Connecting Computers In A Network: A Comprehensive Guide
Connecting Computers in a Network: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Connecting Computers in a Network: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Connecting Computers in a Network: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Connecting Computers in a Network: A Comprehensive Guide
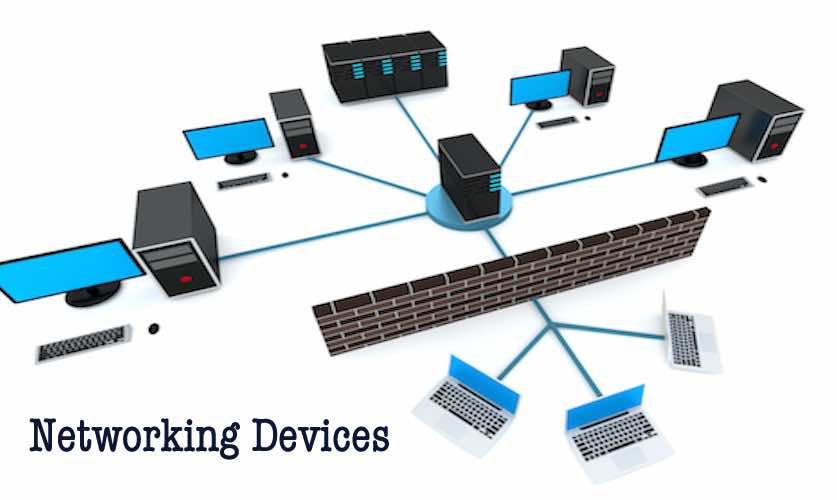
Connecting computers in a network, often referred to as networking, is the foundation of modern communication and collaboration. It enables seamless sharing of resources, data, and information, fostering efficiency and productivity in various settings, from homes and offices to large-scale organizations. This guide delves into the intricacies of network connectivity, exploring its key components, benefits, and considerations.
Understanding Network Fundamentals
A network is essentially a group of interconnected devices, such as computers, servers, printers, and mobile devices, that can communicate with each other. This communication is facilitated through a shared communication channel, typically a physical cable or wireless signal.
Network Topologies: The Structure of Connectivity
The arrangement of devices within a network, known as the network topology, defines how they are connected. Several common topologies exist:
- Bus Topology: A linear structure where all devices share a single cable. While simple to implement, it can be prone to performance issues if many devices are connected.
- Star Topology: A centralized structure where all devices connect to a central hub or switch. This offers enhanced reliability and scalability, making it a popular choice for modern networks.
- Ring Topology: A circular structure where data flows in one direction. This topology is less common due to its complexity and potential for single-point failures.
- Mesh Topology: A highly connected structure where each device connects to multiple others. This offers high redundancy and fault tolerance but can be expensive and complex to implement.
Network Protocols: The Language of Communication
Network protocols are sets of rules that govern how devices communicate with each other. They ensure data is transmitted and received correctly, preventing errors and conflicts. Common network protocols include:
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): The foundation of the internet, TCP/IP defines how data is packaged, addressed, and routed across networks.
- Ethernet: The most prevalent wired network protocol, Ethernet governs data transmission over copper cables.
- Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity): A widely used wireless protocol, Wi-Fi allows devices to connect to networks without physical cables.
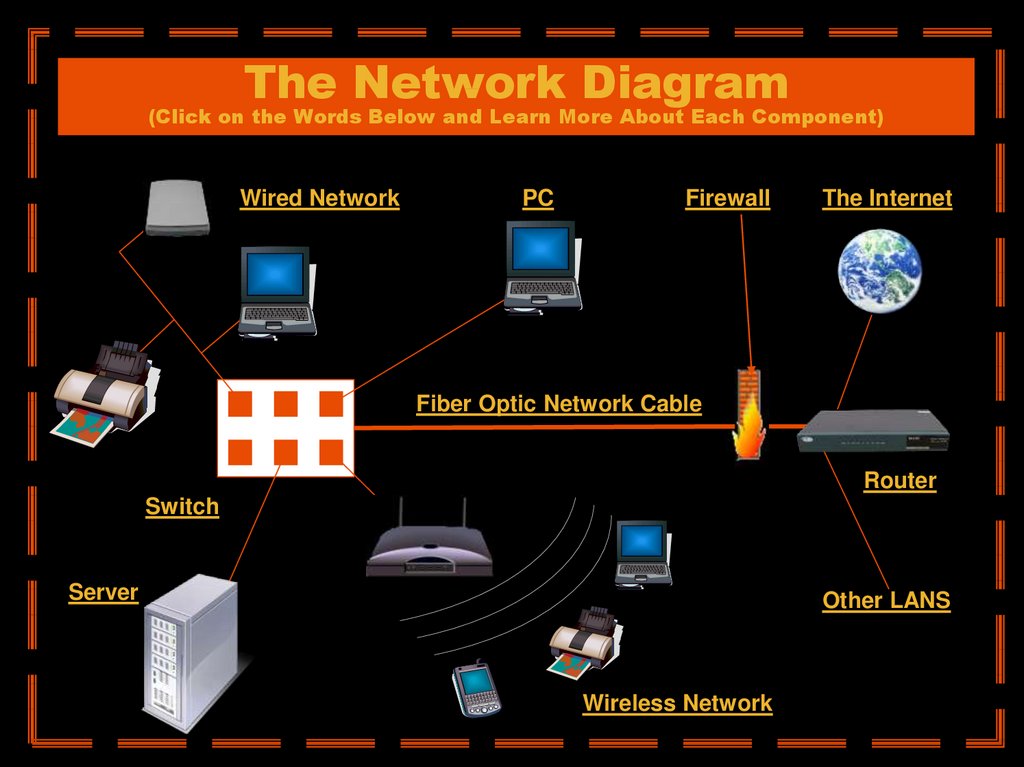
Network Components: The Building Blocks of Connectivity
Several essential components contribute to a functional network:
- Network Interface Card (NIC): A physical component that connects a device to the network.
- Hub: A simple device that connects multiple devices to a network, but does not provide any intelligence or collision avoidance.
- Switch: An intelligent device that forwards data only to the intended recipient, improving performance and security.
- Router: A device that connects different networks, enabling communication between them.
- Firewall: A security device that protects a network from unauthorized access.
Benefits of Connecting Computers in a Network
Connecting computers in a network offers numerous advantages:
- Resource Sharing: Networks facilitate the sharing of resources like printers, scanners, and files, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Data Collaboration: Networked computers allow users to collaborate on projects, share documents, and work on the same data simultaneously.
- Communication Enhancement: Networks provide a platform for real-time communication through email, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
- Centralized Management: Networks allow administrators to manage and control multiple computers from a central location, simplifying maintenance and updates.
- Improved Security: Network security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, can protect data and devices from unauthorized access.
Connecting Computers: A Practical Guide
Connecting computers in a network involves several steps:
- Network Configuration: Configure network settings on each device, including IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
- Physical Connection: Connect devices to the network using cables or wireless signals.
- Network Testing: Verify connectivity between devices and test network performance.
- Security Implementation: Implement security measures, such as firewalls and password protection, to safeguard the network.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the different types of network connections?
A: Network connections can be wired or wireless. Wired connections use physical cables, such as Ethernet cables, while wireless connections utilize radio waves, such as Wi-Fi.
Q: How do I choose the right network topology for my needs?
A: The best network topology depends on the size and complexity of the network, the desired level of reliability, and the budget.
Q: What are the security risks associated with networks?
A: Networks are vulnerable to security threats like malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. Implementing robust security measures is crucial to mitigate these risks.
Q: How do I troubleshoot network problems?
A: Network troubleshooting involves identifying the source of the problem, such as a faulty cable, incorrect settings, or network congestion.
Tips for Connecting Computers in a Network
- Plan the network carefully: Determine the size and purpose of the network, the devices to be connected, and the required security measures.
- Choose the right hardware: Select appropriate network devices, such as routers, switches, and NICs, based on the network’s needs.
- Implement strong security: Use firewalls, password protection, and other security measures to protect the network from threats.
- Regularly monitor and maintain the network: Monitor network performance, update software, and address security vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Connecting computers in a network is a fundamental aspect of modern technology, enabling seamless communication, resource sharing, and data collaboration. Understanding the principles of network connectivity, including its components, protocols, and topologies, empowers individuals and organizations to leverage the benefits of networking effectively. By implementing robust security measures, optimizing network performance, and staying informed about evolving technologies, individuals can ensure a secure, efficient, and productive network environment.

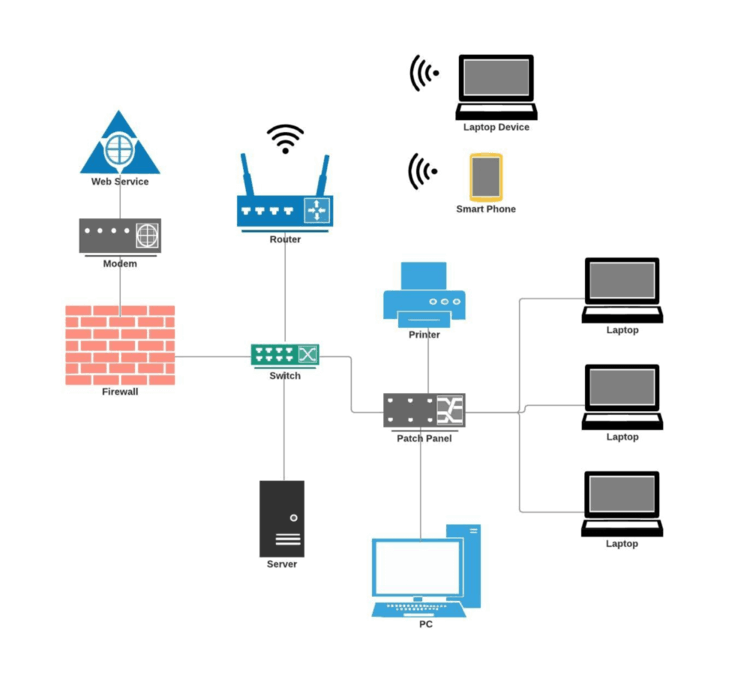
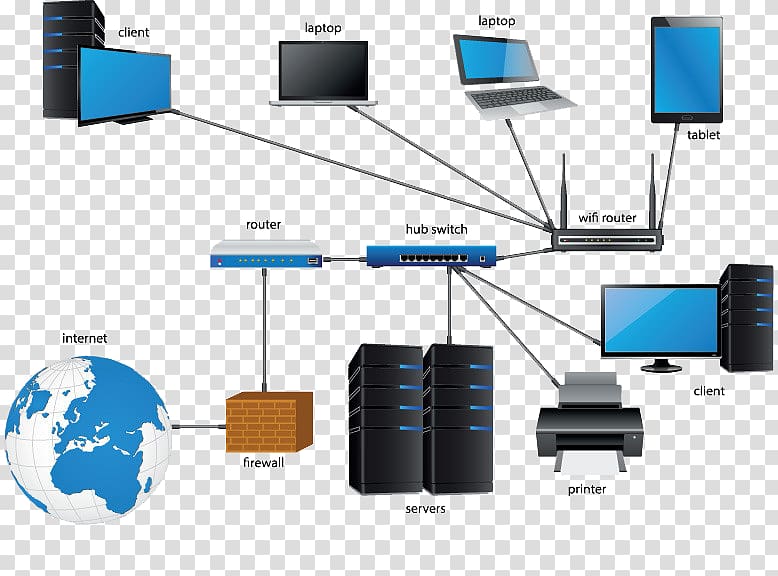



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Connecting Computers in a Network: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
Leave a Reply