Paint 3D: A Comprehensive Guide To The 3D Modeling Tool In Windows 11
Paint 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to the 3D Modeling Tool in Windows 11
Related Articles: Paint 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to the 3D Modeling Tool in Windows 11
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Paint 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to the 3D Modeling Tool in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
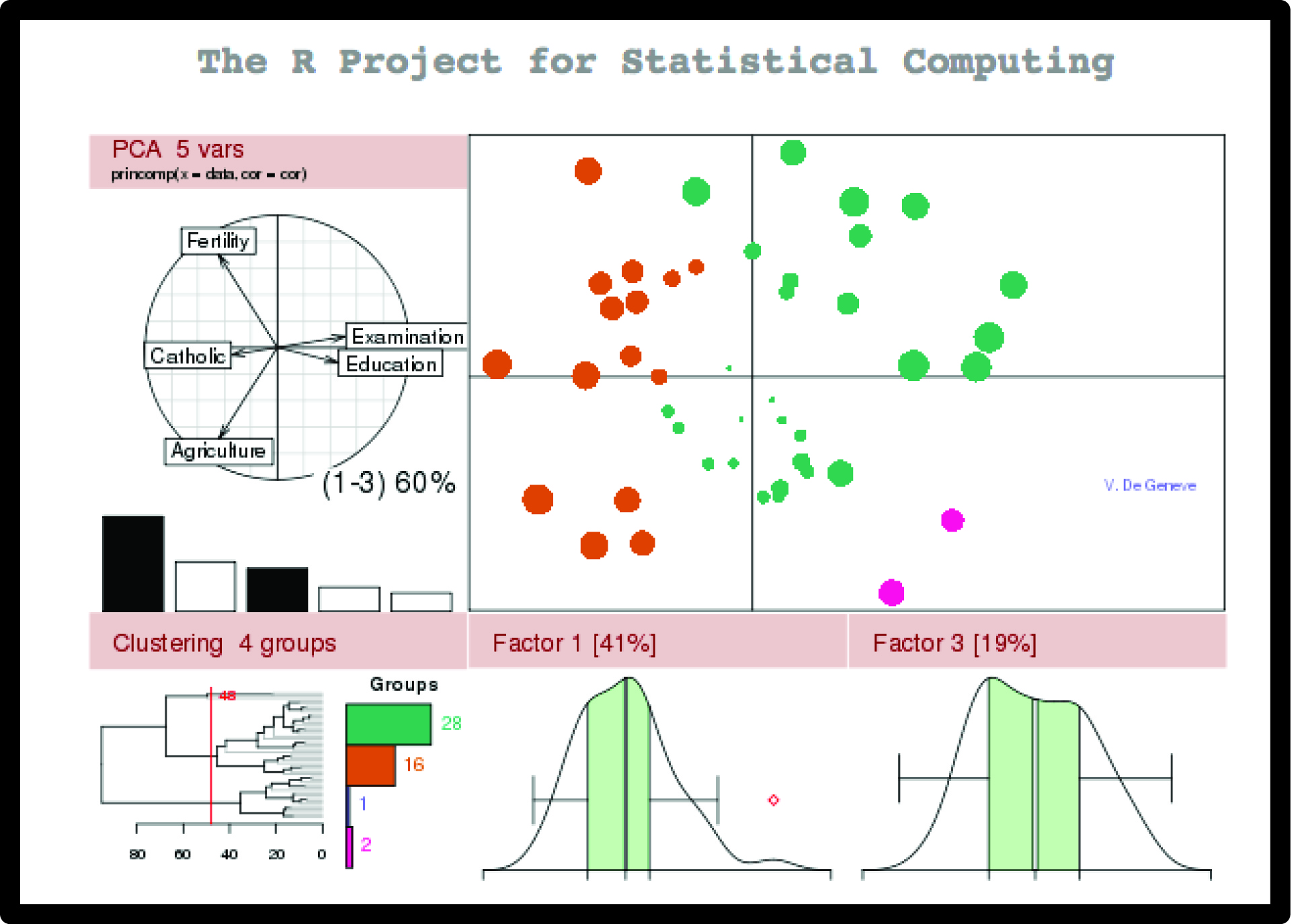
Paint 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to the 3D Modeling Tool in Windows 11
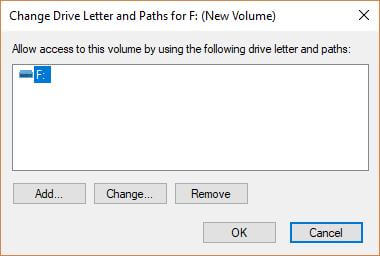
![How To Download and Install Paint 3D In Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ji8A-z7GuTs/maxresdefault.jpg)
Paint 3D, a user-friendly 3D modeling application, is a staple feature of Windows 11, offering a gateway into the world of three-dimensional design. While it may not possess the advanced features of professional software, its accessibility and intuitive interface make it an ideal tool for beginners, hobbyists, and even educators seeking to introduce fundamental 3D concepts.
This article delves into the intricacies of Paint 3D, exploring its functionality, benefits, and practical applications. We will examine its download and installation process, highlighting key features and outlining essential tips for maximizing its potential.
Understanding Paint 3D: A User-Friendly Approach to 3D Modeling
Paint 3D is a versatile tool designed to empower users of all skill levels to create and manipulate 3D objects. Its intuitive interface, resembling the familiar Paint application, simplifies the learning curve, allowing users to quickly grasp fundamental concepts and begin creating.
Key Features and Functionality:
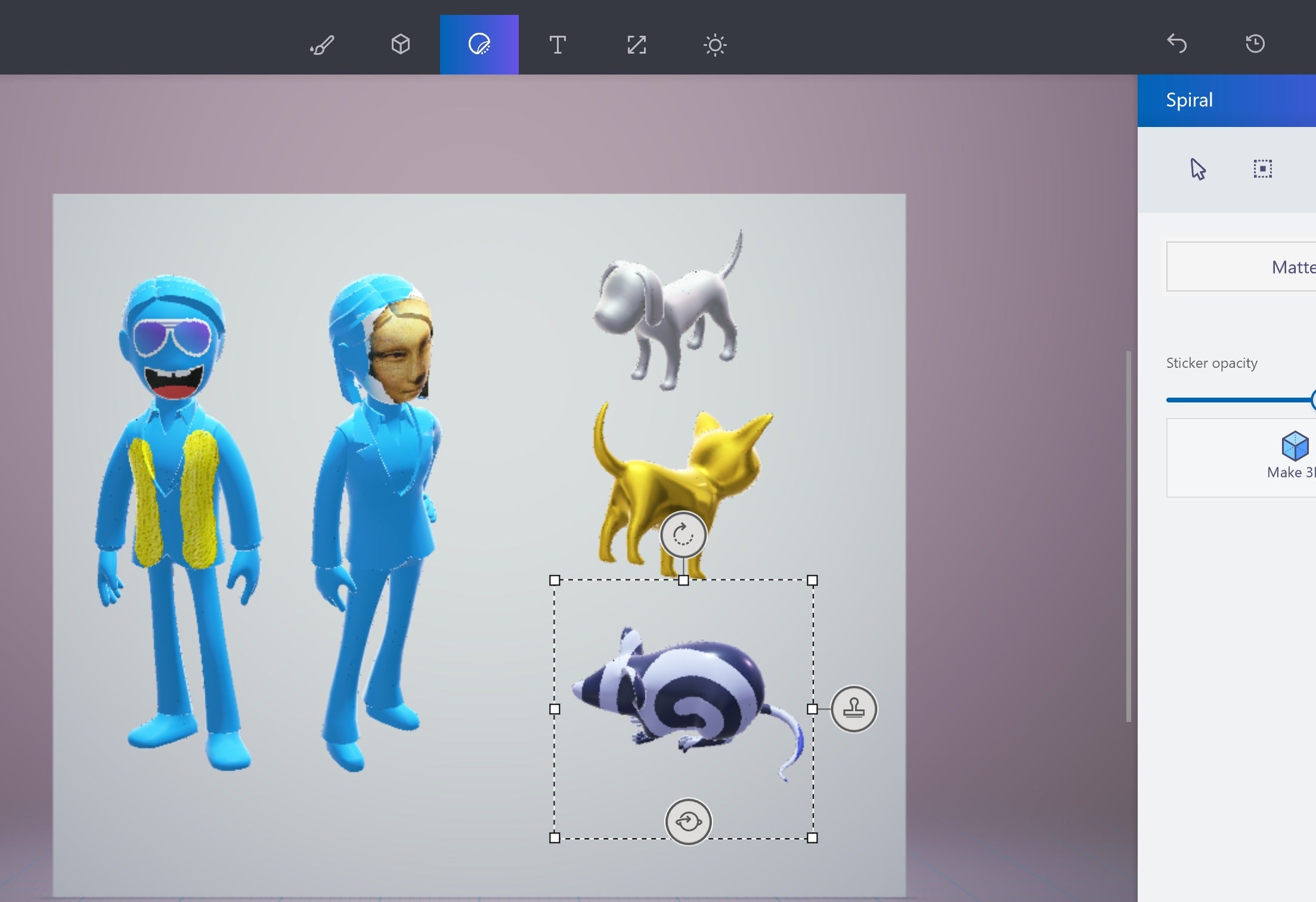
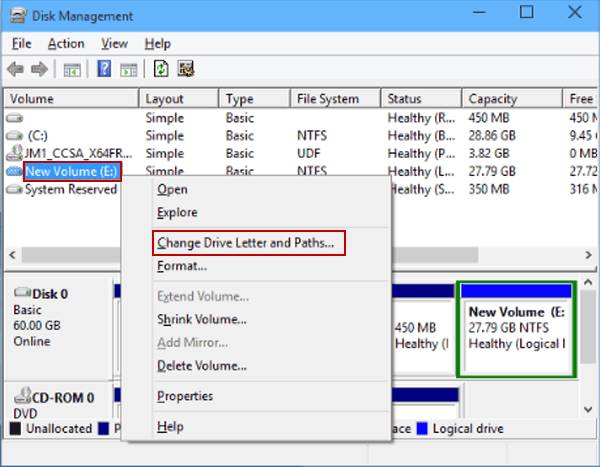
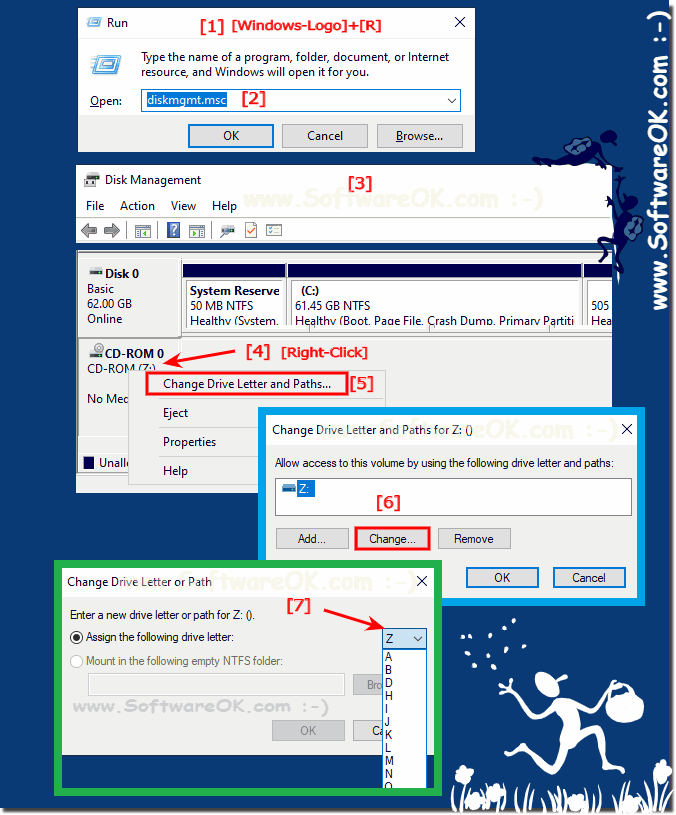
- 3D Object Creation: Paint 3D allows users to create basic 3D shapes, including cubes, spheres, cylinders, and cones. These shapes can be manipulated, resized, and transformed into more complex objects through a variety of tools.
- Texturing and Coloring: Users can apply textures, colors, and patterns to their 3D models, adding depth and realism. Paint 3D offers a range of pre-defined textures, allowing for quick customization.
- 3D Object Import and Export: Paint 3D supports the import and export of 3D models in various file formats, including OBJ, 3MF, and STL. This functionality enables users to work with models created in other software or to share their creations with others.
- Basic Animation: Paint 3D offers rudimentary animation capabilities, allowing users to create simple animations by manipulating the position and rotation of 3D objects over time.
- 2D Image Integration: Users can incorporate 2D images into their 3D scenes, adding context and enhancing the visual appeal of their creations.
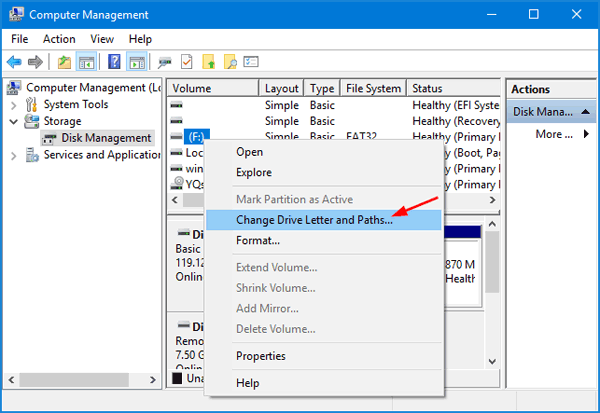
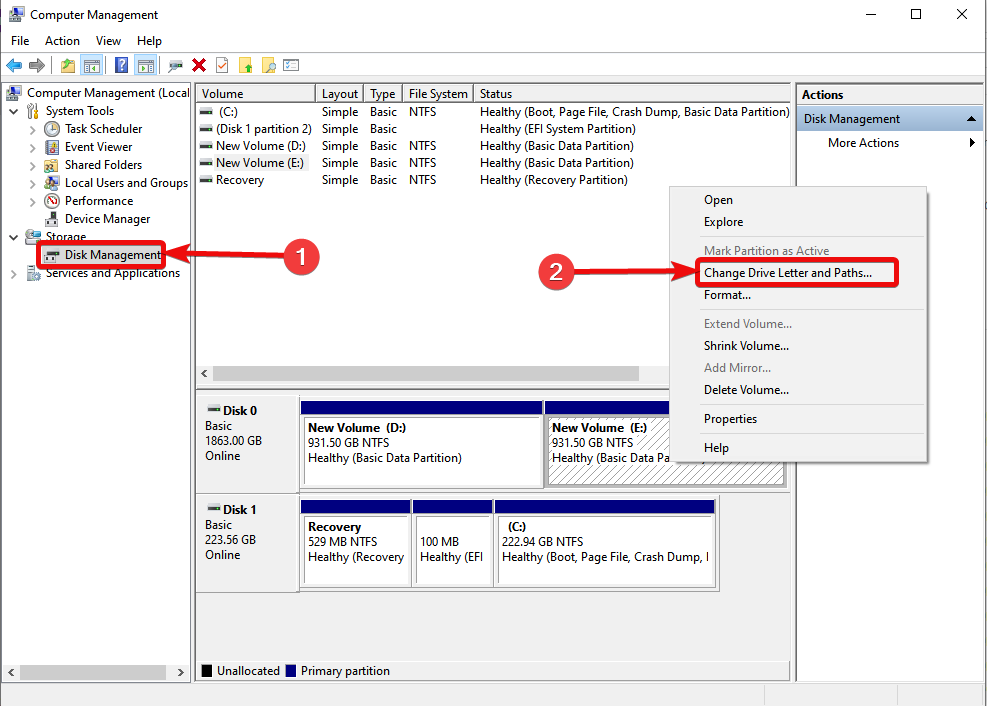
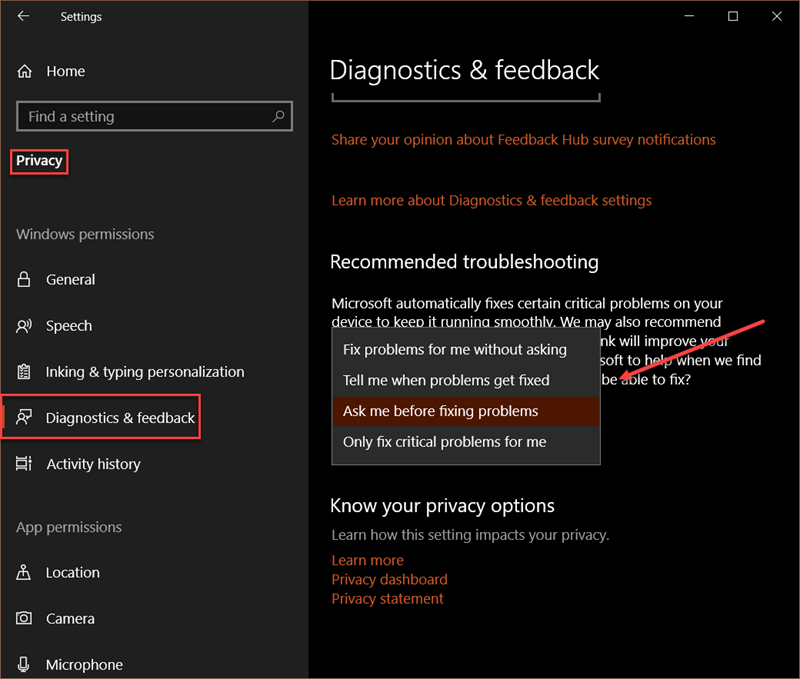
Downloading and Installing Paint 3D in Windows 11:
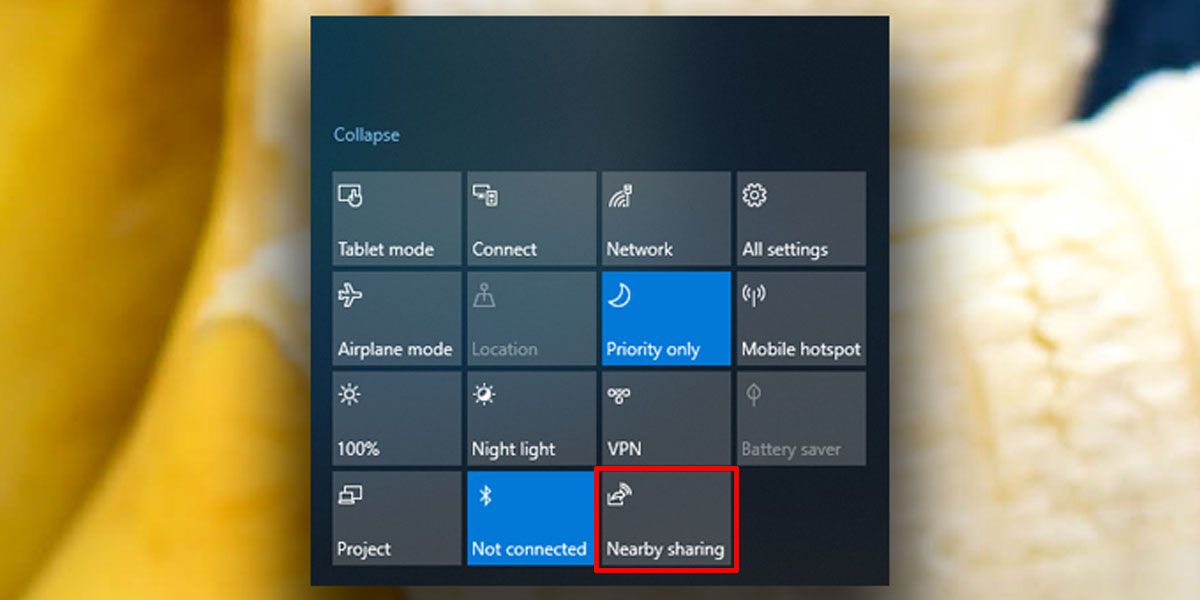
Paint 3D is pre-installed on Windows 11 operating systems. Users can access it through the Start Menu, the search bar, or by navigating to the "Apps" folder.
Benefits of Using Paint 3D:
- Accessibility: Paint 3D’s intuitive interface and straightforward tools make it accessible to users of all skill levels, even those with no prior experience in 3D modeling.
- Creativity and Exploration: Paint 3D encourages experimentation and fosters creativity by providing a safe space to explore 3D design concepts.
- Educational Value: Paint 3D can be used as an educational tool to introduce students to basic 3D design principles and concepts.
- Practical Applications: Paint 3D can be used for a variety of purposes, including creating simple 3D models for personal projects, designing prototypes, or generating visual aids for presentations.
Utilizing Paint 3D Effectively: Tips and Strategies
- Start with Basic Shapes: Begin by experimenting with the fundamental 3D shapes provided by Paint 3D. Explore their properties and learn how to manipulate them.
- Utilize the Selection Tools: Master the selection tools to accurately select, move, rotate, and resize objects.
- Explore Texturing Options: Experiment with various textures and colors to add depth and realism to your 3D models.
- Utilize the 3D Text Tool: Create 3D text objects and customize them to enhance your designs.
- Learn from Tutorials: Numerous online tutorials and resources offer step-by-step guidance on using Paint 3D effectively.
FAQs Regarding Paint 3D:
1. Is Paint 3D a professional 3D modeling software?
While Paint 3D is a powerful tool for beginners and hobbyists, it is not a professional-grade 3D modeling software. It lacks the advanced features and functionality found in industry-standard applications.
2. Can I use Paint 3D to create complex 3D models?
Paint 3D is well-suited for creating simple 3D models. However, for more intricate and detailed models, users may require professional software with advanced modeling tools.
3. Does Paint 3D support animation?
Paint 3D offers basic animation capabilities, allowing users to create simple animations by manipulating the position and rotation of 3D objects over time. However, its animation features are limited compared to dedicated animation software.
4. What file formats does Paint 3D support?
Paint 3D supports the import and export of 3D models in various file formats, including OBJ, 3MF, and STL.
5. Is Paint 3D compatible with other 3D modeling software?
Paint 3D can import and export 3D models in common file formats, allowing for compatibility with other 3D modeling software.
Conclusion: Paint 3D – A Stepping Stone to 3D Design
Paint 3D serves as an accessible and user-friendly entry point into the world of 3D modeling. Its intuitive interface, combined with its basic yet effective features, empowers individuals to explore their creativity and learn the fundamentals of three-dimensional design.
While it may not be a professional-grade tool, Paint 3D provides a valuable platform for experimentation, learning, and creating simple yet engaging 3D models. Its ease of use and accessibility make it an ideal choice for beginners, hobbyists, and educators seeking to introduce the exciting realm of 3D design.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/paint-3d-clown-fish-model-ce7782f12d2e4525bef485625dd44bdb.png)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/paint-3d-scene-59c139b59abed50011811240.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Paint 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to the 3D Modeling Tool in Windows 11. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
































![The Evolution of Gmail [Infographic] - iClarified](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/29018/114035/114035.jpg)