Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide

The inability to boot into Windows 10 can be a frustrating experience, leaving users stranded and unable to access their data or applications. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of common boot issues and equip users with the tools and knowledge to diagnose and resolve them effectively.
Understanding Boot Processes and Common Issues
Before delving into troubleshooting techniques, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental steps involved in the Windows 10 boot process. When a computer powers on, the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) takes control, performing initial hardware checks and loading the operating system from the hard drive. This process involves multiple stages:
- POST (Power-On Self Test): The BIOS performs a series of checks on critical hardware components, including RAM, CPU, and storage devices.
- Boot Device Selection: The BIOS identifies and selects the boot device (usually a hard drive or SSD) containing the operating system.
- Boot Loader Loading: The BIOS loads the boot loader, a small program responsible for initiating the operating system.
- Operating System Initialization: The boot loader loads the Windows kernel and other essential files, ultimately leading to the familiar Windows desktop.
Numerous factors can disrupt this intricate boot sequence, leading to various error messages or a complete failure to load Windows. Common culprits include:
- Hardware Malfunctions: Faulty RAM, a failing hard drive, or a loose connection can prevent the system from booting.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible drivers, corrupted system files, or malware infections can interfere with the boot process.
- Boot Configuration Issues: Incorrect boot order settings in the BIOS, corrupted boot files, or missing system files can hinder the loading of the operating system.
- System Updates: Faulty or incomplete updates can introduce errors that disrupt the boot process.
Troubleshooting Techniques: A Step-by-Step Approach
Addressing Windows 10 boot issues involves a systematic approach, starting with simple checks and progressively moving towards more complex solutions:
1. Basic Checks:
- Power Cycle: A simple restart can resolve temporary glitches or software conflicts.
- Hardware Inspection: Visually inspect the system for loose connections, damaged cables, or dust accumulation.
- BIOS Settings: Check the boot order in the BIOS to ensure the correct boot device is selected.
- External Devices: Disconnect any unnecessary peripherals, such as USB drives or external hard drives, to eliminate potential conflicts.
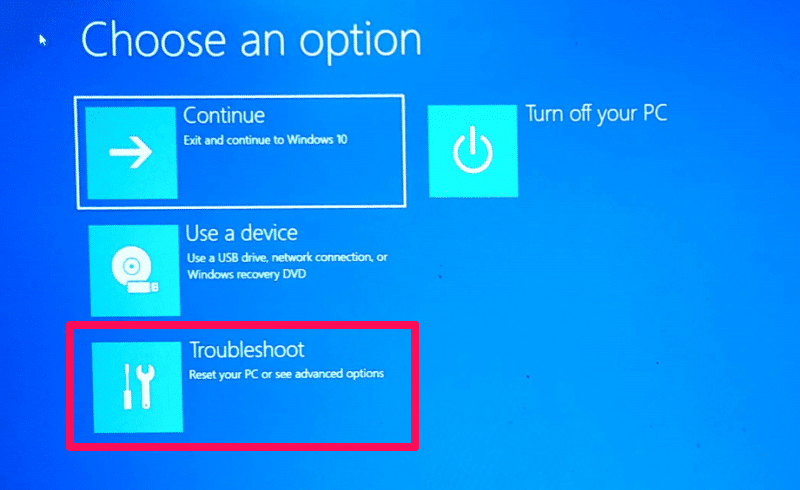
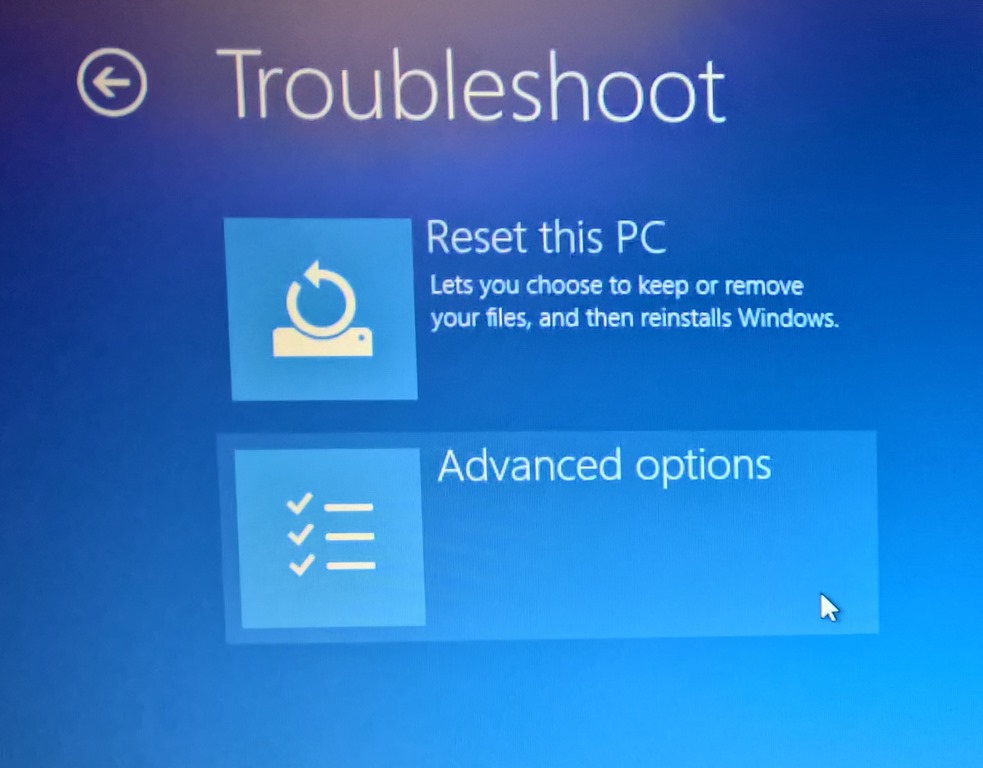
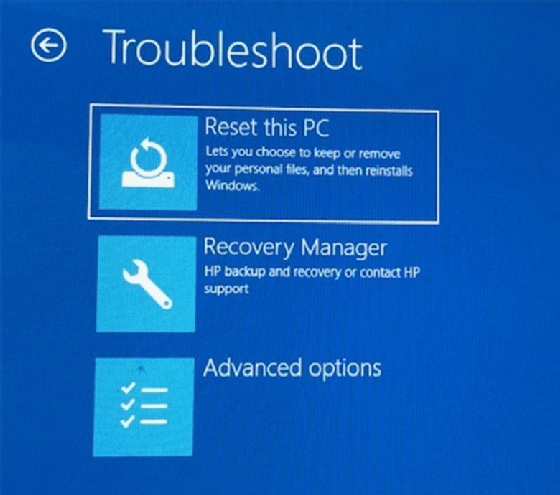
2. Advanced Boot Options:
- Safe Mode: Boot into Safe Mode to isolate issues caused by third-party applications or drivers. This mode loads a minimal set of system files and drivers.
- System Restore: Utilize System Restore to revert the system to a previous working state. This option restores system files and settings to a point before the boot issue occurred.
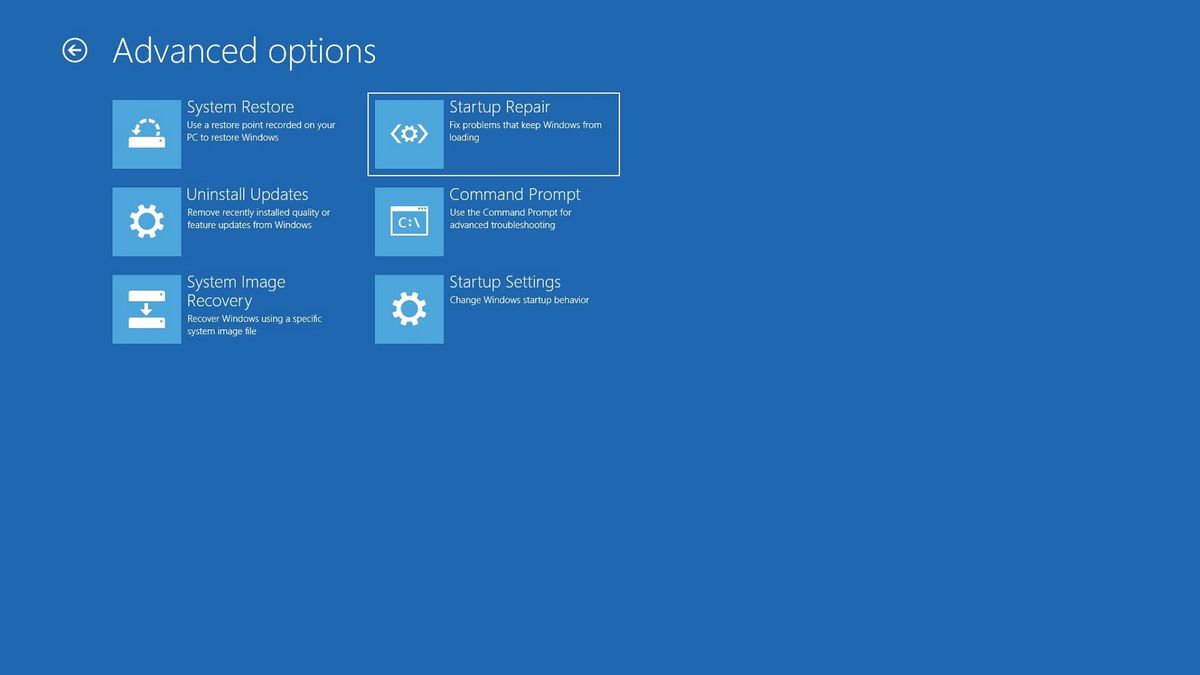
- Startup Repair: This built-in tool attempts to repair common boot problems, such as corrupted boot files or missing system files.
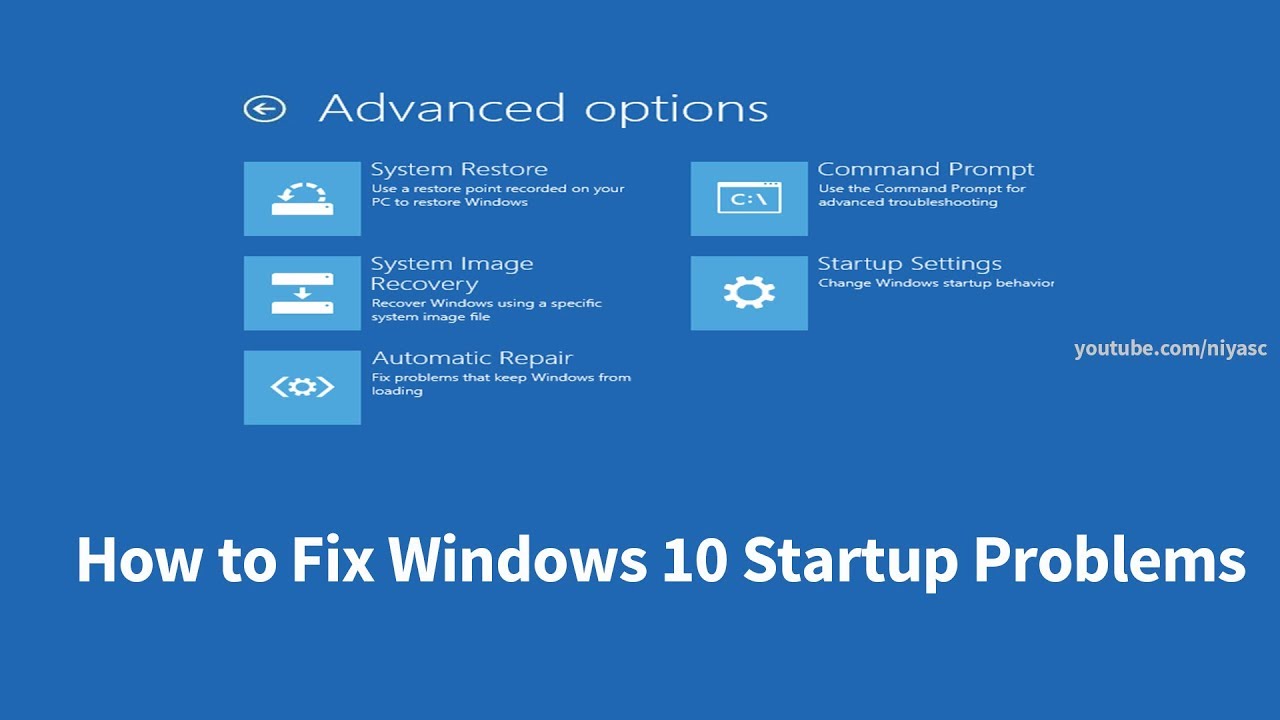
3. Repairing Boot Files:
-
Bootrec.exe: This command-line tool is included in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) and offers several options for repairing boot files:
- bootrec /fixmbr: Repairs the Master Boot Record (MBR), which is the first sector on the hard drive containing essential boot information.
- bootrec /fixboot: Rewrites the boot sector on the system partition, addressing issues with the boot loader.
- bootrec /scanos: Scans the hard drive for Windows installations and lists them.
- bootrec /rebuildbcd: Rebuilds the Boot Configuration Data (BCD), which stores information about the operating systems installed on the computer.
4. Reinstalling Windows:
- Clean Installation: If all other troubleshooting steps fail, a clean installation of Windows 10 may be necessary. This involves formatting the hard drive and reinstalling the operating system from scratch.
- In-place Upgrade: This option upgrades the existing Windows installation to the latest version without deleting user data.
5. Seeking Professional Assistance:
- Data Recovery: If the issue involves a corrupted hard drive or data loss, seeking professional data recovery services is crucial.
- Hardware Repair: If suspected hardware malfunctions are causing the boot issues, consulting a qualified technician for diagnosis and repair is recommended.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
1. What are the most common error messages encountered during the boot process?
- "BOOTMGR is missing": Indicates a corrupted or missing boot manager.
- "Operating System not found": Suggests a problem with the boot loader or the operating system files.
- "STOP error": A blue screen with a STOP code indicates a system crash caused by hardware or software issues.
- "Windows cannot access the specified device": Points to a problem with the hard drive or its connection.
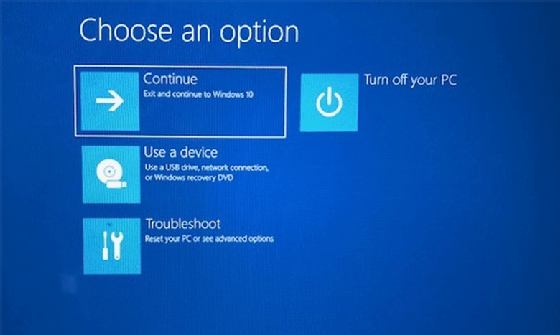
2. How do I access the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)?
- During Boot: Repeatedly press the F8 key during the boot process to access the Advanced Boot Options menu.
- Using a Recovery Drive: Boot from a USB recovery drive or DVD created using the Windows Media Creation Tool.
3. Can I repair the boot files without reinstalling Windows?
Yes, using the Bootrec.exe tool in the Windows Recovery Environment can often repair corrupted boot files without requiring a full reinstall.
4. What if my system won’t boot into Safe Mode?
If Safe Mode is inaccessible, consider using a bootable USB drive or CD containing a recovery tool like Hiren’s BootCD to access advanced options.
5. How do I prevent future boot issues?
- Regularly Back Up Data: Create regular backups of important data to ensure data recovery in case of system failure.
- Update Drivers: Keep device drivers updated to ensure compatibility and stability.
- Run Anti-Malware Scans: Regularly scan for malware to prevent infections that can disrupt the boot process.
- Avoid Installing Unnecessary Software: Limit the number of applications installed to minimize potential conflicts.
Tips for Effective Troubleshooting:
- Document Symptoms: Record detailed error messages, boot behavior, and any recent changes made to the system.
- Isolate the Issue: Try to narrow down the cause of the boot problem by removing or disabling components or applications.
- Use a Bootable USB Drive: Create a bootable USB drive with a recovery tool or a live Linux distribution for troubleshooting.
- Seek Support: If you’re unable to resolve the issue, don’t hesitate to seek help from online forums, technical support websites, or qualified computer technicians.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Approach to Boot Troubleshooting
Windows 10 boot issues can arise from various factors, ranging from hardware malfunctions to software conflicts. By understanding the boot process and employing a methodical troubleshooting approach, users can effectively diagnose and address these problems. Remember to prioritize data backup, keep drivers updated, and practice safe computing habits to minimize the risk of future boot issues. If all else fails, seeking professional assistance can provide the necessary expertise to restore your system to working order.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!



















![[Infographic] All you need to know about AWS API Gateway and resolving the most common request](https://i0.wp.com/dashbird.io/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Screenshot-2022-01-17-at-11.44.33.png)




























![[GUIDE] How To Upgrade To Windows 10 Using ISO File](https://htse.kapilarya.com/GUIDE-How-To-Upgrade-To-Windows-10-Using-ISO-File-12.png)

![[GUIDE] How To Upgrade To Windows 10 Using ISO File](https://htse.kapilarya.com/GUIDE-How-To-Upgrade-To-Windows-10-Using-ISO-File-7.png)

![[GUIDE] How To Upgrade To Windows 10 Using ISO File](https://htse.kapilarya.com/GUIDE-How-To-Upgrade-To-Windows-10-Using-ISO-File.png)
![[GUIDE] How To Upgrade To Windows 10 Using ISO File](https://htse.kapilarya.com/GUIDE-How-To-Upgrade-To-Windows-10-Using-ISO-File-1.png)