Navigating The Ext4 Filesystem On Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the Ext4 Filesystem on Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Ext4 Filesystem on Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Ext4 Filesystem on Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Ext4 Filesystem on Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
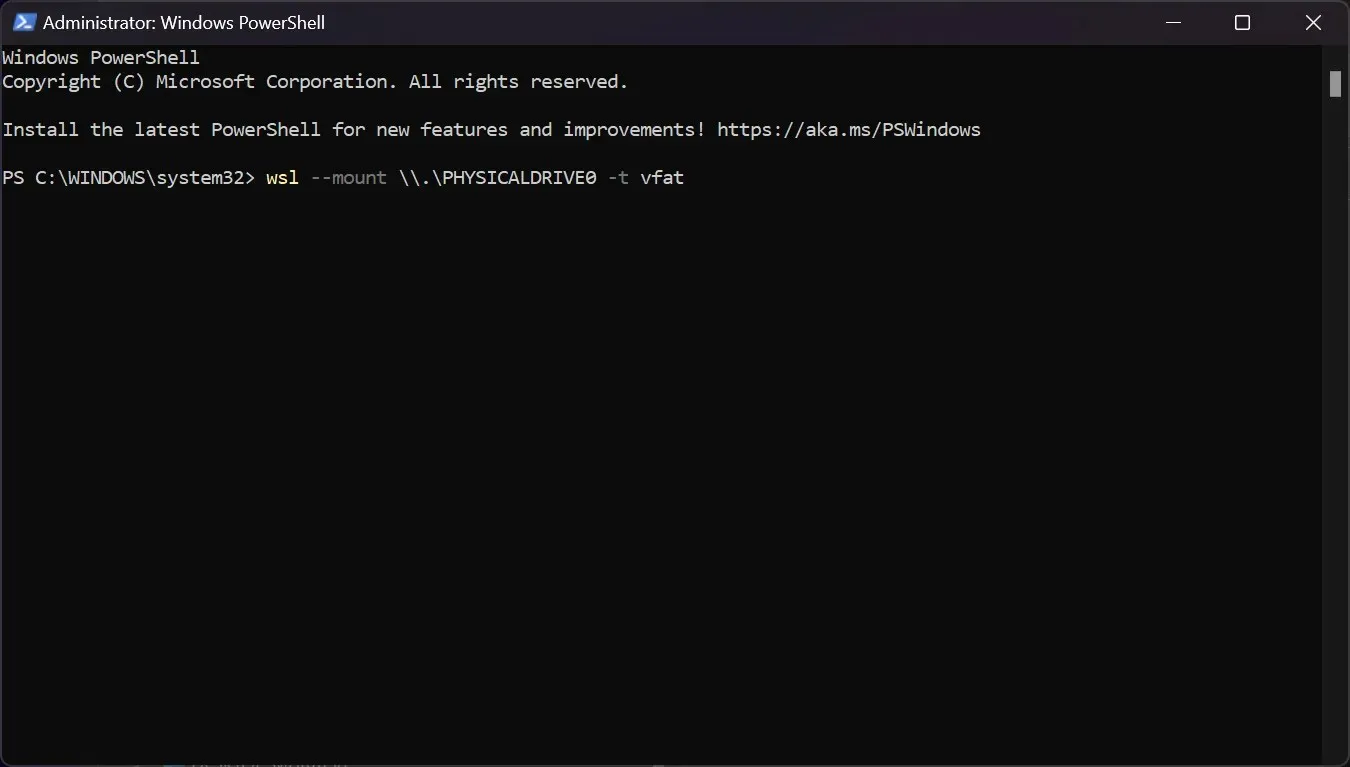
Windows 11, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s operating system, is renowned for its user-friendliness and compatibility with a wide array of hardware and software. However, its native file system, NTFS, is not universally recognized by other operating systems, particularly Linux distributions. This presents a challenge when users need to access data stored on Linux-formatted drives, often formatted with the Ext4 filesystem, within the Windows environment.
Ext4, the fourth generation of the Extended Filesystem, is the default filesystem for most contemporary Linux distributions. It boasts features like journaling, advanced metadata handling, and robust error recovery mechanisms, making it a reliable choice for storing vast amounts of data. While Windows 11 does not natively support Ext4, there are several methods to enable read and write access to Ext4 partitions, unlocking the potential for seamless data exchange between Windows and Linux systems.
Understanding the Ext4 Filesystem
Before delving into the intricacies of accessing Ext4 drives on Windows 11, it is essential to understand the fundamental differences between Ext4 and NTFS.
-
NTFS (New Technology File System): Developed by Microsoft, NTFS is the primary filesystem used in Windows operating systems. It is known for its robust security features, efficient file allocation, and support for large file sizes. However, it is not widely compatible with other operating systems.
