooting Compatibility Problems
If you encounter compatibility issues, several troubleshooting steps can be taken to resolve them.
- Check System Specifications: Verify that your system meets the minimum hardware and software requirements. You can access this information through the System Information tool in Windows.
- Update Drivers: Ensure that all your drivers are up to date. Outdated drivers can lead to compatibility issues.
- Upgrade BIOS/UEFI: Update your system’s BIOS or UEFI to the latest version. This can resolve compatibility issues and improve performance.
- Disable Secure Boot: If you are unable to install Windows 11 due to Secure Boot, temporarily disable it in the BIOS/UEFI settings. However, this is not recommended for security reasons.
- Check for System Updates: Make sure your Windows 10 installation is up to date. System updates often include compatibility improvements and fixes.
- Contact Microsoft Support: If you are unable to resolve the issue, contact Microsoft support for assistance.
Alternatives to Upgrading
If your system does not meet the requirements and upgrading is not feasible, consider these alternatives:
- Remain on Windows 10: Windows 10 will continue to receive security updates until October 2025. You can continue using your current operating system without upgrading.
- Purchase a New Computer: If your system is outdated and upgrading is not possible, consider purchasing a new computer that meets the Windows 11 requirements.
- Use a Virtual Machine: Install Windows 11 within a virtual machine on your current system. This allows you to experience the new operating system without affecting your existing setup.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can I upgrade to Windows 11 without meeting all the requirements?
A: While you may be able to install Windows 11 without meeting all the requirements, it is not recommended. You may encounter performance issues, compatibility problems, and security vulnerabilities.
Q: What happens if I upgrade to Windows 11 and then realize my system doesn’t meet the requirements?
A: You can downgrade back to Windows 10 within 10 days of upgrading. However, this may require a clean installation, which means you will lose all your data.
Q: Is it possible to upgrade a system that doesn’t have a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: Microsoft has released a workaround for systems without a TPM 2.0 chip. However, this is not officially supported and may compromise system security.
Q: Can I use Windows 11 on an older computer?
A: While technically possible, it is not recommended. Older computers may lack the hardware capabilities to run Windows 11 efficiently and securely.
Tips for Smooth Windows 11 Compatibility
- Back Up Your Data: Before upgrading to Windows 11, back up all your important data to an external drive or cloud storage. This will ensure data protection in case of any issues during the upgrade process.
- Check for System Updates: Make sure your Windows 10 installation is up to date before attempting to upgrade.
- Run System Diagnostics: Use the built-in system diagnostics tools to check for hardware and software issues that could affect compatibility.
- Review System Requirements: Carefully review the Windows 11 system requirements to ensure your system meets them.
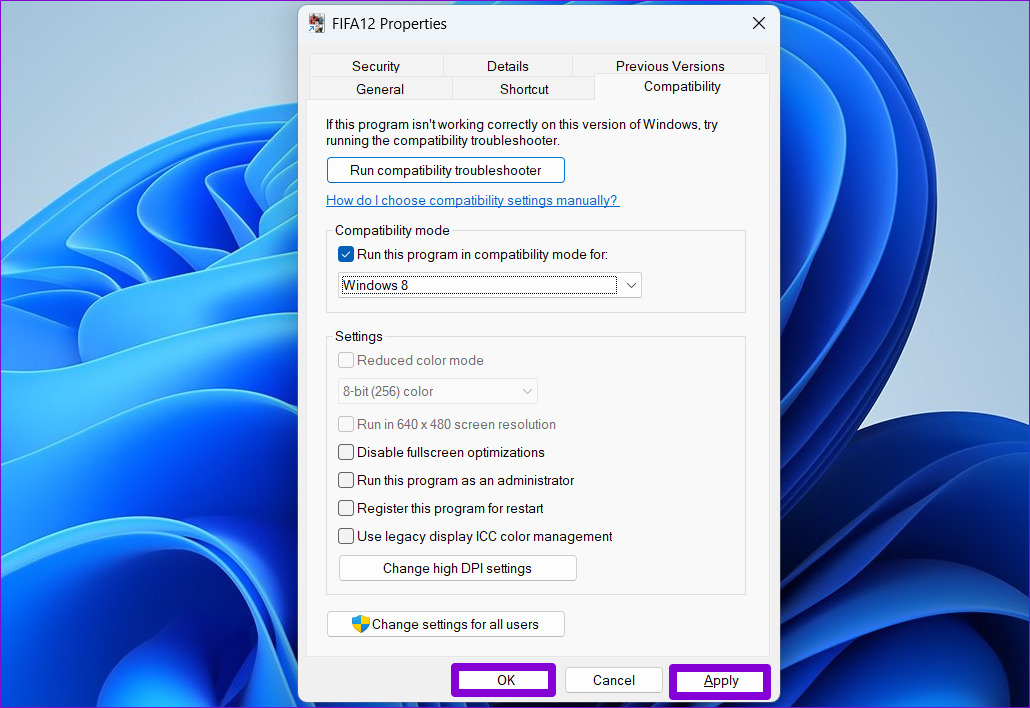
- Consider a Clean Installation: If you encounter compatibility issues, consider a clean installation of Windows 11. This involves formatting the hard drive and installing the operating system from scratch.
Conclusion
Windows 11 offers a modern, streamlined experience with enhanced security and features. However, its compatibility requirements can be a barrier for some users. By understanding the key factors, identifying potential issues, and implementing troubleshooting steps, users can ensure a smooth transition to Windows 11. If upgrading is not feasible, exploring alternatives such as remaining on Windows 10, purchasing a new computer, or using a virtual machine can provide viable options. By taking a proactive approach to compatibility, users can embrace the benefits of Windows 11 while ensuring a seamless and secure computing experience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 11 Compatibility: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply