The Enigma Of The Missing 5G Wi-Fi Signal: A Comprehensive Guide To Troubleshooting
The Enigma of the Missing 5G Wi-Fi Signal: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting
Related Articles: The Enigma of the Missing 5G Wi-Fi Signal: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Enigma of the Missing 5G Wi-Fi Signal: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enigma of the Missing 5G Wi-Fi Signal: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting

The advent of 5G technology has ushered in a new era of wireless connectivity, promising blazing-fast speeds and enhanced reliability. However, the frustration of a missing 5G Wi-Fi signal can be a significant obstacle to enjoying these benefits. This article delves into the common causes behind this issue, providing a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting and resolving it.
Understanding the Fundamentals of 5G Wi-Fi
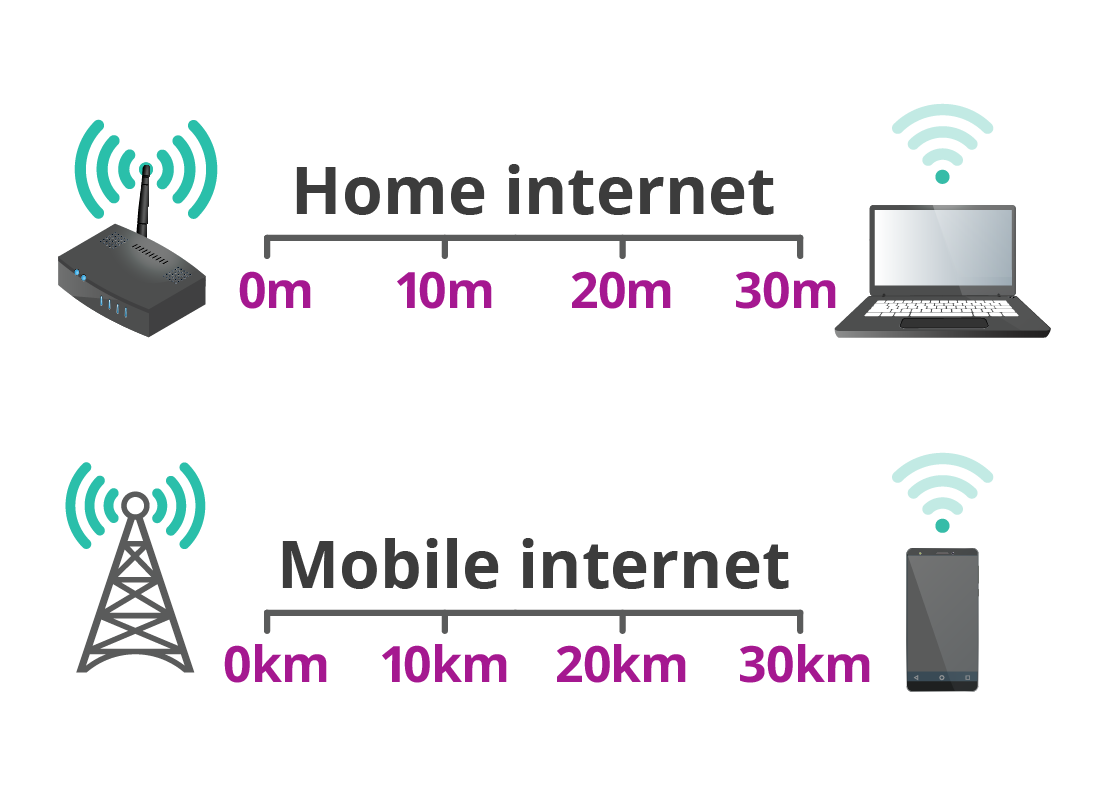
Before embarking on troubleshooting, it’s essential to grasp the basics of 5G Wi-Fi. 5G Wi-Fi, also known as Wi-Fi 6E, operates on the 6 GHz frequency band, offering several advantages over traditional 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi:
- Increased Bandwidth: The 6 GHz band provides significantly more bandwidth, allowing for faster data transfer rates and smoother streaming experiences.
- Reduced Interference: Operating on a less congested frequency band minimizes interference from other devices, leading to a more stable connection.
- Lower Latency: 5G Wi-Fi boasts lower latency, crucial for real-time applications like online gaming and video conferencing.
The Missing 5G Wi-Fi Signal: Common Culprits
The absence of a 5G Wi-Fi signal can stem from a variety of factors, each requiring a specific approach to resolution:
1. Compatibility Issues:
- Device Compatibility: Not all devices support 5G Wi-Fi. Older devices or those lacking the necessary hardware may not be able to detect or connect to 6 GHz networks.
- Router Compatibility: Ensure your router is capable of broadcasting 5G Wi-Fi. Check the router’s specifications or documentation to confirm its compatibility.