-
Ext4 (Extended Filesystem): Developed for Linux, Ext4 is a journaling filesystem designed for high performance and reliability. It offers advanced features like file system quotas, delayed allocation, and extensive metadata capabilities. Its compatibility with Windows is limited, requiring specific software solutions.
Methods for Accessing Ext4 Partitions on Windows 11
The ability to read and write data on Ext4 partitions from Windows 11 can be achieved through various approaches, each with its own advantages and limitations:
-
Third-Party Software: Numerous third-party applications are available for Windows that provide read/write access to Ext4 partitions. These solutions often leverage drivers and libraries to bridge the compatibility gap between the two file systems. Some popular options include:
- Ext2Fsd: This free and open-source driver allows read/write access to Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4 filesystems. It is a reliable and widely used solution.
- Ext4 IFS: This commercial software offers a more comprehensive solution, providing advanced features like file system analysis and repair capabilities.
- Paragon ExtFS: Another commercial option, Paragon ExtFS provides a user-friendly interface for accessing Ext4 partitions. It also includes features like data recovery and disk management.
-
Dual Boot Setup: Installing a Linux distribution alongside Windows 11 provides a more direct and robust method to access Ext4 partitions. This approach allows you to boot into either operating system, providing native access to the respective file systems. This option requires partitioning your hard drive and installing the chosen Linux distribution.
-
Virtual Machine Environments: Utilizing a virtual machine (VM) like VirtualBox or VMware allows you to run a Linux distribution within the Windows environment. This approach provides a sandboxed environment for accessing Ext4 partitions within the Linux VM, without directly interacting with the Windows filesystem.
Choosing the Right Method
The optimal approach for accessing Ext4 partitions on Windows 11 depends on individual needs and preferences.
- Third-party software: Offers a convenient and straightforward solution for basic read/write access.
- Dual boot: Provides a more direct and robust approach, offering native access to both Windows and Linux filesystems.
- Virtual machine: Offers a safe and isolated environment for running Linux and accessing Ext4 partitions without affecting the Windows system.
Benefits of Accessing Ext4 Partitions on Windows 11
Enabling read and write access to Ext4 partitions on Windows 11 opens up a world of possibilities for users:
- Data Transfer: Seamlessly transfer files between Windows and Linux systems, facilitating data exchange between different operating environments.
- Cross-Platform Collaboration: Work on projects that utilize applications or data stored on both Windows and Linux systems, fostering collaboration between users of different operating systems.
- Accessing Linux Distributions: Utilize Linux distributions on Windows, taking advantage of their unique features and software libraries.
- Data Recovery: Recover data from damaged or corrupted Ext4 partitions, utilizing tools and utilities available within the Linux environment.
FAQs Regarding Accessing Ext4 Partitions on Windows 11
Q: Is it safe to access Ext4 partitions on Windows 11?
A: Accessing Ext4 partitions on Windows 11 is generally safe, provided you use reliable and reputable software solutions. However, it is crucial to choose software from trusted sources and avoid suspicious or untrusted applications.
Q: Can I format an Ext4 partition on Windows 11?
A: Windows 11 does not natively support formatting Ext4 partitions. You need to use specific tools available within Linux distributions or third-party software designed for this purpose.
Q: What are the potential risks of accessing Ext4 partitions on Windows 11?
A: The primary risk lies in using unreliable or poorly developed software that could potentially damage the Ext4 partition or corrupt data. Always ensure you use trusted and reputable software solutions.
Q: Can I use Ext4 partitions for storing Windows system files?
A: It is not recommended to store Windows system files on an Ext4 partition. Windows relies on NTFS for its core functionality, and attempting to install or run Windows from an Ext4 partition could lead to instability and system errors.
Tips for Accessing Ext4 Partitions on Windows 11
- Choose reputable software: Opt for well-established and trusted software solutions from reputable developers.
- Backup your data: Before attempting to access or modify Ext4 partitions, ensure you have a reliable backup of your data to prevent potential data loss.
- Understand the risks: Be aware of the potential risks involved in accessing foreign file systems, and use caution when working with Ext4 partitions on Windows 11.
- Consult documentation: Refer to the documentation of the chosen software solution for detailed instructions and troubleshooting information.
Conclusion
Accessing Ext4 partitions on Windows 11 offers a valuable bridge between the two operating systems, enabling seamless data exchange and enhancing cross-platform compatibility. By understanding the different methods and choosing the appropriate solution based on individual needs, users can unlock the potential of Ext4 partitions within the Windows environment. Remember to exercise caution, utilize reliable software, and prioritize data backup to ensure a safe and successful experience.
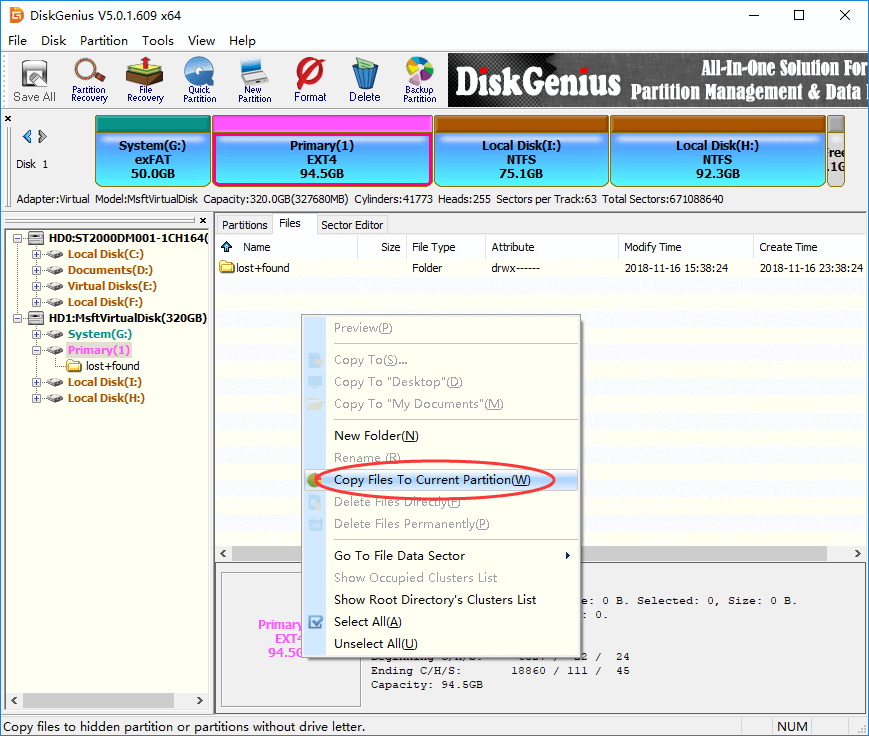
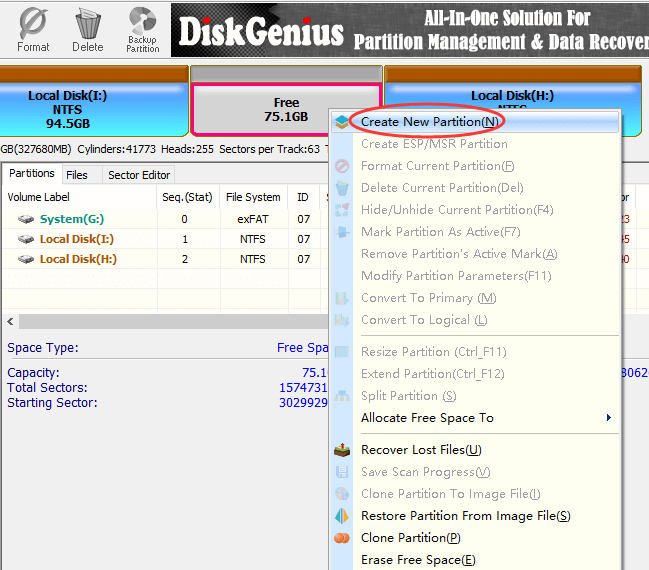
![How to Mount, Read, or Format EXT4 on Windows 11 [2024 Guide]](https://cdn.windowsreport.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/ext4-windows-11-886x590.jpg)
![How to Access and Read EXT4 Partition and Data on Windows 11/10 [2024 Updated]](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/mount-ext4-on-windows-via-ext2fsd.jpg)
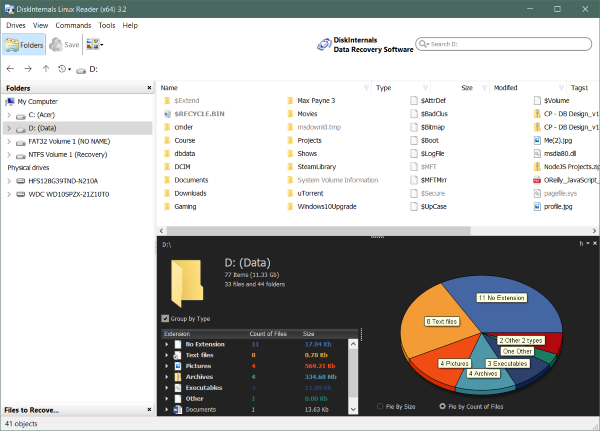
![How to Access and Read EXT4 Partition and Data on Windows 11/10 [2024 Updated]](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/mount-ext4-on-windows-via-diskinternal-linux-reader-2.jpg)
![How to Access and Read EXT4 Partition and Data on Windows 11/10 [2024 Updated]](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/mount-ext4-on-windows-via-ext2explore-2.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Ext4 Filesystem on Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply