Navigating The World Of SD Cards In Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide To FAT32
Navigating the World of SD Cards in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to FAT32
Related Articles: Navigating the World of SD Cards in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to FAT32
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of SD Cards in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to FAT32. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of SD Cards in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to FAT32

The ubiquitous SD card, a cornerstone of portable storage, plays a vital role in our digital lives. From capturing memories on cameras to storing documents and files, SD cards offer a convenient and reliable way to move data across devices. Windows 11, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s operating system, seamlessly integrates with these cards, ensuring a smooth and efficient data transfer experience.
This article delves into the intricacies of interacting with SD cards formatted in the FAT32 file system within the Windows 11 environment. We will explore the inherent advantages of FAT32, unravel the process of reading and accessing data on these cards, and address common queries and troubleshooting tips.
Understanding FAT32: A Legacy of Compatibility
The File Allocation Table (FAT) file system, introduced with the early versions of MS-DOS, has evolved through various iterations, including FAT16 and FAT32. While newer file systems like NTFS offer enhanced features and larger storage capacity, FAT32 remains a ubiquitous choice due to its widespread compatibility.
Here’s why FAT32 continues to hold relevance in the modern computing landscape:
- Broad Compatibility: FAT32 is supported by a vast array of devices, including cameras, smartphones, gaming consoles, and older operating systems. This universal acceptance makes it ideal for sharing files across diverse platforms.
- Simplicity and Efficiency: The FAT32 file system is known for its straightforward structure, which translates into efficient data access and minimal overhead. This simplicity contributes to its reliability and performance.
- Accessibility: FAT32 is readily recognized by Windows 11, requiring minimal configuration for data access. This ease of use makes it a user-friendly choice for everyday storage needs.
Reading SD Cards in Windows 11: A Straightforward Process
Accessing data stored on a FAT32 formatted SD card in Windows 11 is remarkably simple. The operating system automatically recognizes the card upon insertion, presenting it as a drive letter in the File Explorer window.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to reading data from an SD card:
- Insert the SD card: Carefully insert the SD card into the SD card reader of your computer.
- Identify the drive letter: Windows 11 will automatically assign a drive letter to the SD card, typically denoted as "D:" or "E:" depending on the existing drives connected to your system.
- Access the data: Open File Explorer (Windows key + E) and navigate to the designated drive letter. You will see the folders and files stored on the SD card, allowing you to browse, copy, move, or delete them as needed.
Addressing Common Queries and Troubleshooting Tips
While the process of reading SD cards in Windows 11 is generally straightforward, users may encounter occasional issues. Here are some common queries and their solutions:
1. SD card not detected:
- Check the physical connection: Ensure the SD card is properly inserted into the card reader.
- Verify the card reader: If the card reader is malfunctioning, try using a different one.
- Restart your computer: A simple restart can sometimes resolve connectivity issues.
- Run a hardware troubleshooter: Windows 11 offers built-in troubleshooting tools that can diagnose and fix hardware problems.
2. SD card is read-only:
- Check the write protection switch: Some SD cards have a physical write protection switch. Ensure it is not engaged, allowing write access to the card.
- Format the card: Formatting the SD card will erase all data but may resolve write protection issues. However, this should be done as a last resort, as it results in data loss.
- Run a disk check: Use the "chkdsk" command in the Command Prompt to check for file system errors and potentially resolve write protection issues.
3. SD card is corrupted:
- Run a disk check: Use the "chkdsk" command to scan the card for errors and attempt repair.
- Use data recovery software: If the card is corrupted, specialized data recovery software can attempt to recover lost data.
- Replace the SD card: If the card is beyond repair, consider replacing it with a new one.
4. Slow performance:
- Ensure sufficient free space: A full SD card can lead to performance degradation. Free up space by deleting unnecessary files.
- Defragment the card: Defragmentation can improve read/write speeds by organizing data more efficiently.
- Use a high-speed card reader: Consider using a faster card reader for enhanced performance.
5. Data transfer errors:
- Ensure sufficient free space on the destination drive: Ensure there is enough space on the target drive to accommodate the files being transferred.
- Check for viruses: Scan both the source and destination drives for viruses to rule out any potential interference.
- Restart your computer: A simple restart can sometimes resolve data transfer errors.
Conclusion: Seamless Integration for Enhanced Data Management
Windows 11 provides a seamless and user-friendly experience for interacting with SD cards formatted in FAT32. The operating system’s automatic recognition and intuitive file management tools empower users to effortlessly access, manage, and transfer data. By understanding the nuances of FAT32 and the troubleshooting tips outlined in this article, users can confidently navigate the world of SD cards within the Windows 11 environment.
![[4+] Format SD Card FAT32 in Windows 11 with Free Software](https://www.resize-c.com/img/howto/format-fat32-windows-dispart.gif)
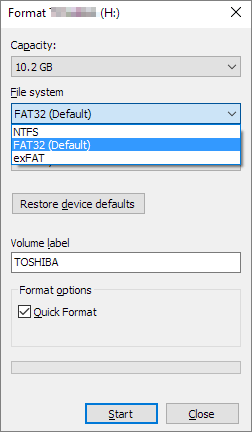
![[4+] Format SD Card FAT32 in Windows 11 with Free Software](https://www.resize-c.com/img/howto/format-sd-card-fat32.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/win3-a7202d9dac2942f6812bb9c8b3069f4a-66da1bc0d20048e494867dbe64fbfb0c.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of SD Cards in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide to FAT32. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply