Shielding Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide To Ransomware Protection
Shielding Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Ransomware Protection
Related Articles: Shielding Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Ransomware Protection
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Shielding Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Ransomware Protection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shielding Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Ransomware Protection

Ransomware, a malicious software designed to encrypt a user’s data and hold it hostage for a ransom payment, poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. The ubiquitous nature of Windows 10, coupled with its diverse user base, makes it a prime target for ransomware attacks. This article provides a comprehensive guide to ransomware protection solutions for Windows 10, emphasizing the importance of proactive measures and outlining various strategies to mitigate this threat.
Understanding the Ransomware Threat
Ransomware operates by infiltrating a system, typically through malicious email attachments, compromised websites, or software vulnerabilities. Once installed, it encrypts files, rendering them inaccessible. The attacker then demands a ransom payment, often in cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key.
The consequences of a successful ransomware attack can be severe:
- Data Loss: Irrecoverable loss of critical files, including personal documents, photos, financial records, and business data.
- Financial Loss: Ransom payments can be substantial, ranging from hundreds to millions of dollars.
- Business Disruption: Operational downtime, lost productivity, and potential reputational damage.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance Issues: Data breaches and ransomware attacks can trigger legal actions and regulatory fines.
Layered Approach to Ransomware Protection
Effective ransomware protection for Windows 10 requires a layered approach that combines multiple security measures. This approach ensures a robust defense mechanism, reducing the risk of successful ransomware attacks.
1. Operating System Security
- Keep Windows 10 Updated: Regular updates from Microsoft patch vulnerabilities that ransomware exploits. Enable automatic updates to ensure timely security patches.
- Enable Windows Defender: Windows 10 includes built-in antivirus protection, Windows Defender, which helps detect and remove malware, including ransomware.
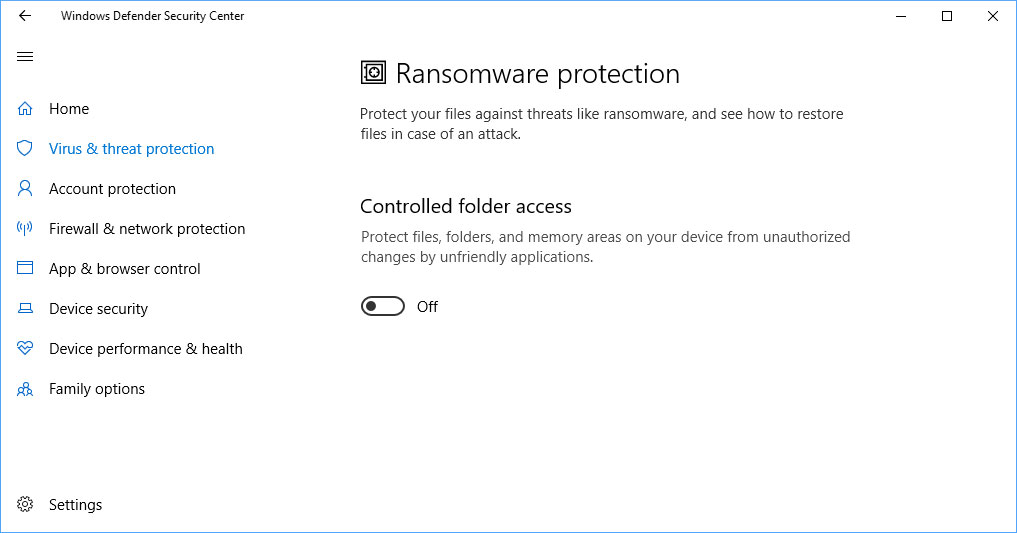
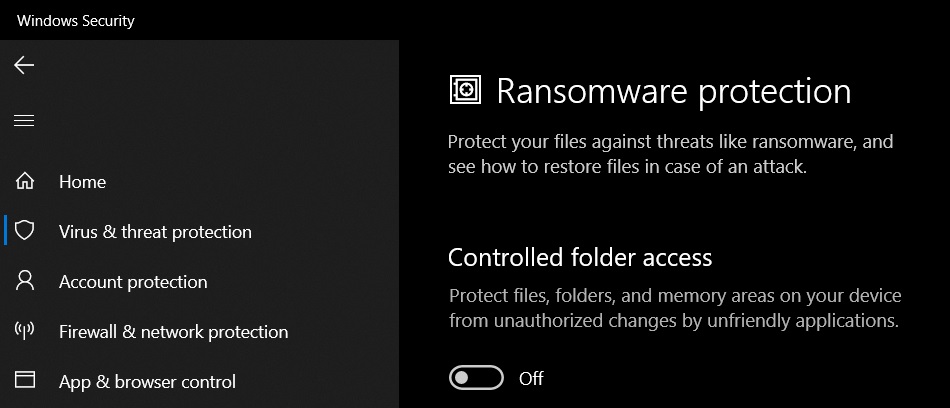
- Utilize Advanced Security Features: Windows 10 offers advanced security features like Controlled Folder Access, which limits access to specific folders, and Exploit Protection, which mitigates vulnerabilities in applications.
2. Backup and Recovery
- Implement Regular Backups: Create regular backups of critical data on external drives, cloud storage services, or network-attached storage devices.
- Test Backup Recovery: Regularly test the backup and recovery process to ensure data can be restored effectively.
- Offline Backups: Consider storing backups offline, such as on a separate physical drive or at a remote location, to protect against ransomware encryption.
3. User Education and Awareness
- Train Users on Best Practices: Educate users about ransomware threats, phishing scams, and safe browsing habits.
- Implement Strong Password Policies: Encourage the use of strong, unique passwords for all accounts and discourage the sharing of credentials.
- Promote Email Security Awareness: Train users to identify phishing emails, avoid suspicious attachments, and verify sender authenticity.
4. Network Security
- Firewall Protection: Implement a strong firewall to prevent unauthorized access to your network and block malicious traffic.
- Network Segmentation: Segment the network to limit the impact of a compromised device.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Utilize MFA for critical network access points to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
5. Advanced Security Solutions
- Ransomware Protection Software: Consider specialized ransomware protection software that monitors file activity, detects suspicious behavior, and can roll back changes made by ransomware.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities, including ransomware detection and remediation.
- Threat Intelligence Services: Utilize threat intelligence services to stay informed about emerging ransomware threats and best practices for mitigation.
FAQs on Ransomware Protection for Windows 10
Q: What are the most common ways ransomware attacks occur?
A: Common attack vectors include:
- Malicious Email Attachments: Opening infected attachments can trigger ransomware installation.
- Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities: Outdated software can be vulnerable to ransomware exploits.
- Phishing Websites: Visiting malicious websites can lead to ransomware downloads.
- Exploiting Network Vulnerabilities: Weak network security can allow ransomware to spread within a network.
Q: How can I tell if my computer has been infected with ransomware?
A: Signs of a ransomware infection include:
- Files becoming inaccessible: Data files may be encrypted and appear as gibberish.
- Ransom demands: A ransom note may appear on your screen demanding payment.
- Unusual system behavior: Your computer may run slower, freeze, or crash frequently.
Q: What should I do if I suspect my computer has been infected with ransomware?
A: If you suspect a ransomware infection, take the following steps:
- Disconnect from the network: Disconnect your computer from the internet to prevent further spread.
- Do not pay the ransom: Paying the ransom does not guarantee file recovery and may encourage further attacks.
- Contact cybersecurity professionals: Seek expert assistance from cybersecurity specialists or IT professionals.
Q: Are there any free ransomware protection tools available for Windows 10?
A: While free tools may offer basic protection, comprehensive ransomware protection often requires paid software solutions. However, several free tools can help, including:
- Windows Defender: Windows 10’s built-in antivirus protection.
- Malwarebytes: A free antivirus software with ransomware protection features.
- HitmanPro.Alert: A free tool that monitors file activity and alerts users to suspicious behavior.
Tips for Effective Ransomware Protection
- Regularly review and update security settings: Ensure your Windows 10 security settings are up-to-date and configured for maximum protection.
- Be cautious of email attachments and links: Avoid opening attachments from unknown senders or clicking suspicious links.
- Use strong and unique passwords: Implement strong passwords for all online accounts and avoid reusing the same password across multiple accounts.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for critical accounts: MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification beyond a password.
- Keep software up to date: Regularly update all software, including operating systems, applications, and antivirus programs.
- Back up your data regularly: Implement a robust backup strategy to ensure you can recover your data in case of a ransomware attack.
- Consider using a dedicated ransomware protection solution: Invest in specialized ransomware protection software for enhanced security.
Conclusion
Ransomware presents a significant threat to Windows 10 users. By implementing a layered approach to security, including operating system updates, regular backups, user education, and advanced security solutions, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to ransomware attacks. Proactive security measures, combined with vigilance and awareness, are crucial for safeguarding data and mitigating the impact of potential ransomware incidents. Remember, staying informed and taking preventive steps is the best defense against this evolving threat.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shielding Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide to Ransomware Protection. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!




















![How To Partition A Hard Drive In Windows 10 [Free, No Software Required]](http://www.techworm.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Disk-Partition-In-Windows-10-1.jpg)














![Windows Out Of Box Experience: OOBESETTINGSMULTIPLEPAGE error on Windows 10 Learn [Solve IT]](https://i1.wp.com/techdirectarchive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Screenshot-2020-05-23-at-14.23.35.png?resize=1200%2C950u0026ssl=1)


![How to Fix: No Sound After Windows 10/11 Update - Sound Missing 2024 [Solved] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/tvjynf0zMG8/maxresdefault.jpg)