2. Network Settings:
- Hidden Network: Some routers allow users to hide their Wi-Fi network. If the 5G network is hidden, it won’t be visible to devices attempting to connect.
- Incorrect SSID: The 5G network might have a different SSID than the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz network. Verify the SSID in your router settings and ensure it’s correctly entered in your device’s Wi-Fi settings.
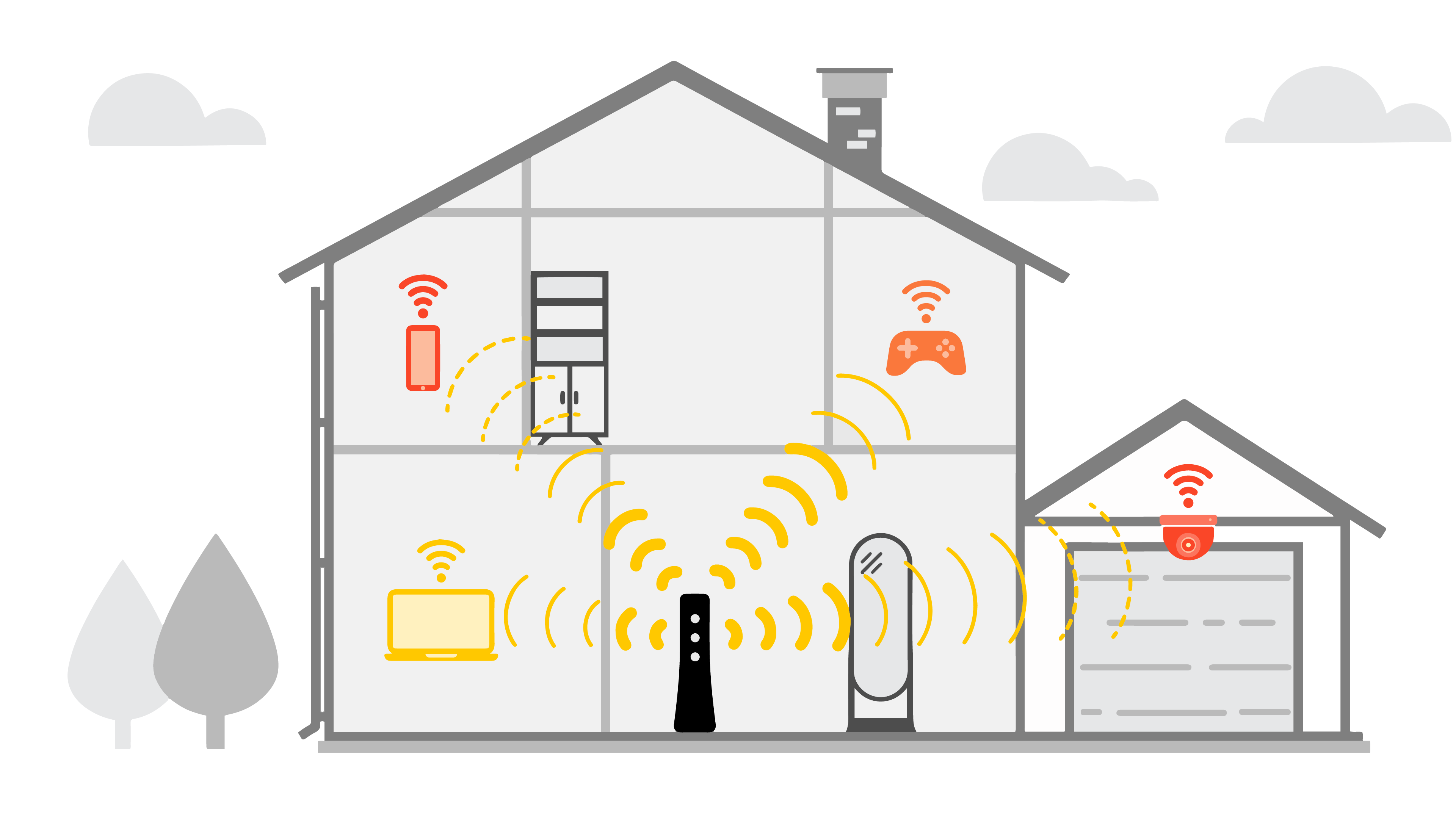
3. Physical Limitations:
- Distance: The 6 GHz frequency band has a shorter range than 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz. Ensure your device is within close proximity to the router.
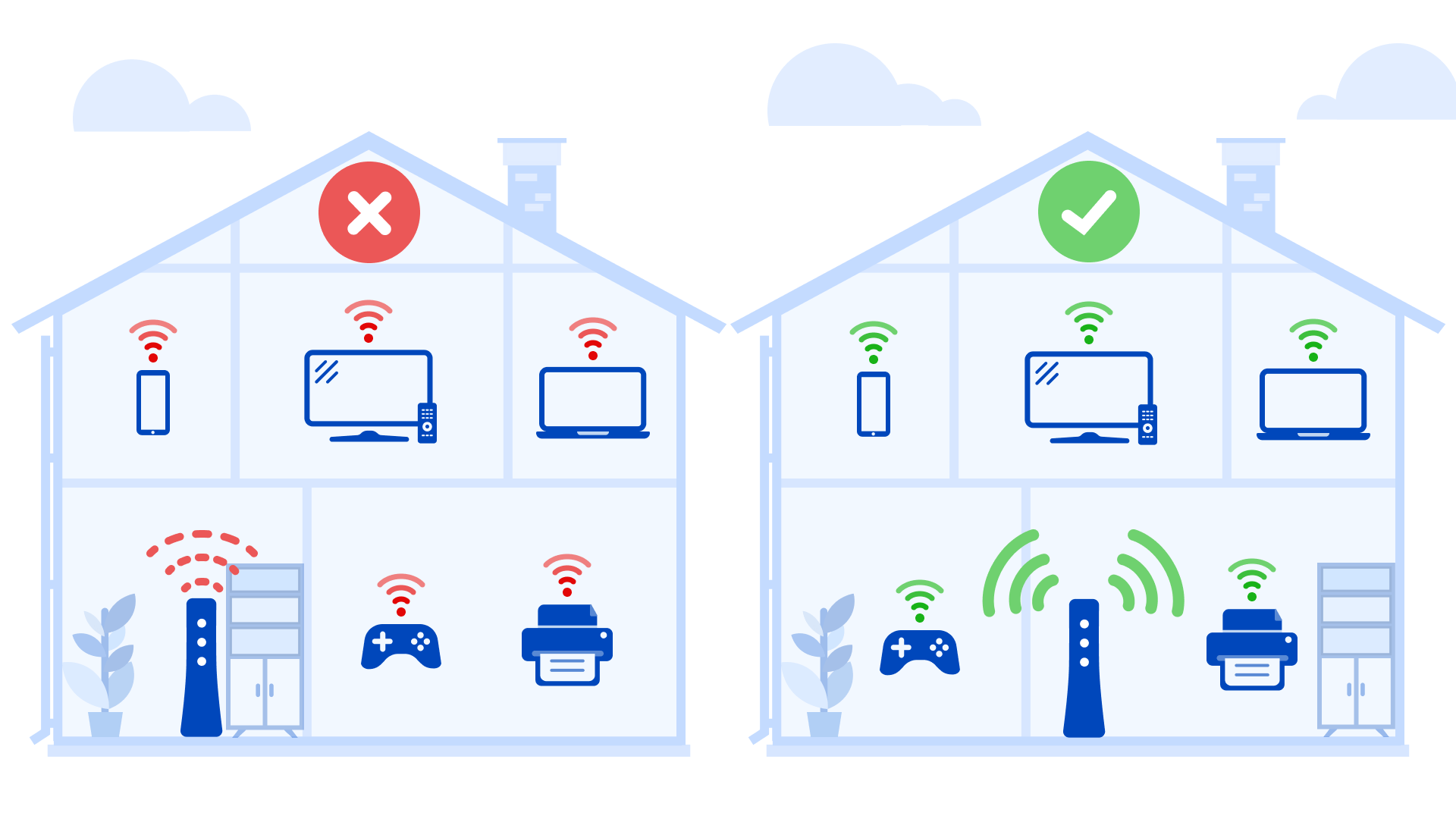
- Obstacles: Walls, furniture, and other objects can obstruct the 6 GHz signal. Consider relocating your router or device to minimize interference.
4. Router Configuration:
- Disabled 5G Network: Check your router settings to ensure the 5G network is enabled. It might be disabled by default or accidentally turned off.
- Channel Congestion: The 6 GHz band is divided into multiple channels. If the channel selected for your 5G network is congested, it can impact signal strength and visibility.
5. Software and Firmware Issues:
- Outdated Drivers: Ensure your device’s Wi-Fi drivers are up-to-date. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues and prevent the detection of 5G networks.
- Outdated Router Firmware: Similarly, outdated router firmware can hinder 5G functionality. Update your router’s firmware to the latest version.
Troubleshooting and Resolution Strategies
Once you have identified the potential cause of the missing 5G Wi-Fi signal, you can implement the following troubleshooting steps:
1. Verify Device Compatibility:
- Check the device’s specifications or user manual to confirm 5G Wi-Fi support.
- If the device is compatible, ensure the Wi-Fi settings are properly configured to scan for 6 GHz networks.
2. Verify Router Compatibility:
- Consult the router’s documentation or manufacturer website to confirm 5G Wi-Fi capabilities.
- If the router supports 5G, ensure it’s enabled in the router’s settings.
3. Check Network Settings:
- Access your router’s settings and verify that the 5G network is not hidden.
- Check the SSID of the 5G network and ensure it matches the one displayed in your device’s Wi-Fi settings.
4. Optimize Physical Environment:
- Relocate your router or device to minimize distance and obstacles obstructing the signal.
- Consider using a Wi-Fi extender to boost the signal in areas with weak coverage.
5. Update Drivers and Firmware:
- Download and install the latest Wi-Fi drivers for your device.
- Update your router’s firmware to the latest version available from the manufacturer’s website.
6. Reset Router Settings:
- If all else fails, try resetting your router to factory defaults. This will erase all custom settings and potentially resolve any configuration issues.
7. Contact Technical Support:
- If you’ve exhausted all troubleshooting options, contact your internet service provider or router manufacturer for technical assistance.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: What if my device doesn’t support 5G Wi-Fi?
A: If your device lacks 5G Wi-Fi support, you can still connect to the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz networks offered by your router. However, you won’t be able to experience the benefits of 5G connectivity. Consider upgrading to a newer device that supports 5G Wi-Fi.
Q: Why is my 5G network so slow?
A: Slow 5G speeds can be caused by various factors, including network congestion, interference, or outdated hardware. Check your router’s settings to ensure the 5G network is using a less congested channel. Also, ensure your device’s Wi-Fi drivers and router firmware are up-to-date.
Q: Can I use 5G Wi-Fi with my older router?
A: Older routers may not support 5G Wi-Fi. Consider upgrading to a newer router that supports 6 GHz connectivity to enjoy the benefits of 5G.
Tips for Optimizing 5G Wi-Fi Performance
- Minimize Interference: Place your router in an open area, away from other electronic devices that might cause interference.
- Use a Wired Connection: For tasks requiring high bandwidth and low latency, consider using a wired Ethernet connection for optimal performance.
- Prioritize Devices: Some routers allow you to prioritize devices on the network, ensuring higher bandwidth for critical applications.
- Enable QoS (Quality of Service): QoS settings in your router can help prioritize traffic for specific applications, improving performance for demanding tasks.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Wireless Connectivity
The absence of a 5G Wi-Fi signal can be a frustrating experience, but by understanding the potential causes and implementing the appropriate troubleshooting steps, you can resolve this issue and unlock the full potential of 5G connectivity. By embracing the advancements in wireless technology, you can enjoy faster speeds, reduced latency, and a more reliable internet experience, transforming your digital world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enigma of the Missing 5G Wi-Fi Signal: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!




![How to Reset Windows 11? [Step-by-Step Guide] - MiniTool Partition Wizard](https://www.partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/articles/2021/07/how-to-reset-windows-11/how-to-reset-windows-11-3.png)

![How to Reset Windows 11? [Step-by-Step Guide] - MiniTool Partition Wizard](https://www.partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/articles/2021/07/how-to-reset-windows-11/how-to-reset-windows-11-2.png)

![How to Reset Windows 11? [Step-by-Step Guide] - MiniTool Partition Wizard](https://www.partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/articles/2021/07/how-to-reset-windows-11/how-to-reset-windows-11-8.png)










.png)







![[Detailed Guide] How to Install Windows 11 on Your PC or Laptop](https://geekermag.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Windows-11-notification-area.png)










![Microsoft Windows 10 Preview - Quick look - What's new? [HD][Guide] 2023 - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/BnvaFpaduIE/maxresdefault.jpg)