Navigating The BIOS: A Comprehensive Guide To Windows 11 Boot Settings
Navigating the BIOS: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Boot Settings
Related Articles: Navigating the BIOS: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Boot Settings
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the BIOS: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Boot Settings. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the BIOS: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Boot Settings
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is the fundamental software that governs your computer’s hardware operations. It is the first program your computer runs when you turn it on, initializing and testing components before handing control over to the operating system. While most users interact with the BIOS only occasionally, understanding its functions and how to access it can be invaluable for troubleshooting issues, optimizing performance, and customizing your system.
Accessing the BIOS in Windows 11
Accessing the BIOS on a Windows 11 system is typically achieved during the boot process. This involves entering a specific key sequence, often a function key like F2, F10, or Delete, immediately after powering on the computer. The exact key combination varies depending on the motherboard manufacturer and model.
Methods for Entering the BIOS:
- During Boot: As the computer starts, pay close attention to the initial screen displaying the manufacturer’s logo or system information. This screen often includes a prompt indicating the key to press to enter the BIOS. The message may appear briefly, so be prepared to act quickly.
- Using the Boot Menu: Some computers provide a boot menu that allows you to select various boot options, including entering the BIOS. This menu is typically accessed by pressing a key like F8, F11, or Esc during the boot process.
- Through the Windows Settings: In Windows 11, navigate to Settings > System > Recovery. Under "Advanced startup," select Restart now. This will initiate a blue screen with options, including "Troubleshoot" and "Advanced options." Choose "UEFI Firmware Settings" to access the BIOS.
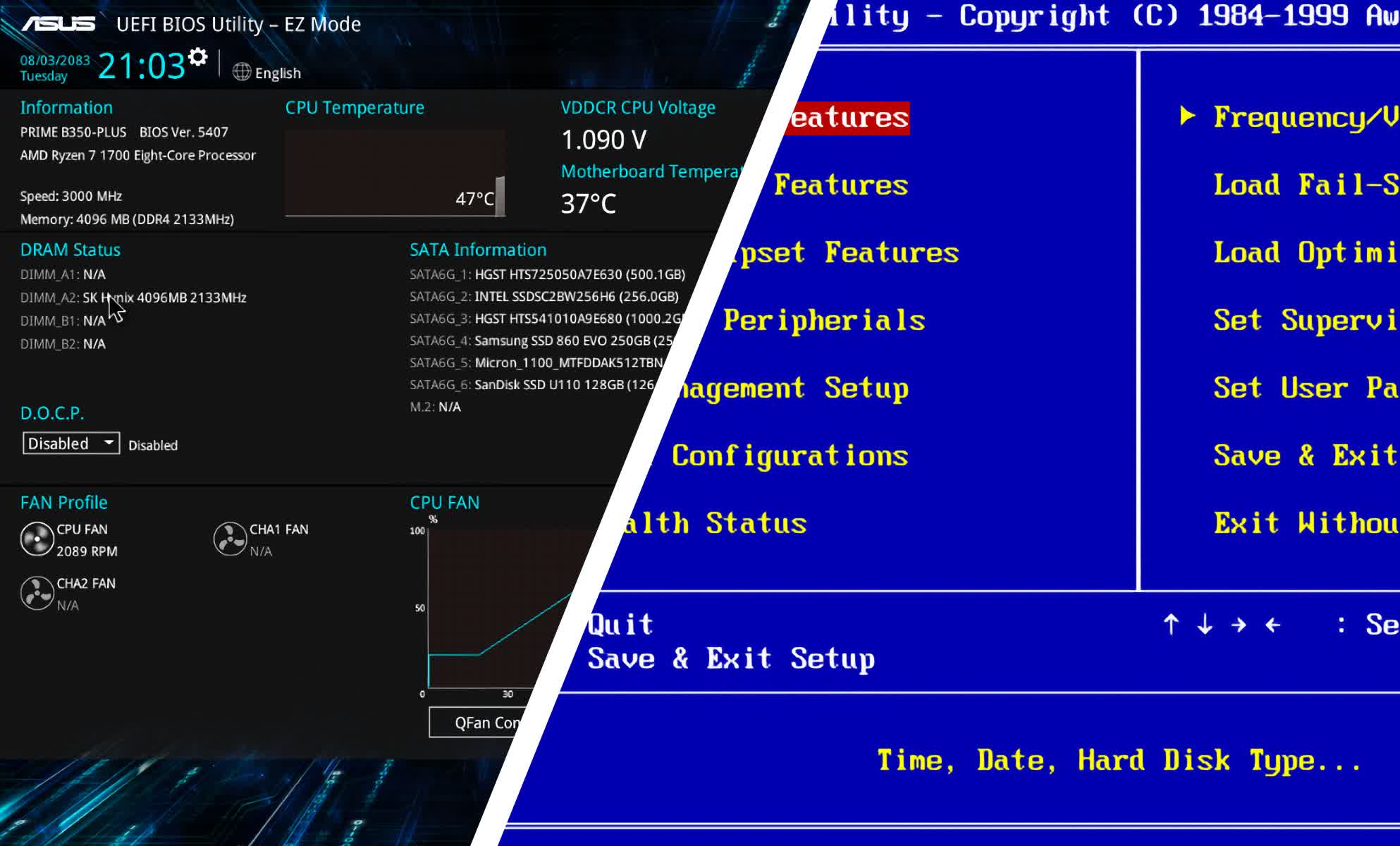
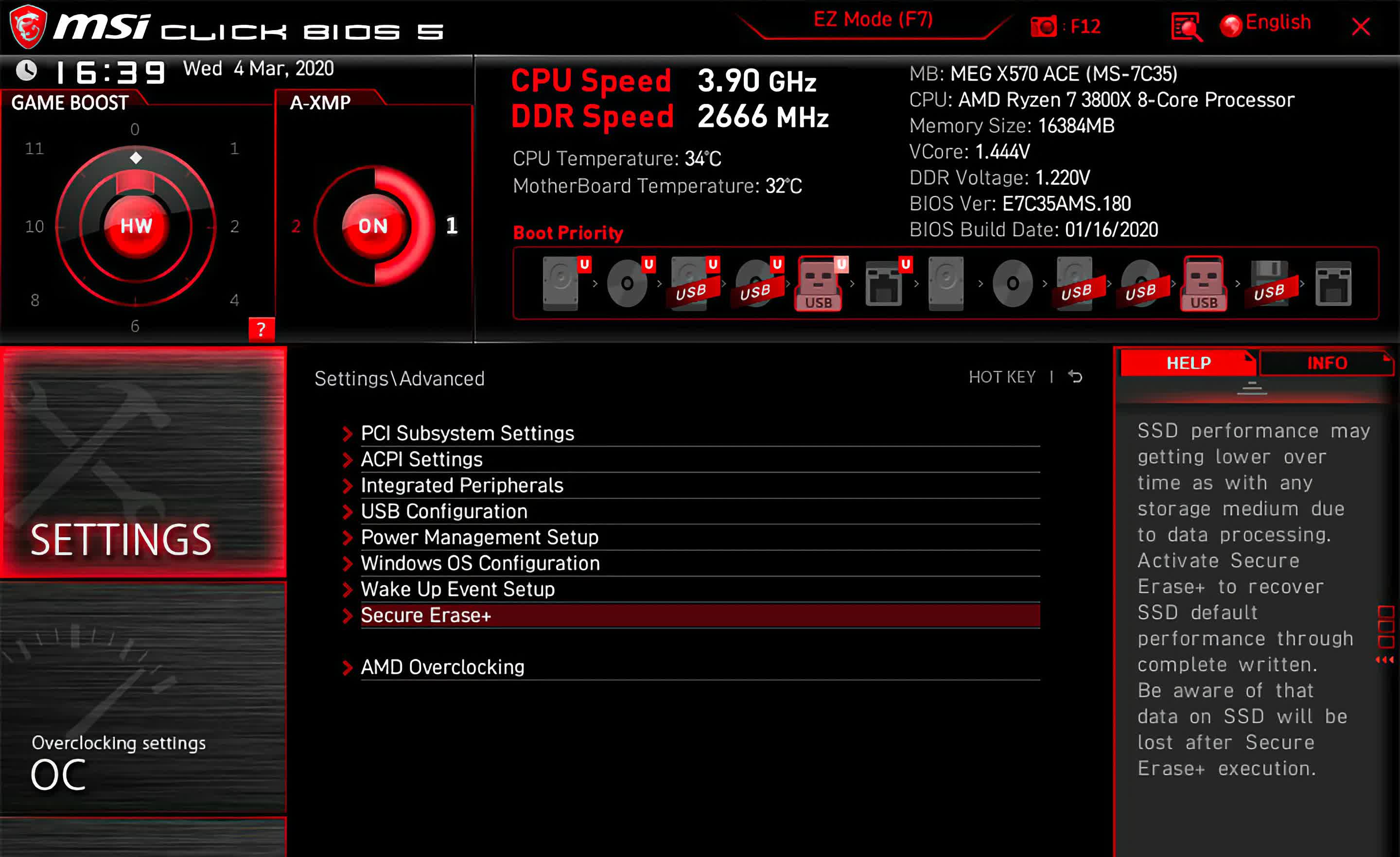
Understanding the BIOS Interface
The BIOS interface is a text-based menu system, often with a blue or black background. It presents various settings categorized into tabs or sections. The specific options and their arrangement may differ between manufacturers. However, common sections include:
- Main: Displays basic system information like the date, time, and boot sequence.
- Advanced: Contains settings related to the CPU, memory, and other hardware components.
- Boot: Manages the boot order, allowing you to prioritize boot devices like hard drives, USB drives, or network drives.
- Security: Enables or disables security features like Secure Boot, which helps prevent malware from loading during startup.
- Exit: Allows you to save changes and exit the BIOS or discard changes and exit.
Key BIOS Settings to Understand:
- Boot Order: This setting determines the order in which the computer searches for a bootable device. Prioritizing a specific drive or USB device can be crucial for installing a new operating system or troubleshooting boot issues.
- Secure Boot: This feature helps protect your computer from malicious software by verifying the digital signature of boot files. Enabling Secure Boot can enhance system security.
- UEFI Mode: The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a modern replacement for the traditional BIOS. It offers a more user-friendly interface, faster boot times, and enhanced security features.
- XMP Profiles: For overclocking enthusiasts, XMP (Extreme Memory Profiles) allow you to automatically configure your RAM for higher performance.
Importance of Navigating the BIOS:
Understanding and navigating the BIOS is crucial for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting Boot Issues: If your computer fails to boot properly, the BIOS can help you identify the cause. You can check the boot order, ensure that the hard drive is detected, or examine other settings that might be interfering with the boot process.
- Installing New Hardware: When installing new hardware, like a hard drive or a graphics card, you may need to adjust BIOS settings to ensure compatibility and proper functioning.
- Overclocking and Performance Tuning: The BIOS allows you to fine-tune various hardware settings, such as the CPU clock speed and memory timing, to enhance system performance. However, overclocking requires careful consideration and should only be attempted by experienced users.
- Security Configuration: The BIOS provides security settings like Secure Boot and password protection, allowing you to enhance your system’s security and prevent unauthorized access.
Navigating the BIOS: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Enter the BIOS: Power on your computer and press the appropriate key combination (F2, F10, Delete, or another key) as indicated on the initial boot screen.
- Navigate the Menus: Use the arrow keys to move between tabs or sections within the BIOS.
- Adjust Settings: Use the arrow keys to select the desired setting and press Enter to modify it. Some settings may require you to use the "+" and "-" keys to adjust values.
- Save Changes: Once you have made the desired changes, navigate to the "Exit" section. Select "Save and Exit" to apply the changes and restart your computer. Alternatively, select "Discard Changes and Exit" to exit without saving.
FAQs on Navigating the BIOS:
Q: What if I accidentally change a BIOS setting and my computer doesn’t boot?
A: If you make changes to the BIOS that prevent your computer from booting, you can usually reset the BIOS to its default settings. Look for an option like "Load Default Settings" or "Factory Reset" within the BIOS menu. This will restore the BIOS to its original configuration, allowing you to boot into the operating system.
Q: Can I change the BIOS settings without knowing what they do?
A: It is generally not recommended to change BIOS settings unless you understand their purpose. Modifying settings without proper knowledge can lead to system instability, hardware damage, or other issues. If you are unsure about a setting, it is best to leave it at its default value.
Q: Should I always enable Secure Boot?
A: Enabling Secure Boot is generally recommended as it enhances system security. However, some older or specialized hardware may not be compatible with Secure Boot. If you experience issues after enabling Secure Boot, you may need to disable it.
Q: How often should I access the BIOS?
A: Most users only need to access the BIOS occasionally. However, if you are installing new hardware, experiencing boot issues, or want to adjust performance settings, you may need to access the BIOS more frequently.
Tips for Navigating the BIOS:
- Read the documentation: Refer to the motherboard manual or manufacturer’s website for detailed information about specific BIOS settings and their functionality.
- Use caution: Avoid making changes to BIOS settings unless you are confident about their purpose and potential consequences.
- Backup your BIOS settings: Before making any significant changes, consider backing up your current BIOS settings. This allows you to easily restore them if necessary.
- Seek help if needed: If you are unsure about a BIOS setting or are experiencing difficulties, consult a qualified technician or online resources for assistance.
Conclusion:
The BIOS plays a critical role in the operation of your computer. Understanding its functions and how to access it can be invaluable for troubleshooting issues, optimizing performance, and customizing your system. By navigating the BIOS carefully and making informed changes, you can ensure your computer runs smoothly and efficiently. Remember to approach BIOS settings with caution and consult resources if you are unsure about a particular setting.

![How to Boot to BIOS in Windows 11 [TechSpot] – Up My Tech](https://static.techspot.com/images2/news/ts3_thumbs/2022/08/2022-08-11-ts3_thumbs-221.jpg)
![Windows 11 BIOS Settings [Enable TPM 2.0, Secure Boot, UEFI]](https://newscutzy.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Enable-Secure-boot-on-Lenevo.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the BIOS: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 11 Boot Settings. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!



























![How To Open 7z Files? [Windows 10 / Mac] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fjMRV8vfuBE/maxresdefault.jpg)




![This Operation Has Been Cancelled Due to Restrictions? [Resolved] - MiniTool Partition Wizard](https://www.partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/articles/2022/02/this-operation-has-been-cancelled-due-to-restrictions/this-operation-has-been-cancelled-due-to-restrictions-3.png)








/speed-test-580e7a2b5f9b58564ce47143.png)